0.目录
1.循环链表的实现
2.双向链表的实现
3.小结
1.循环链表的实现
什么是循环链表?
- 概念上
- 任意数据元素都有一个前驱和一个后继
- 所有的数据元素的关系构成一个逻辑上的环
- 实现上
- 循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
- 尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
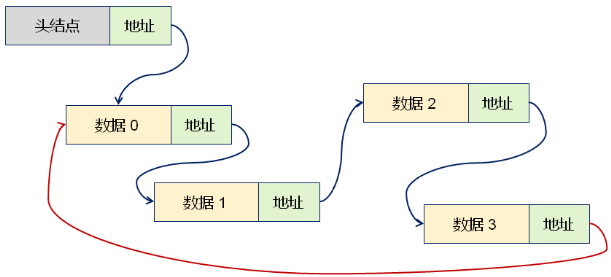
循环链表的逻辑构成:
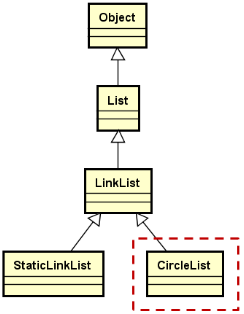
循环链表的继承层次结构:
循环链表的实现思路:
- 通过模板定义CircleList类,继承自LinkList类
- 定义内部函数 last_to_first(),用于将单链表首尾相连
- 特殊处理:首元素的插入操作和删除操作
- 重新实现:清空操作和遍历操作
循环链表的实现要点:
- 插入位置为 0 时:
- 头结点和尾结点均指向新结点
- 新结点成为首结点插入链表
- 删除位置为 0 时:
- 头结点和尾结点指向位置为 1 的结点
- 安全销毁首结点
实现循环链表(CircleList.h):
需要将父类LinkList.h中相关的函数声明为虚函数
#ifndef LINKLIST_H
#define LINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace StLib
{
template <typename T>
class LinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
};
mutable struct : public Object
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
} m_header;
int m_length;
int m_step;
Node* m_current;
Node* position(int i) const
{
Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);
for(int p=0; p<i; p++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
LinkList()
{
m_header.next = NULL;
m_length = 0;
m_step = 1;
m_current = NULL;
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* node = create();
if( node != NULL )
{
Node* current = position(i);
node->value = e;
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert new element ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* current = position(i);
Node* toDel = current->next;
if( m_current == toDel )
{
m_current = toDel->next;
}
current->next = toDel->next;
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
position(i)->next->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int i) const
{
T ret;
if( get(i, ret) )
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = position(i)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
Node* node = m_header.next;
while ( node )
{
if( node->value == e )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
else
{
node = node->next;
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while ( m_header.next )
{
Node* toDel = m_header.next;
m_header.next = toDel->next;
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
}
virtual bool move(int i, int step = 1)
{
bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0);
if( ret )
{
m_current = position(i)->next;
m_step = step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current == NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if( !end() )
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ...");
}
}
virtual bool next()
{
int i = 0;
while( (i < m_step) && !end() )
{
m_current = m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
~LinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKLIST_H
实现CircleList.h
#ifndef CIRCLELIST_H
#define CIRCLELIST_H
#include "LinkList.h"
namespace StLib
{
template <typename T>
class CircleList : public LinkList<T>
{
protected:
typedef typename LinkList<T>::Node Node;
int mod(int i) const
{
return (this->m_length == 0) ? 0 : (i % this->m_length);
}
Node* last() const
{
return this->position(this->m_length-1)->next;
}
void last_to_first() const
{
last()->next = this->m_header.next;
}
public:
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(this->m_length, e);
}
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret;
i = i % (this->m_length + 1);
ret = LinkList::insert(i, e);
if( ret && (i == 0) )
{
last_to_first();
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret;
i = mod(i);
if( i == 0 )
{
Node* toDel = this->m_header.next;
if( toDel != NULL )
{
this->m_header.next = toDel->next;
this->m_length--;
if( this->m_length > 0 )
{
last_to_first();
if( this->m_current == toDel )
{
this->m_current = toDel->next;
}
}
else
{
this->m_header.next = NULL;
this->m_current = NULL;
}
this->destroy(toDel);
}
else
{
ret = false;
}
}
else
{
ret = LinkList<T>::remove(i);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
return LinkList<T>::set(mod(i), e);
}
T get(int i) const
{
return LinkList<T>::get(mod(i));
}
T get(int i, const T& e) const
{
return LinkList<T>::get(mod(i), e);
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
Node* slider = this->m_header.next;
for(int i=0; i<this->m_length; i++)
{
if( slider->value == e )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
slider = slider->next;
}
return ret;
}
void clear()
{
while( this->m_length > 1 )
{
remove(1);
}
if( this->m_length == 1 )
{
Node* toDel = this->m_header.next;
this->m_header.next = NULL;
this->m_length = 0;
this->m_current = NULL;
this->destroy(toDel);
}
}
bool move(int i, int step)
{
return LinkList<T>::move(mod(i), step);
}
bool end()
{
return (this->m_length == 0) || (this->m_current == NULL);
}
~CircleList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // CIRCLELIST_H
循环链表的应用——约瑟夫环问题:
已知 n 个人( 以编号 0,1,2,3,... ,n-1 分别表示 )围坐在一张圆桌周围。从编号为 k 的人开始报数,数到 m 的那个人出列;他的下一个人又从 1 开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列;依此规律重复下去,直到圆桌周围的人全部出列。
小故事:
在罗马人占领乔塔帕特后,39个犹太人与 Josephus 及他的朋友躲到一个洞中,39个犹太人决定宁愿死也不要被敌人抓到,于是决定了一个自杀方式,41个人排成一个圆圈,由第1个人开始报数,每报数到第3人该人就必须自杀,然后再由下一个重新报数,直到所有人都自杀身亡为止。然而 Josephus 和他的朋友并不想遵从。那么,一开始要站在什么地方才能避免被处决?
main.cpp解决约瑟夫环问题,测试CircleList.h:
#include <iostream>
#include "CircleList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
void josephus(int n, int s, int m)
{
CircleList<int> c1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
c1.insert(i);
}
c1.move(s-1, m-1);
while( c1.length() > 0 )
{
c1.next();
cout << c1.current() << ", ";
c1.remove(c1.find(c1.current()));
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
josephus(41, 1, 3);
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 1, 5, 10, 14, 19, 23, 28, 32, 37, 41, 7, 13, 20, 26, 34, 40, 8, 17, 29, 38, 11, 25, 2, 22, 4, 35, 16, 31,
2.双向链表的实现
单链表的另一个缺陷:
- 单向性
- 只能从头结点开始高效访问链表中的数据元素
- 缺陷
- 如果需要逆向访问单链表中的数据元素将极其低效

新的线性表
- 设计思路:
- 在“单链表”的结点中增加一个指针 pre,用于指向当前结点的前驱结点。

双向链表的继承层次结构:
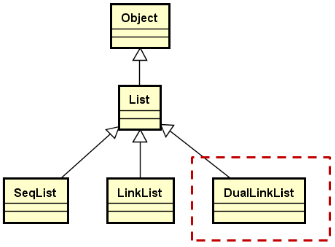
DualLinkList 的定义:

实现DualLinkList.h:
#ifndef DUALLINKLIST_H
#define DUALLINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace StLib
{
template <typename T>
class DualLinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
Node* pre;
};
mutable struct : public Object
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
Node* pre;
} m_header;
int m_length;
int m_step;
Node* m_current;
Node* position(int i) const
{
Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);
for(int p=0; p<i; p++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
DualLinkList()
{
m_header.next = NULL;
m_header.pre = NULL;
m_length = 0;
m_step = 1;
m_current = NULL;
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* node = create();
if( node != NULL )
{
Node* current = position(i);
Node* next = current->next;
node->value = e;
node->next = next;
current->next = node;
if( current != reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header) )
{
node->pre = current;
}
else
{
node->pre = NULL;
}
if( next != NULL )
{
next->pre = node;
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert new element ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
Node* current = position(i);
Node* toDel = current->next;
Node* next = toDel->next;
if( m_current == toDel )
{
m_current = next;
}
current->next = next;
if( next != NULL )
{
next->pre = toDel->pre;
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
position(i)->next->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int i) const
{
T ret;
if( get(i, ret) )
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = position(i)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
Node* node = m_header.next;
while ( node )
{
if( node->value == e )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
else
{
node = node->next;
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while ( m_length > 0 )
{
remove(0);
}
}
virtual bool move(int i, int step = 1)
{
bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0);
if( ret )
{
m_current = position(i)->next;
m_step = step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current == NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if( !end() )
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ...");
}
}
virtual bool next()
{
int i = 0;
while( (i < m_step) && !end() )
{
m_current = m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
virtual bool pre()
{
int i = 0;
while( (i < m_step) && !end() )
{
m_current = m_current->pre;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
~DualLinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // DUALLINKLIST_H
main.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "DualLinkList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
DualLinkList<int> d1;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
d1.insert(0, i);
d1.insert(0, 5);
}
cout << "begin" << endl;
d1.move(d1.length()-1);
while( !d1.end() )
{
if( d1.current() == 5 )
{
cout << d1.current() << endl;
d1.remove(d1.find(d1.current()));
}
else
{
d1.pre();
}
}
cout << "end" << endl;
for(d1.move(d1.length()-1); !d1.end(); d1.pre())
{
cout << d1.current() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
begin
5
5
5
5
5
end
0
1
2
3
4
深度思考——开放性问题:
- DualLinkList 和 LinkList 中存在很多完全一样的代码,如何进行重构降低代码的冗余性?冗余代码的出现是否意味着 DualLinkList 和 LinkList 之间应该是继承关系?
扩展练习——双向链表的子类:
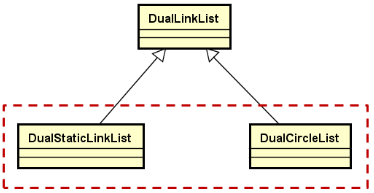
3.小结
- 循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
- 尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
- 特殊处理首元素的插入操作和删除操作
- 重新实现清空操作和遍历操作
- 双向链表是为了弥补单链表的缺陷而重新设计的
- 在概念上,双向链表不是单链表,没有继承关系
- 双向链表中的游标能够直接访问当前结点的前驱和后继
- 双向链表是线性表概念的最终实现( 更贴近理论上的线性表 )