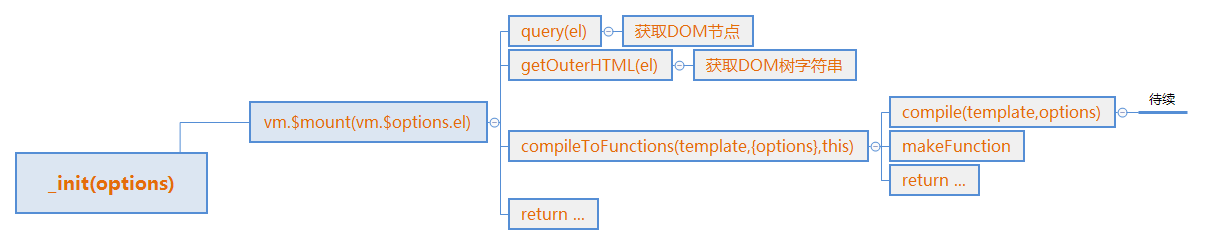
讲完了数据劫持原理和一堆初始化 现在是DOM相关的代码了
上一节是从这个函数开始的:
// Line-3924 Vue.prototype._init = function(options) { // 大量初始化 // ... // Go! if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el); } };
弄完data属性的数据绑定后,开始处理el属性,也就是挂载的DOM节点,这里的vm.$options.el也就是传进去的'#app'字符串。
有一个值得注意的点是,源码中有2个$mount函数都是Vue$3的原型函数,其中一个标记了注释public mount method,在7531行,另外一个在9553行。打断点进入的是后面,因为定义的晚,覆盖了前面的函数。
(时隔多日,我终于看懂了,这里首先定义了原型方法$mount,然后将其赋给了一个变量mount,然后重新定义此方法,所以调用mount.call会调用第一次定义的$mount,vue原型上最终只有第二次定义的$mount) => 多此一举! 2017.7.31
// Line-7531 // public mount method Vue$3.prototype.$mount = function(el,hydrating) { el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined; return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) }; // Line-9552 var mount = Vue$3.prototype.$mount; Vue$3.prototype.$mount = function( el, hydrating ) { // ...很多代码 return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) };
现在进入后面的$mount函数看看内部结构:
// Line-9552 var mount = Vue$3.prototype.$mount; Vue$3.prototype.$mount = function(el,hydrating) { // 将el格式化为DOM节点 el = el && query(el); // 判断是否挂载到body或者html标签上 if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { "development" !== 'production' && warn( "Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead." ); return this } var options = this.$options; // 处理template/el 转换为渲染函数 if (!options.render) { // ...非常多代码 } return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) };
代码前半段首先将el转换为DOM节点,并判断是否挂载到body或者html标签,看看简单的query函数:
// Line-4583 function query(el) { // 如果是字符串就调用querySelector if (typeof el === 'string') { var selected = document.querySelector(el); if (!selected) { "development" !== 'production' && warn( 'Cannot find element: ' + el ); // 找不到就返回一个div return document.createElement('div') } return selected } // 不是字符串就默认传进来的是DOM节点 else { return el } }
函数比较简单,值得注意的一个点是,由于调用的是querySelector方法,所以可以传标签名、类名、C3新选择器等,都会返回查询到的第一个。当然,总是传一个ID或者确定的DOM节点才是正确用法。
下面看接下来的代码:
// Line-9552 var mount = Vue$3.prototype.$mount; Vue$3.prototype.$mount = function(el,hydrating) { // ...el转换为DOM节点 // ... // 没有render属性 进入代码段 if (!options.render) { var template = options.template; // 没有template 跳 if (template) { if (typeof template === 'string') { if (template.charAt(0) === '#') { template = idToTemplate(template); /* istanbul ignore if */ if ("development" !== 'production' && !template) { warn( ("Template element not found or is empty: " + (options.template)), this ); } } } else if (template.nodeType) { template = template.innerHTML; } else { { warn('invalid template option:' + template, this); } return this } } // 有el 获取字符串化的DOM树 else if (el) { template = getOuterHTML(el); } if (template) { // ...小段代码 } } return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) };
由于没有template属性,会直接进入第二个判断条件,调用getOuterHTML来初始化template变量,函数比较简单, 来看看:
// Line-9623 function getOuterHTML(el) { if (el.outerHTML) { return el.outerHTML } // 兼容IE中的SVG else { var container = document.createElement('div'); container.appendChild(el.cloneNode(true)); return container.innerHTML } }
简单来讲,就是调用outerHTML返回DOM树的字符串形式,看图就明白了: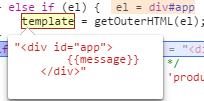
下面看最后一段代码:
// Line-9552 var mount = Vue$3.prototype.$mount; Vue$3.prototype.$mount = function(el,hydrating) { // ...el转换为DOM节点 // ... // 没有render属性 进入代码段 if (!options.render) { // ...处理template // ... if (template) { // 编译开始 if ("development" !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile'); } // 将DOM树字符串编译为函数 var ref = compileToFunctions(template, { shouldDecodeNewlines: shouldDecodeNewlines, delimiters: options.delimiters }, this); // options添加属性 var render = ref.render; var staticRenderFns = ref.staticRenderFns; options.render = render; options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns; // 编译结束 if ("development" !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile end'); measure(((this._name) + " compile"), 'compile', 'compile end'); } } } return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) };
忽略2段dev模式下的提示代码,剩下的代码做了3件事,调用compileToFunctions函数肢解DOM树字符串,将返回的对象属性添加到options上,再次调用mount函数。
首先看一下compileToFunctions函数,该函数接受3个参数,分别为字符串、配置对象、当前vue实例。
由于函数比较长,而且部分是错误判断,简化后如下:
// Line-9326 function compileToFunctions(template,options,vm) { // 获取配置参数 options = options || {}; // ... var key = options.delimiters ? String(options.delimiters) + template : template; // 检测缓存 if (functionCompileCache[key]) { return functionCompileCache[key] } // 1 var compiled = compile(template, options); // ... // 2 var res = {}; var fnGenErrors = []; res.render = makeFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors); var l = compiled.staticRenderFns.length; res.staticRenderFns = new Array(l); for (var i = 0; i < l; i++) { res.staticRenderFns[i] = makeFunction(compiled.staticRenderFns[i], fnGenErrors); } // ... // 3 return (functionCompileCache[key] = res) }
可以看到,这个函数流程可以分为4步,获取参数 => 调用compile函数进行编译 => 将得到的compiled转换为函数 => 返回并缓存。
第一节现在这样吧。一张图总结下: