1 SVD 相关理论
1.1 奇异值分解定义
SVD,即奇异值分解,矩阵论中学过内容,公式为:
![]()
用一张图来形象表达一下:
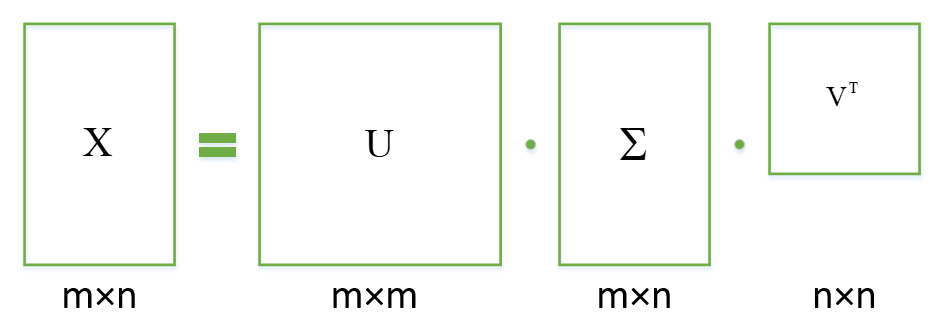
其中的奇异值矩阵,奇异值从大到小排列,而且减少的特别快,我们可以用前面最大的k个奇异值来表示这个原有矩阵,且保留大部分信息。如图:
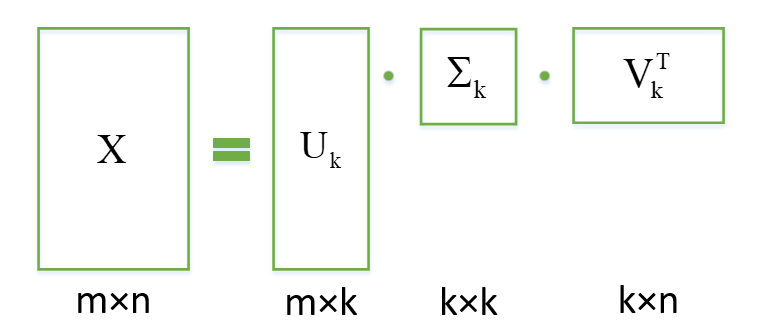
1.2 与PCA有何勾结
之前我们解释过 PCA ,PCA 的本质就是将原数据投影到低维坐标系中,获取主要信息值,起到降维作用。
究竟 SVD 与其有何关系呢?我们看一下下面的公式推导,就明白了。

由上图可以比较出,PCA 中得到的 P 就是奇异值分解中的 V。
如果需要给列降维到 k ,则:
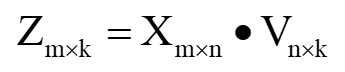
如果需要给行降维到 k ,则:
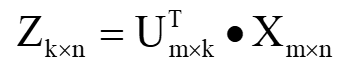
即左奇异矩阵负责给行降维,一般用来减小无效样本。
右奇异矩阵负责给列降维,一般用来缩减特征。
1.3 优点与用途
优点:
当我们使用PCA的时候,用到协方差矩阵,但是当样本数量m大特征n也大的时候,协方差就不好计算,特征值和特征向量就不易求出。此时如果使用SVD,速度快很多,有人会说,奇异值分解时不也是利用了协方差矩阵么?其实不然这只是求取分解的一种方法,一般会使用迭代的办法,这里不赘述,只需明白它的计算速度远远加快,有兴趣可以看看这两篇文章:
并行计算奇异值:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang/articles/2575948.html
一篇关于奇异值计算的论文:http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/inderjit/public_papers/HLA_SVD.pdf
用途:
-
特征降维
-
去除噪声
-
推荐系统
-
信息搜索(潜在语义分析,LSA)
-
2 Python 实例
2.1 基于 SVD 的图像压缩
1 from numpy import * 2 from numpy import linalg as la 3 4 def printMat(inMat,thresh=0.8): 5 for i in range(32): 6 for k in range(32): 7 if float(inMat[i,k])>thresh: 8 # pycharm中会自动换行,此处加上 end=‘’ ,以达到效果 9 print('1',end='') 10 else: 11 print('0',end='') 12 print('') 13 14 def imgCompress(numSV=3,thresh=0.8): 15 my1=[] 16 for line in open('0_5.txt').readlines(): 17 newRow=[] 18 for i in range(32): 19 newRow.append(int(line[i])) 20 my1.append(newRow) 21 myMat=mat(my1) 22 print(myMat) 23 print("***** original matrix *****") 24 printMat(myMat,thresh) 25 U,Sigma,VT=la.svd(myMat) 26 SigRecon=mat(zeros((numSV,numSV))) 27 for k in range(numSV): 28 SigRecon[k,k]=Sigma[k] 29 reconMat=U[:,:numSV]*SigRecon*VT[:numSV,:] 30 print("***** reconstructed matrix using %d singular values *****") 31 printMat(reconMat,thresh) 32 33 imgCompress(2)
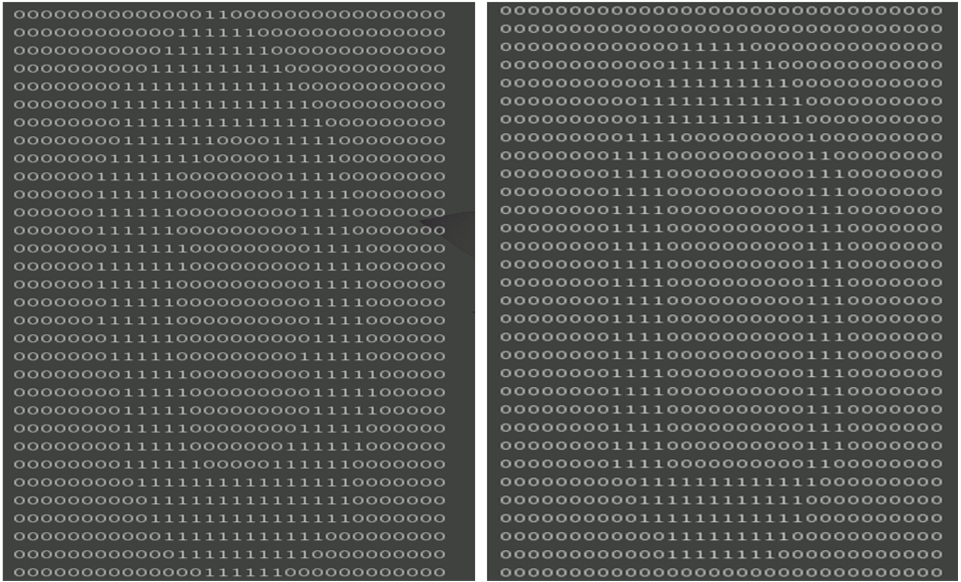
分析:
- 左边原始矩阵,右边是奇异值分解后处理矩阵,得到的图像基本一致,可以看到只需要两个奇异值就能相对准确地对图像重建。
- 内存使用:原始图像:32*32=1024,奇异值分解后:2*32+2+2*32=130,缩小了将近10倍。
2.2 餐馆菜肴推荐引擎
过程:
- 寻找用户没有评级的菜肴,即在用户-物品矩阵中的 0 值。
- 在用户没有评级的所有物品中,对每个物品预计一个可能的评级的分数。(利用相似度进行计算)
- 对这些物品的评分从高到低排序,返回前 N 个物品。
程序:

1 from numpy import * 2 from numpy import linalg as la 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 # 1. 输入数据,用户-物品评级矩阵 6 def loadExData2(): 7 return [[2, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], 8 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5], 9 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 4, 0], 10 [3, 3, 4, 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0], 11 [5, 5, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], 12 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 5, 0], 13 [4, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5], 14 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4], 15 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 5, 0], 16 [0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 5, 0], 17 [1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 0, 4, 5, 0]] 18 19 # 2. 几种计算相似度的方法, 20 # 欧式距离 21 def ecludSim(inA,inB): 22 return 1.0/(1.0+la.norm(inA-inB)) 23 # 皮尔逊距离 24 def pearsSim(inA,inB): 25 if len(inA)<3: 26 return 1.0 27 return 0.5+0.5*corrcoef(inA,inB,rowvar=0)[0][1] 28 # 余弦距离 29 def cosSim(inA,inB): 30 num =float(inA.T*inB) 31 denom=la.norm(inA)*la.norm(inB) 32 return 0.5+0.5*(num/denom) 33 34 # 3. 计算给定相似度计算方法下的估计评分值 35 # 指定用户 user 给未评定物品 item 评分 36 def standEst(dataMat,user,simMeas,item): 37 n=shape(dataMat)[1] 38 simTotal=0.0 39 ratSimTotal=0.0 40 # 遍历每一个物品,根每一个有过评分的物品比较,计算相似度,推测出评分 41 for j in range(n): 42 userRating=dataMat[user,j] 43 # 如果某个用户没有对这个物品评分,跳过这个值 44 if userRating==0: 45 continue 46 # 比较目标物品和已被评分过的物品重合程度 47 overLap=nonzero(logical_and(dataMat[:,item].A>0,dataMat[:,j].A>0))[0] 48 # 如果重合为0,则相似度为0 49 if len(overLap)==0: 50 similarity=0 51 else: 52 # 如果有重合,基于这些特征重合计算相似度 53 similarity=simMeas(dataMat[overLap,item],dataMat[overLap,j]) 54 # print("the %d and %d similarity is: %f "%(item,j,similarity)) 55 # 累加相似度 56 simTotal+=similarity 57 # 累加相似度和评分的乘积,可以得到评分总和,(归一化的) 58 ratSimTotal+=similarity*userRating 59 if simTotal==0: 60 return 0 61 else: 62 return ratSimTotal/simTotal 63 64 # 4. 使用 SVD 降维后进行相似度计算 65 def svdEst(dataMat,user,simMeas,item): 66 n=shape(dataMat)[1] 67 simTotal=0.0 68 ratSimTotal=0.0 69 U, Sigma, VT = la.svd(dataMat) 70 # 取 sigma 前4的值,构建对角矩阵 71 Sig4=mat(eye(4)*Sigma[:4]) 72 # 将原数据投影到左奇异矩阵上,使其行降维,即减少无效用户 73 xformedItems=dataMat.T*U[:,:4]*Sig4.I 74 for j in range(n): 75 userRating=dataMat[user,j] 76 if userRating==0 or j==item: 77 continue 78 similarity=simMeas(xformedItems[item,:].T,xformedItems[j,:].T) 79 # print("the %d and %d similarity is: %f "%(item,j,similarity)) 80 simTotal += similarity 81 # 累加相似度和评分的乘积,可以得到评分总和,(归一化的) 82 ratSimTotal += similarity * userRating 83 if simTotal == 0: 84 return 0 85 else: 86 return ratSimTotal / simTotal 87 88 # 5. 推荐引擎,返回得分较高的前 N 个物品 89 def recommend(dataMat,user,N=3,simMeas=cosSim,estMethod=standEst): 90 # 寻找未评级的物品 91 unratedItems=nonzero(dataMat[user,:].A==0)[1] 92 if len(unratedItems)==0: 93 return print("you rated everything") 94 itemScores=[] 95 for item in unratedItems: 96 estimatedScore=estMethod(dataMat,user,simMeas,item) 97 itemScores.append((item,estimatedScore)) 98 return sorted(itemScores,key=lambda jj:jj[1],reverse=True)[:N] 99 100 myMat=mat(loadExData2()) 101 print(recommend(myMat,1,estMethod=svdEst)) 102 print(recommend(myMat,1)) 103 U,Sigma,VT=linalg.svd(myMat) 104 Sig2=Sigma**2 105 fig=plt.figure() 106 ax=fig.add_subplot(111) 107 ax.pie(Sig2,autopct='%1.1f') 108 plt.show()
结果:
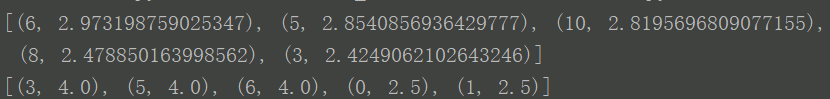
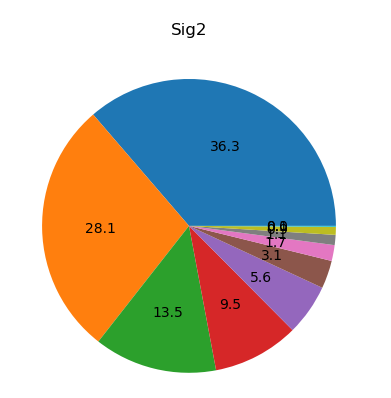
分析:
- 对奇异值分析可知,前五个值占了绝大部分信息(注意这里与书里有些不一致)
- 使用SVD分解后的数据推荐引擎更准确
提高构建推荐引擎时的效率:
- SVD 大量数据分解速度慢,尽量运行一次或者离线运行。
- 零元素太多,通过储存非零元素节省资源。
- 每次需要推荐一个得分时,都需要计算多个物品的相似度,离线计算并保存相似度。
- 冷启动问题:如何在缺乏数据时给出好的推荐。将推荐看成搜索问题。
参考文献:
- 奇异值分解与在降维中的应用 https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6251584.html
