这里的编译前指的是开始触发主要的事件流this-compilaiton、compilation之前,由于还有一些准备代码,这一节全部弄出来。
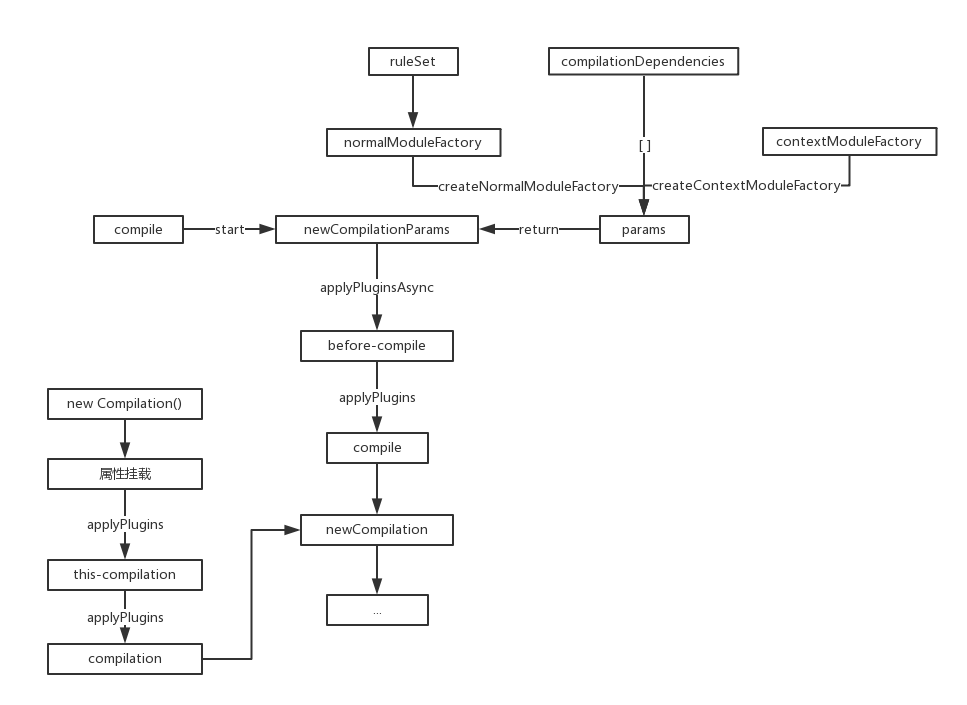
模块基本上只走构造函数,具体的方法调用的时候再具体讲解。
上一节NormalModuleFactory模块的构造函数中,在处理完rules后,注入两个事件流就结束了,所以可以回到如下代码:
createNormalModuleFactory() { // 构造完成 const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory(this.options.context, this.resolvers, this.options.module || {}); // 该事件流默认是没有的 this.applyPlugins("normal-module-factory", normalModuleFactory); return normalModuleFactory; }
由于没有对应的事件流,所以会回到params参数的构建:
newCompilationParams() { const params = { // done normalModuleFactory: this.createNormalModuleFactory(), contextModuleFactory: this.createContextModuleFactory(), compilationDependencies: [] }; return params; }
这里的contextModuleFactory模块并没有任何初始化好讲的,简单贴一下代码跳过:
createContextModuleFactory() { const contextModuleFactory = new ContextModuleFactory(this.resolvers, this.inputFileSystem); this.applyPlugins("context-module-factory", contextModuleFactory); return contextModuleFactory; } class ContextModuleFactory extends Tapable { constructor(resolvers) { super(); this.resolvers = resolvers; }; // methods... }
完成了params对象的构建后,会回到compile函数,继续触发其余的事件流:
compile(callback) { const params = this.newCompilationParams(); // 暂无 this.applyPluginsAsync("before-compile", params, err => { if (err) return callback(err); // 暂无 this.applyPlugins("compile", params); const compilation = this.newCompilation(params); this.applyPluginsParallel("make", compilation, err => { /**/ }); }); }
然而在打包中,'before-compile'、'compile'事件流是空的,代码会继续下面一行:
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
这行代码源码如下:
createCompilation() { return new Compilation(this); } newCompilation(params) { // 生成一个Compilation类 const compilation = this.createCompilation(); // 空对象{} compilation.fileTimestamps = this.fileTimestamps; // 空对象{} compilation.contextTimestamps = this.contextTimestamps; // undefined compilation.name = this.name; // 空对象{} compilation.records = this.records; // 空数组[] compilation.compilationDependencies = params.compilationDependencies; // 编译 this.applyPlugins("this-compilation", compilation, params); this.applyPlugins("compilation", compilation, params); return compilation; }
除去第一行代码,其余的都是进行属性挂载,在初次打包时都是空的对象或数组,所以作用也看不出,后面再进行详解。
Compilation
剩余的就是Compilation对象的实例化,只过构造函数,源码如下:
class Compilation extends Tapable { constructor(compiler) { super(); // 获取配置属性 this.compiler = compiler; this.resolvers = compiler.resolvers; this.inputFileSystem = compiler.inputFileSystem; const options = this.options = compiler.options; this.outputOptions = options && options.output; this.bail = options && options.bail; this.profile = options && options.profile; this.performance = options && options.performance; // 引入模板解析模块 this.mainTemplate = new MainTemplate(this.outputOptions); this.chunkTemplate = new ChunkTemplate(this.outputOptions); this.hotUpdateChunkTemplate = new HotUpdateChunkTemplate(this.outputOptions); this.moduleTemplate = new ModuleTemplate(this.outputOptions); this.semaphore = new Semaphore(options.parallelism || 100); this.entries = []; // ...其余属性初始化 }; // methods... }
构造函数中主要有三块内容:
1、获取配置文件中的一些属性
2、引入模板解析的辅助模块
3、初始化其余本地属性
配置文件的属性获取与初始化本地属性跳过,这里简单过一下几个辅助模块,分别为:MainTemplate、ChunkTemplate、HotUpdateChunkTemplate、ModuleTemplate,从名字应该能看出作用了吧?
MainTemplate
源码简化如下:
// require function shortcuts: // __webpack_require__.s = the module id of the entry point // __webpack_require__.c = the module cache // __webpack_require__.m = the module functions // __webpack_require__.p = the bundle public path // __webpack_require__.i = the identity function used for harmony imports // __webpack_require__.e = the chunk ensure function // __webpack_require__.d = the exported propery define getter function // __webpack_require__.o = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call // __webpack_require__.n = compatibility get default export // __webpack_require__.h = the webpack hash // __webpack_require__.oe = the uncatched error handler for the webpack runtime // __webpack_require__.nc = the script nonce class MainTemplate extends Template { constructor(outputOptions) { super(outputOptions); this.plugin("startup", (source, chunk, hash) => { /**/ }); this.plugin("render", (bootstrapSource, chunk, hash, moduleTemplate, dependencyTemplates) => { /**/ }); this.plugin("local-vars", (source, chunk, hash) => { /**/ }); this.plugin("require", (source, chunk, hash) => { /**/ }); this.plugin("module-obj", (source, chunk, hash, varModuleId) => { /**/ }); this.plugin("require-extensions", (source, chunk, hash) => { /**/ }); this.requireFn = "__webpack_require__"; }; render(hash, chunk, moduleTemplate, dependencyTemplates) { /**/ } renderRequireFunctionForModule(hash, chunk, varModuleId) { /**/ } renderAddModule(hash, chunk, varModuleId, varModule) { /**/ } renderCurrentHashCode(hash, length) { /**/ } entryPointInChildren(chunk) { /**/ } getPublicPath(options) { /**/ } updateHash(hash) { /**/ } updateHashForChunk(hash, chunk) { /**/ } useChunkHash(chunk) { /**/ } };
注意头部的注释,这里解释了打包后文件中模块生成函数__webpack_require__上各个参数的意义,属于Template的主模块。
最后的requireFn就是那个函数的名字,如果改了打包后文件的名字也会变哦,演示一下:
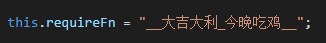
执行一下webpack指令,会看到打包文件如下:
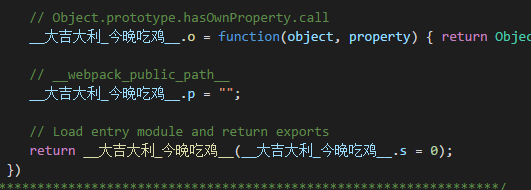
还挺好玩的。
ChunkTemplate
class ChunkTemplate extends Template { constructor(outputOptions) { super(outputOptions); }; render(chunk, moduleTemplate, dependencyTemplates) {/**/}; updateHash(hash) {/**/}; updateHashForChunk(hash, chunk) {/**/}; };
HotUpdateChunkTemplate
class HotUpdateChunkTemplate extends Template { constructor(outputOptions) { super(outputOptions); }; render(id, modules, removedModules, hash, moduleTemplate, dependencyTemplates) { /**/ }; updateHash(hash) { /**/ }; };
ModuleTemplate
class ModuleTemplate extends Template { constructor(outputOptions) { super(outputOptions); } render(module, dependencyTemplates, chunk) { /**/ } updateHash(hash) { /**/ } };
这三个模块都是辅助用,简单看一下方法有个印象就行了。
可以注意到4个模块都有一个爹,叫做Template。
这个模块属于纯工具模块,内部定义了大量的静态方法以便操作字符串,这里讲一下得了,不然这节没啥内容,源码整理后如下:
"use strict"; const Tapable = require("tapable"); const ConcatSource = require("webpack-sources").ConcatSource; const START_LOWERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE = "a".charCodeAt(0); // ...其余常量定义 module.exports = class Template extends Tapable { constructor(outputOptions) { super(); this.outputOptions = outputOptions || {}; }; static getFunctionContent(fn) { /**/ }; static toIdentifier(str) { /**/ }; static toPath(str) { /**/ }; static numberToIdentifer(n) { /**/ }; indent(str) { /**/ } prefix(str, prefix) { /**/ } asString(str) { /**/ } getModulesArrayBounds(modules) { /**/ } renderChunkModules(chunk, moduleTemplate, dependencyTemplates, prefix) { /**/ } }; function stringifyIdSortPredicate(a, b) { /**/ } function moduleIdIsNumber(module) { /**/ }
内部主要包括四部分:
1、常量定义
2、静态方法
3、工具方法
4、内部函数
一个一个来。
常量const
// a的Unicode编码 => 97 const START_LOWERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE = "a".charCodeAt(0); // A的Unicode编码 => 65 const START_UPPERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE = "A".charCodeAt(0); // 122 - 97 + 1 = 26 返回字母数量 const DELTA_A_TO_Z = "z".charCodeAt(0) - START_LOWERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE + 1; // 匹配函数内容 const FUNCTION_CONTENT_REGEX = /^functions?()s?{ ?| ?}$/g; // 全行匹配tab制表符 const INDENT_MULTILINE_REGEX = /^ /mg; // 匹配非大小写字母$_开头 const IDENTIFIER_NAME_REPLACE_REGEX = /^[^a-zA-Z$_]/; // 匹配非大小写字母数字$_ const IDENTIFIER_ALPHA_NUMERIC_NAME_REPLACE_REGEX = /[^a-zA-Z0-9$_]/g; // 神奇的字符 已经不知道匹配的是啥了 const PATH_NAME_NORMALIZE_REPLACE_REGEX = /[^a-zA-Z0-9_!§$()=-^°]+/g; // 匹配以-开始或结尾 const MATCH_PADDED_HYPHENS_REPLACE_REGEX = /^-|-$/g;
大部分都非常简单,有两个比较特殊,一个是匹配函数内容,这个需要配合静态方法来讲解。
另一个就是PATH_NAME_NORMALIZE_REPLACE_REGEX,里面有几个字符可能这辈子在代码里都不会看到吧……
静态方法
class Template extends Tapable { constructor(outputOptions) { /**/ }; // 抽取函数内容 static getFunctionContent(fn) { return fn.toString().replace(FUNCTION_CONTENT_REGEX, "").replace(INDENT_MULTILINE_REGEX, ""); }; // 头部数字、所有的特殊字符置换为'_' static toIdentifier(str) { if (typeof str !== "string") return ""; return str.replace(IDENTIFIER_NAME_REPLACE_REGEX, "_").replace(IDENTIFIER_ALPHA_NUMERIC_NAME_REPLACE_REGEX, "_"); }; // 特殊字符置换为'-' // 去掉头尾的'-' static toPath(str) { if (typeof str !== "string") return ""; return str.replace(PATH_NAME_NORMALIZE_REPLACE_REGEX, "-").replace(MATCH_PADDED_HYPHENS_REPLACE_REGEX, ""); }; // 数字转换为字母 static numberToIdentifer(n) { // n ∈ [0,26) 返回 a-z if (n < DELTA_A_TO_Z) return String.fromCharCode(START_LOWERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE + n); // n ∈ [26,52) 返回 A-Z n -= DELTA_A_TO_Z; if (n < DELTA_A_TO_Z) return String.fromCharCode(START_UPPERCASE_ALPHABET_CODE + n); // n ∈ [52,正无穷大) 返回 '_ + (n-52)' n -= DELTA_A_TO_Z; return "_" + n; } }
也非常的简单,这里每一个都举个小例子:
1、getFunctionContent
const fn1 = function() { console.log(1); }; // console.log(1) const result = Template.getFunctionContent(fn1.toString());
这个方法就是抽取出函数内容,注意,必须是函数表达式,使用箭头函数或者具名函数将失效。
const fn1 = () => { console.log(1); }; /* 失败 () => { console.log(1); } */ const result = Template.getFunctionContent(fn1.toString());
const fn1 = function fn1() { console.log(1); }; /* 失败 function fn1() { console.log(1); } */ const result = Template.getFunctionContent(fn1.toString());
2、toIdentifier
// __1_2_3_4_5_6 const result = Template.toIdentifier('0/1.2,3;4[5]6');
3、toPath
// d-workspace-doc const result = Template.toPath('d://workspace//doc//');
4、numberToIdentifer
// a const result = Template.numberToIdentifer(0); // E const result2 = Template.numberToIdentifer(30); // _48 const result3 = Template.numberToIdentifer(100);
简单易懂,包教包会!
工具方法
class Template { indent(str) { // 数组map处理 if (Array.isArray(str)) { return str.map(this.indent.bind(this)).join(" "); } else { // 去除右空白 实验性方法 str = str.trimRight(); if (!str) return ""; var ind = (str[0] === " " ? "" : " "); // 两个制表符 return ind + str.replace(/ ([^ ])/g, " $1"); } } prefix(str, prefix) { // 传入数组换行拼接 if (Array.isArray(str)) { str = str.join(" "); } // 去除两侧空白 str = str.trim(); if (!str) return ""; const ind = (str[0] === " " ? "" : prefix); // 加前缀 return ind + str.replace(/ ([^ ])/g, " " + prefix + "$1"); } asString(str) { // 数组换行拼接或返回原字符串 if (Array.isArray(str)) { return str.join(" "); } return str; } }
前三个比较简单,直接看源码就懂了。
1、indent
这个方法简单讲解就是把每行往后推两个制表符,如果传入字符数组则如下所示:
const tmp = new Template(); const str = ['a', 'b', 'c']; /* a b c */ const result = tmp.indent(str);
2、prefix
简单讲就是给字符串加前缀:
const tmp = new Template(); // -a const result = tmp.prefix(`a`, `-`);
3、asString
传入数组会分别进行换行拼接,非数组直接返回:
const tmp = new Template(); /* a b c */ const result = tmp.asString(['a', 'b', 'c']);
4、getModulesArrayBounds
Template.prototype.getModulesArrayBounds = (modules) => { // typeof module.id === 'number' if (!modules.every(moduleIdIsNumber)) return false; var maxId = -Infinity; var minId = Infinity; // 获取modules中的最大与最小id // 一个模块对应一个id modules.forEach(function(module) { if (maxId < module.id) maxId = module.id; if (minId > module.id) minId = module.id; }); // 当最小id小于16 + 位数 置0 if (minId < 16 + ("" + minId).length) { // add minId x ',' instead of 'Array(minId).concat(...)' minId = 0; } // map返回每一个module.id位数+2 // reduce将数组元素相加 起始值为-1 var objectOverhead = modules.map(function(module) { var idLength = (module.id + "").length; return idLength + 2; }).reduce(function(a, b) { return a + b; }, -1); // 这里的应用到实际调用的时候再看吧 var arrayOverhead = minId === 0 ? maxId : 16 + ("" + minId).length + maxId; return arrayOverhead < objectOverhead ? [minId, maxId] : false; }
这个函数并不复杂,但是不懂是如何应用的。
5、renderChunkModules
这个没法单独讲,调用的时候做讲解。
内部函数
// 这是按字符串排序 // 即 2 > 11 function stringifyIdSortPredicate(a, b) { var aId = a.id + ""; var bId = b.id + ""; if (aId < bId) return -1; if (aId > bId) return 1; return 0; } // 这个工具方法有使用 function moduleIdIsNumber(module) { return typeof module.id === "number"; }
比较简单。
至此,该模块内容基本完事,有一个方法需要在用的时候做解析。
接下来几节就将正式进入编译阶段。