Scenario:
user (68.85.2.101) connects to School network’s Ethernet switch and downloads a webpage from Google;
Ethernet switch is connected to School’s router (68.85.2.1), within which DHCP server is running;
School’s router is connected to ISP (Comcast.net), which provides DNS service for the school;
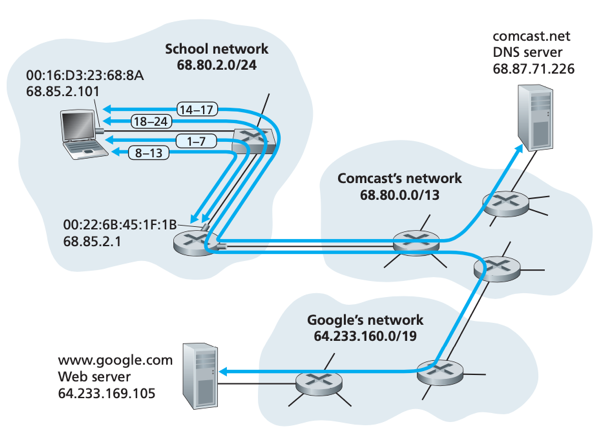
DHCP – for client to obtain IP address, only the last 2 DHCP steps of the 4 are necessary.
user client (00:16:D3:23:68:8A)
-> creates a DHCP request message
-> puts the DHCP message within a UDP segment
-> puts the UDP segment within an IP datagram with destination IP address 255.255.255.255 (broadcast) and source IP address 0.0.0.0
-> put the IP datagram within an Ethernet frame with destination MAC addresses FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF (broadcast);
Ethernet switch
-> receives the Ethernet frame and broadcast it;
gateway router (00:22:68:45:1F:1B)
-> receives the Ethernet frame, extracts the IP datagram
-> demultiplexes the datagram’s payload to UDP
-> extracts the DHCP request message to DHCP server;
-> DHCP server allocates IP address (68.85.2.101) to user client, creates a DHCP ACK message that contains the allocated 1) IP address, 2) IP address of DNS server, 3) IP address of default gateway router (68.85.2.1), and network mask (68.80.2.0/24);
-> puts the DHCP message within a UDP segment;
-> puts the UDP segment within an IP datagram;
-> puts the IP datagram within an Ethernet frame addressed to MAC address of the user;
Ethernet switch
-> forwards the Ethernet frame to user (it knows how to forward because it is self-learning and previously received frame from user);
user client
-> receives the Ethernet frame, extracts the IP datagram;
-> extracts the UDP segment;
-> extracts the DHCP ACK message;
-> records the allocated IP address and the IP address of DNS server; Installs the address of default gateway into its IP forwarding table (so all datagrams with destination outside of its subnet will be sent to the gateway);
DNS and ARP
user client
Web browser creates a TCP socket that will be used to send HTTP request. To create the socket, need to know IP address of the web URI:
-> creates a DNS query message;
-> puts the DNS message within a UDP segment;
-> puts the UDP segment within an IP datagram, addressed to IP address of the DNS server (68.87.71.226);
-> puts the IP datagram within an Ethernet frame;
To send the Ethernet frame to gateway, need to know MAC address of the school’s gateway router:
-> creates an ARP query message addressed to default gateway’s IP address (68.85.2.1);
-> puts the ARP message within an Ethernet frame, with broadcast destination address;
Ethernet switch
-> receives the Ethernet frame, broadcasts it;
gateway router
-> receives the Ethernet frame, finds the target IP address matches the IP address of its interface, thus creates an ARP reply indicating its MAC address 00:22:6B:45:1F:1B corresponds to IP address 68.85.2.1;
-> puts the ARP message within an Ethernet frame, sends it to user client.
user client
-> receives the ARP reply message, extracts the MAC address of the gateway router, thus can address the Ethernet frame that contains the DNS query;
-> sends the Ethernet frame to switch, … .
Intra-Domain Routing
gateway router
-> receives the Ethernet frame, extracts the IP datagram;
-> looks up the forwarding table to determines where to forward the datagram;
-> puts the IP datagram within a link-layer frame appropriate for the link connecting the router to the target router;
router in another (Camcast’s) network
-> receives the frame, extracts the IP datagram;
-> looks up the forwarding table to determine where to forward the datagram. The forwarding table has been filled by intra-domain protocols (e.g. RIP, OSPF, IS-IS) and inter-domain protocol BGP.
DNS server
-> receives …, extracts the DNS query message;
-> looks up the DNS database, finds the corresponding DNS resource record;
-> creates a DNS reply message, puts the DNS reply message within a UDP segment, puts the UDP segment within an IP datagram addressed to user;
… the datagram is forwarded back to user, user then can contact the target server.
Web Client-Server Interaction
user client
-> creates a TCP socket, perform a three-way handshake with the TCP in server side:
--> creates a TCP SYN segment (addressed to port 80 for HTTP);
--> puts the TCP segment within an IP datagram (addressed to server’s IP address);
--> puts the IP datagram within a frame (addressed to MAC address of the gateway router);
… the datagram is forwarded to server.
Server (www.google.com)
--> receives …, extracts the TCP SYN message;
--> demultiplexes to welcome socket (associated with port 80), thus creates a connection socket;
--> creates a TCP SYNACK segment;
--> puts the TCP segment within a datagram (addressed to user’s IP address);
--> puts the datagram within a link-layer frame (addressed to its first-hop router);
… The datagram is forwarded to user (ethernet card in his PC).
user client
--> receives …, demultiplexes to TCP socket, TCP socket thus enters the connected state;
-> browser creates HTTP GET message containing the URL to be fetched;
-> writes the HTTP GET message into socket, thus puts the message within a TCP segment;
-> puts the TCP segment within a datagram addressed to server.
… The datagram is forwarded to server.
Server (www.google.com)
-> receives …, reads the HTTP GET message from TCP socket;
-> creates an HTTP response message, puts the requested Web page content in the body of the message;
-> sends the HTTP response message into TCP socket;
…
… the datagram is forwarded to user;
user client
-> receives …, Web browser reads the HTTP response from socket;
-> Web browser extracts the html from HTTP response, the Web page is displayed.
Possible additional protocols omitted:
· NAT (running in gateway router);
· wireless access (to the network);
· security protocols (for accessing the network or encrypting segments/datagrams)
· network management protocols;
· Web caching, DNS hierarchy (possibly encountered in public Internet).