0.目录
1.字符串类的创建
2.小结
1.字符串类的创建
1.1 基本字符串类的创建
历史遗留问题:
- C语言不支持真正意义上的字符串
- C语言用字符数组和一组函数实现字符串操作
- C语言不支持自定义类型,因此无法获得字符串类型
从C到C++的进化过程引入了自定义类型
在C++中可以通过类完成字符串类型的定义
问题:
- C++中的原生类型系统是否包含字符串类型?
StLib中字符串类的设计:
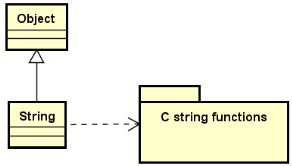
StLib中字符串类的实现:

实现时的注意事项:
- 无缝实现 String 对象与 char* 字符串的互操作
- 操作符重载函数需要考虑是否支持 const 版本
- 通过C语言中的字符串函数实现 String 的成员函数
在StLib中实现自定义 String 类:
StString.h
#ifndef STSTRING_H
#define STSTRING_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace StLib
{
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_str;
int m_length;
void init(const char* s);
public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s);
int length() const;
const char* str() const;
bool operator == (const String& s) const;
bool operator == (const char* s) const;
bool operator != (const String& s) const;
bool operator != (const char* s) const;
bool operator > (const String& s) const;
bool operator > (const char* s) const;
bool operator < (const String& s) const;
bool operator < (const char* s) const;
bool operator >= (const String& s) const;
bool operator >= (const char* s) const;
bool operator <= (const String& s) const;
bool operator <= (const char* s) const;
String operator + (const String& s) const;
String operator + (const char* s) const;
String& operator += (const String& s);
String& operator += (const char* s);
String& operator = (const String& s);
String& operator = (const char* s);
String& operator = (char c);
~String();
};
}
#endif // STSTRING_H
StString.cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "StString.h"
#include "Exception.h"
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
void String::init(const char *s)
{
m_str = strdup(s);
if( m_str )
{
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create String object ...");
}
}
String::String()
{
init("");
}
String::String(char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
init(s);
}
String::String(const char *s)
{
init(s ? s : "");
}
String::String(const String &s)
{
init(s.m_str);
}
int String::length() const
{
return m_length;
}
const char *String::str() const
{
return m_str;
}
bool String::operator == (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) == 0);
}
bool String::operator == (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") == 0);
}
bool String::operator != (const String& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator != (const char* s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator > (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) > 0);
}
bool String::operator > (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") > 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) < 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") < 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) >= 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") >= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) <= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") <= 0);
}
String String::operator + (const String& s) const
{
return (*this + s.m_str);
}
String String::operator + (const char* s) const
{
String ret;
int len = m_length + strlen(s ? s : "");
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + 1));
if( str )
{
strcpy(str, m_str);
strcat(str, s ? s : "");
free(ret.m_str);
ret.m_str = str;
ret.m_length = len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to add String values ...");
}
return ret;
}
String& String::operator += (const String& s)
{
return (*this = *this + s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator += (const char* s)
{
return (*this = *this + s);
}
String& String::operator = (const String& s)
{
return (*this = s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator = (const char* s)
{
if( m_str != s )
{
char* str = strdup(s ? s : "");
if( str )
{
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to assign new String value ...");
}
}
return *this;
}
String& String::operator = (char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
return (*this = s);
}
String::~String()
{
free(m_str);
}
}
main.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "StString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
void test_1()
{
cout << "test_1() begin ..." << endl;
String s;
s = 'D';
cout << s.str() << endl;
cout << s.length() << endl;
cout << (s == "D") << endl;
cout << (s > "CCC") << endl;
s += " Hello World ";
cout << s.str() << endl;
cout << s.length() << endl;
cout << (s == "D Hello World ") << endl;
cout << "test_1() end ..." << endl;
}
void test_2()
{
cout << "test_2() begin ..." << endl;
String a[] = {"E", "D", "C", "B", "A"};
String min = a[0];
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
if( min > a[i] )
{
min = a[i];
}
}
cout << "min = " << min.str() << endl;
cout << "test_2() end ..." << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_1();
test_2();
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
test_1() begin ...
D
1
1
1
D Hello World
14
1
test_1() end ...
test_2() begin ...
min = A
test_2() end ...
1.2 字符串类的功能扩展
字符串类中的常用成员函数:

重载数组访问操作符 [ ]:
- char& operator [] (int i);
- char operator [] (int i) const;
注意事项:
- 当 i 的取值不合法时,抛出异常
- 合法范围:( 0 <= i ) && ( i < m_length )
重载数组访问操作符 [ ]:
public:
char& operator [] (int i);
char operator [] (int i) const;
具体实现:
char& String::operator [] (int i)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
return m_str[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
}
char String::operator [] (int i) const
{
return (const_cast<String&>(*this))[i];
}
判断是否以指定字符串开始或结束:
- bool startWith(const char* s) const;
- bool startWith(const String& s) const;
- bool endOf(const char* s) const;
- bool endOf(const String& s) const;

判断是否以指定字符串开始或结束:
加入一个equal函数用于比较。
protected:
bool equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const;
public:
bool startWith(const char* s) const;
bool startWith(const String& s) const;
bool endOf(const char* s) const;
bool endOf(const String& s) const;
具体实现:
bool String::equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const
{
bool ret = true;
for(int i=0; i<len && ret; i++)
{
ret = ret && (l[i] == r[i]);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(m_str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const String& s) const
{
return startWith(s.m_str);
}
bool String::endOf(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = m_str + (m_length - len);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::endOf(const String& s) const
{
return endOf(s.m_str);
}
在指定位置处插入字符串:
- String& insert(int i, const char* s);
- String& insert(int i, const String& s);
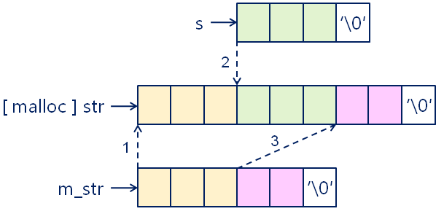
在指定位置处插入字符串:
public:
String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String& s);
具体实现:
String& String::insert(int i, const char* s)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i <= m_length) )
{
if( (s != NULL) && (s[0] != '�') )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length + len + 1));
if( str != NULL )
{
strncpy(str, m_str, i);
strncpy(str + i, s, len);
strncpy(str + i + len, m_str + i, m_length - i);
str[m_length + len] = '�';
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = m_length + len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert string value ...");
}
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
return *this;
}
String& String::insert(int i, const String& s)
{
return insert(i, s.m_str);
}
去掉字符串两端的空白字符:
- String& trim();
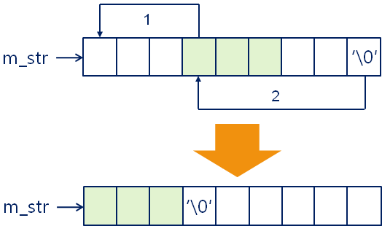
去掉字符串两端的空白字符:
public:
String& trim();
具体实现:
String& String::trim()
{
int b = 0;
int e = m_length - 1;
while( m_str[b] == ' ' ) b++;
while( m_str[e] == ' ' ) e--;
if( b == 0 )
{
m_str[e + 1] = '�';
m_length = e + 1;
}
else
{
for(int i=0, j=b; j<=e; i++, j++)
{
m_str[i] = m_str[j];
}
m_str[e - b + 1] = '�';
m_length = e - b + 1;
}
return *this;
}
main.cpp测试:
#include <iostream>
#include "StString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
String s = " ABC ";
if( s.trim().insert(0, "Hello").endOf("ABC") && s.startWith("Hello") )
{
cout << "[" <<s.str() << "]" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为;
[HelloABC]
2.小结
- C/C++语言本身不支持字符串类型
- C语言通过字符数组和一组函数支持字符串操作
- C++通过自定义字符串类型支持字符串操作
- 字符串类型通过C语言中的字符串函数实现
最终的自定义字符串类代码:
StString.h
#ifndef STSTRING_H
#define STSTRING_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace StLib
{
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_str;
int m_length;
void init(const char* s);
bool equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const;
public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s);
int length() const;
const char* str() const;
bool startWith(const char* s) const;
bool startWith(const String& s) const;
bool endOf(const char* s) const;
bool endOf(const String& s) const;
String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String& s);
String& trim();
char& operator [] (int i);
char operator [] (int i) const;
bool operator == (const String& s) const;
bool operator == (const char* s) const;
bool operator != (const String& s) const;
bool operator != (const char* s) const;
bool operator > (const String& s) const;
bool operator > (const char* s) const;
bool operator < (const String& s) const;
bool operator < (const char* s) const;
bool operator >= (const String& s) const;
bool operator >= (const char* s) const;
bool operator <= (const String& s) const;
bool operator <= (const char* s) const;
String operator + (const String& s) const;
String operator + (const char* s) const;
String& operator += (const String& s);
String& operator += (const char* s);
String& operator = (const String& s);
String& operator = (const char* s);
String& operator = (char c);
~String();
};
}
#endif // STSTRING_H
StString.cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "StString.h"
#include "Exception.h"
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
void String::init(const char *s)
{
m_str = strdup(s);
if( m_str )
{
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create String object ...");
}
}
String::String()
{
init("");
}
String::String(char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
init(s);
}
String::String(const char *s)
{
init(s ? s : "");
}
String::String(const String &s)
{
init(s.m_str);
}
int String::length() const
{
return m_length;
}
const char* String::str() const
{
return m_str;
}
bool String::equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const
{
bool ret = true;
for(int i=0; i<len && ret; i++)
{
ret = ret && (l[i] == r[i]);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(m_str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const String& s) const
{
return startWith(s.m_str);
}
bool String::endOf(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = m_str + (m_length - len);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::endOf(const String& s) const
{
return endOf(s.m_str);
}
String& String::insert(int i, const char* s)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i <= m_length) )
{
if( (s != NULL) && (s[0] != '�') )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length + len + 1));
if( str != NULL )
{
strncpy(str, m_str, i);
strncpy(str + i, s, len);
strncpy(str + i + len, m_str + i, m_length - i);
str[m_length + len] = '�';
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = m_length + len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert string value ...");
}
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
return *this;
}
String& String::insert(int i, const String& s)
{
return insert(i, s.m_str);
}
String& String::trim()
{
int b = 0;
int e = m_length - 1;
while( m_str[b] == ' ' ) b++;
while( m_str[e] == ' ' ) e--;
if( b == 0 )
{
m_str[e + 1] = '�';
m_length = e + 1;
}
else
{
for(int i=0, j=b; j<=e; i++, j++)
{
m_str[i] = m_str[j];
}
m_str[e - b + 1] = '�';
m_length = e - b + 1;
}
return *this;
}
char& String::operator [] (int i)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
return m_str[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
}
char String::operator [] (int i) const
{
return (const_cast<String&>(*this))[i];
}
bool String::operator == (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) == 0);
}
bool String::operator == (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") == 0);
}
bool String::operator != (const String& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator != (const char* s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator > (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) > 0);
}
bool String::operator > (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") > 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) < 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") < 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) >= 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") >= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) <= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") <= 0);
}
String String::operator + (const String& s) const
{
return (*this + s.m_str);
}
String String::operator + (const char* s) const
{
String ret;
int len = m_length + strlen(s ? s : "");
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + 1));
if( str )
{
strcpy(str, m_str);
strcat(str, s ? s : "");
free(ret.m_str);
ret.m_str = str;
ret.m_length = len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to add String values ...");
}
return ret;
}
String& String::operator += (const String& s)
{
return (*this = *this + s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator += (const char* s)
{
return (*this = *this + s);
}
String& String::operator = (const String& s)
{
return (*this = s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator = (const char* s)
{
if( m_str != s )
{
char* str = strdup(s ? s : "");
if( str )
{
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to assign new String value ...");
}
}
return *this;
}
String& String::operator = (char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
return (*this = s);
}
String::~String()
{
free(m_str);
}
}