|__all together ship
|__SLAM__
|__Graph SLAM__
|__完成约束
|__完成Graph SLAM__
| |__完成约束(格子)
| |__加入地标
|
|__ Ω和§
| |__编程(Init_pos,move1,move2)
| |__加入检测(加入每次测量Z0,Z1,Z2)
|__引入噪音
|__完整的SLAM编程

PID:P的主要功能是让误差最小,因为转向角正比于误差。D使用得当能避免超调。系统漂移与偏置最好用I解决。
是时候了,put all together to make a system,这个系统采用车辆模型,并且使用了之前的robot类,得到连续空间里的最短路径
steering_noise = 0.1 distance_noise = 0.03 measurement_noise = 0.3 class robot: def __init__(self,length = 0.5): self.x = 0.0 self.y = 0.0 self.orientation = 0.0 self.length = length self.steering_noise = 0.0 self.distance_noise = 0.0 self.measurement_noise = 0.0 self.num_collisions = 0 self.num_steps = 0 def set(self,new_x,new_y,new_orientation): self_x = float(new_x) self_y = float(new_y) self_orientation = float(new_orientation) % (2.0*pi) def set_noise(self,new_s_noise,new_d_noise,new_m_noise): self.steering_noise = float(new_s_noise) self.distance_noise = float(new_d_noise) self.measurement_noise = float(new_m_noise) def check_collisions(self,grid): #检查是否与网格碰撞 for i in range(len(grid)): for j in range(len(grid[0])): if grid[i][j] == 1: dist = sqrt((self.x - float(i))**2 + (self.y - float(j) )**2) if dist < 0.5: num_collisions+=1 return False return True def check_goal(self,goal,threshold = 1.0): #检查是否到达目标(threshold阀值) dist = sqrt((float(i) - self.x)**2 + (float(j) - self.y)**2 ) return goal < threshold def move(self,grid,steering,distance tolerance = 0.001,max_steering_angle = pi/4.0): if steering > max_steering_angle: steering = max_steering_angle if steering < -max_steering_angle: steering = -max_steering_angle if distance < 0.0: distance = 0.0 # make a new copy res = robot() res.length = self.length res.steering_noise = self.steering_noise res.distance_noise = self.distance_noise res.measurement_noise = self.measurement_noise res.num_collisions = self.num_collisions res.num.step = self.num_step + 1 #应用 noise steering2 = random.guass(steering,self.steering_noise) distance2 = random.guass(distance,self.distance_noise) #执行motion turn = tan(steering2)*distance2 / res.length if abs(turn) < tolerance: res.x = self.x + (distance2*cos(self.orientation)) res.y = self.y + (distance2*sin(self.orientation)) res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0*pi) else: radius = distance2 / turn cx = self.x-(sin(self.orientation) * radius) cy = self.x+(cos(self.orientation) * radius) res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2*pi) res.x = cx +(sin(res.orientation) * radius) res.y = cy - (cos(res.orientation) * radius) return res def sense(self): return [random.guass(self.x,self.measurement_noise), random.guass(self.y,self.measurement_noise)] def measurement_prob(self, measurement): error_x = measurement[0] - self.x error_y = measurement[1] - self.y error = exp(- (error_x ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) / sqrt(2.0 * pi * (sigma ** 2)) error*= exp(- (error_y ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) / sqrt(2.0 * pi * (sigma ** 2)) return error def __repr__(self): return '[x=%.5s y=%.5s orient=%.5s]' % (self.x,self.y,self.orientation) #输入数据和参数 grid = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]] init = [0,0] goal = [len(gird) - 1,len(grid[0])-1] myrobot = robot() myrobot.set_noise(steering_noise,distance_noise,measurement_noise) while not myrobot.check_goal(goal): theta = atan2(goal[1] - myrobot.y,goal[0] - myrobot.x) -myrobot.orientation myrobot = myrobot.move(grib,theta,0.1) if not myrobot.check_collision(grib): print ####Collision####
main()会调用A*、路径平滑算法和在run里面的控制器,控制器里有粒子滤波算法。这里会有一个循环来计算轨迹误差CTE,只用了PD
theta和P(x,y)是粒子滤波器输出的定位,cte是误差,U是行驶的路程可由点积求出,然后求的小u是用分母归一化后的结果,只要大于1就说明超过了线段,到了下一个线段(每一小步的线段)。CTE同样方式得出。然后程序化这些数学公式,这里设置了一个index变量,当U超过1时,index就要加1,以防超过线段,下面的程序输出一段有效的,不会碰撞的路径,返回值有是否成功、碰撞次数、步数。有时候也会极少发生碰撞,因为障碍物较多,系统噪音的影响。
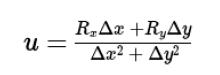
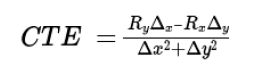
from math import * import random steering_noise = 0.1 distance_noise = 0.03 measurement_noise = 0.3 #------------------------------------------------ # # this is the plan class class plan: # init:creates an empty plan def __init__(self, grid, init, goal, cost = 1): self.cost = cost self.grid = grid self.init = init self.goal = goal self.make_heuristic(grid, goal, self.cost) self.path = [] self.spath = [] #------------------------------------------------------- # make heuristic function for a grid def make_heuristic(self, grid, goal, cost): self.heuristic = [[0 for row in range(len(grid[0]))] for col in range(len(grid))] for i in range(len(self.grid)): for j in range(len(self.grid[0])): self.heuristic[i][j] = abs(i - self.goal[0]) + abs(j - self.goal[1]) #-------------------------------------------------------- # A* for searching a path to the goal def astar(self): if self.heuristic == []: raise ValueError, "Heuristic must be defined to run A*" # internal motion parameters delta = [[-1, 0], # go up [ 0, -1], # go left [ 1, 0], # go down [ 0, 1]] # do right # open list elements are of the type: [f, g, h, x, y] closed = [[0 for row in range(len(self.grid[0]))] for col in range(len(self.grid))] action = [[0 for row in range(len(self.grid[0]))] for col in range(len(self.grid))] closed[self.init[0]][self.init[1]] = 1 x = self.init[0] y = self.init[1] h = self.heuristic[x][y] g = 0 f = g + h open = [[f, g, h, x, y]] found = False # flag that is set when search complete resign = False # flag set if we can't find expand count = 0 while not found and not resign: # check if we still have elements on the open list if len(open) == 0: resign = True print '###### Search terminated without success' else: # remove node from list open.sort() open.reverse() next = open.pop() x = next[3] y = next[4] g = next[1] # check if we are done if x == goal[0] and y == goal[1]: found = True # print '###### A* search successful' else: # expand winning element and add to new open list for i in range(len(delta)): x2 = x + delta[i][0] y2 = y + delta[i][1] if x2 >= 0 and x2 < len(self.grid) and y2 >= 0 and y2 < len(self.grid[0]): if closed[x2][y2] == 0 and self.grid[x2][y2] == 0: g2 = g + self.cost h2 = self.heuristic[x2][y2] f2 = g2 + h2 open.append([f2, g2, h2, x2, y2]) closed[x2][y2] = 1 action[x2][y2] = i count += 1 # extract the path invpath = [] x = self.goal[0] y = self.goal[1] invpath.append([x, y]) while x != self.init[0] or y != self.init[1]: x2 = x - delta[action[x][y]][0] y2 = y - delta[action[x][y]][1] x = x2 y = y2 invpath.append([x, y]) self.path = [] for i in range(len(invpath)): self.path.append(invpath[len(invpath) - 1 - i]) # ----------------------------------------------------- # this is the smoothing function def smooth(self, weight_data = 0.1, weight_smooth = 0.1, tolerance = 0.000001): if self.path == []: raise ValueError, "Run A* first before smoothing path" self.spath = [[0 for row in range(len(self.path[0]))] for col in range(len(self.path))] for i in range(len(self.path)): for j in range(len(self.path[0])): self.spath[i][j] = self.path[i][j] change = tolerance while change >= tolerance: change = 0.0 for i in range(1, len(self.path)-1): for j in range(len(self.path[0])): aux = self.spath[i][j] self.spath[i][j] += weight_data * (self.path[i][j] - self.spath[i][j]) self.spath[i][j] += weight_smooth * (self.spath[i-1][j] + self.spath[i+1][j] - (2.0 * self.spath[i][j])) if i >= 2: self.spath[i][j] += 0.5 * weight_smooth * (2.0 * self.spath[i-1][j] - self.spath[i-2][j] - self.spath[i][j]) if i <= len(self.path) - 3: self.spath[i][j] += 0.5 * weight_smooth * (2.0 * self.spath[i+1][j] - self.spath[i+2][j] - self.spath[i][j]) change += abs(aux - self.spath[i][j]) # ------------------------------------------------ # # this is the robot class class robot: # init: creates robot and initializes location/orientation to 0, 0, 0 def __init__(self, length = 0.5): self.x = 0.0 self.y = 0.0 self.orientation = 0.0 self.length = length self.steering_noise = 0.0 self.distance_noise = 0.0 self.measurement_noise = 0.0 self.num_collisions = 0 self.num_steps = 0 # set: sets a robot coordinate def set(self, new_x, new_y, new_orientation): self.x = float(new_x) self.y = float(new_y) self.orientation = float(new_orientation) % (2.0 * pi) # set_noise: sets the noise parameters def set_noise(self, new_s_noise, new_d_noise, new_m_noise): # makes it possible to change the noise parameters # this is often useful in particle filters self.steering_noise = float(new_s_noise) self.distance_noise = float(new_d_noise) self.measurement_noise = float(new_m_noise) # check: checks of the robot pose collides with an obstacle, or is too far outside the plane def check_collision(self, grid): for i in range(len(grid)): for j in range(len(grid[0])): if grid[i][j] == 1: dist = sqrt((self.x - float(i)) ** 2 + (self.y - float(j)) ** 2) if dist < 0.5: self.num_collisions += 1 return False return True def check_goal(self, goal, threshold = 1.0): dist = sqrt((float(goal[0]) - self.x) ** 2 + (float(goal[1]) - self.y) ** 2) return dist < threshold # move: steering = front wheel steering angle, limited by max_steering_angle # distance = total distance driven, most be non-negative def move(self, grid, steering, distance, tolerance = 0.001, max_steering_angle = pi / 4.0): if steering > max_steering_angle: steering = max_steering_angle if steering < -max_steering_angle: steering = -max_steering_angle if distance < 0.0: distance = 0.0 # make a new copy res = robot() res.length = self.length res.steering_noise = self.steering_noise res.distance_noise = self.distance_noise res.measurement_noise = self.measurement_noise res.num_collisions = self.num_collisions res.num_steps = self.num_steps + 1 # apply noise steering2 = random.gauss(steering, self.steering_noise) distance2 = random.gauss(distance, self.distance_noise) # Execute motion turn = tan(steering2) * distance2 / res.length if abs(turn) < tolerance: # approximate by straight line motion res.x = self.x + (distance2 * cos(self.orientation)) res.y = self.y + (distance2 * sin(self.orientation)) res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi) else: # approximate bicycle model for motion radius = distance2 / turn cx = self.x - (sin(self.orientation) * radius) cy = self.y + (cos(self.orientation) * radius) res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi) res.x = cx + (sin(res.orientation) * radius) res.y = cy - (cos(res.orientation) * radius) # check for collision # res.check_collision(grid) return res # sense: def sense(self): return [random.gauss(self.x, self.measurement_noise), random.gauss(self.y, self.measurement_noise)] # measurement_prob: computes the probability of a measurement def measurement_prob(self, measurement): # compute errors error_x = measurement[0] - self.x error_y = measurement[1] - self.y # calculate Gaussian error = exp(- (error_x ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) / sqrt(2.0 * pi * (self.measurement_noise ** 2)) error *= exp(- (error_y ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) / sqrt(2.0 * pi * (self.measurement_noise ** 2)) return error def __repr__(self): # return '[x=%.5f y=%.5f orient=%.5f]' % (self.x, self.y, self.orientation) return '[%.5f, %.5f]' % (self.x, self.y) # ---------------------------------------------------------------- # # this is the particle filter class class particles: # init: creates particle set with given initial position def __init__(self, x, y, theta, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, N = 100): self.N = N self.steering_noise = steering_noise self.distance_noise = distance_noise self.measurement_noise = measurement_noise self.data = [] for i in range(self.N): r = robot() r.set(x, y, theta) r.set_noise(steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise) self.data.append(r) # extract position from a particle set def get_position(self): x = 0.0 y = 0.0 orientation = 0.0 for i in range(self.N): x += self.data[i].x y += self.data[i].y # orientation is tricky because it is cyclic. By normalizing # around the first particle we are somewhat more robust to # the 0=2pi problem orientation += (((self.data[i].orientation - self.data[0].orientation + pi) % (2.0 * pi)) + self.data[0].orientation - pi) return [x / self.N, y / self.N, orientation / self.N] # motion of the particles def move(self, grid, steer, speed): newdata = [] for i in range(self.N): r = self.data[i].move(grid, steer, speed) newdata.append(r) self.data = newdata # sensing and resampling def sense(self, Z): w = [] for i in range(self.N): w.append(self.data[i].measurement_prob(Z)) # resampling (注意这是浅拷贝) p3 = [] index = int(random.random() * self.N) beta = 0.0 mw = max(w) for i in range(self.N): beta += random.random() * 2.0 * mw while beta > w[index]: beta -= w[index] index = (index + 1) % self.N p3.append(self.data[index]) self.data = p3 # -------------------------------------------------- # run: runs control program for the robot def run(grid, goal, spath, params, printflag = False, speed = 0.1, timeout = 1000): myrobot = robot() myrobot.set(0., 0., 0.) myrobot.set_noise(steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise) filter = particles(myrobot.x, myrobot.y, myrobot.orientation, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise) cte = 0.0 err = 0.0 N = 0 index = 0 # index into the path while not myrobot.check_goal(goal) and N < timeout: diff_cte = - cte # compute the CTE # start with the present robot estimate estimate = filter.get_position()
#-------------------------------------------------- # some basic vector calculations
dx = spath[index+1][0] spath[index][0]
dy = spath[index+1][1] spath[index][1]
drx = estimate[0] spath[index][0]
dry = estimate[1] spath[index][1]
# u is the robot estimate projected into the path segment
u = (drx * dx + dry * dy)/(dx * dx + dy * dy)
#the cte is the estimate projected onto the normal of the path segment
cte = (dry * dx drx * dy)/(dx * dx + dy * dy)
if u > 1:
index += 1 # ---------------------------------------- diff_cte += cte steer = - params[0] * cte - params[1] * diff_cte myrobot = myrobot.move(grid, steer, speed) filter.move(grid, steer, speed) Z = myrobot.sense() filter.sense(Z) if not myrobot.check_collision(grid): print '##### Collision ####' err += (cte ** 2) N += 1 if printflag: print myrobot, cte, index, u return [myrobot.check_goal(goal), myrobot.num_collisions, myrobot.num_steps] # ------------------------------------------------------------------- # # this is our main routine def main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, weight_data, weight_smooth, p_gain, d_gain): path = plan(grid, init, goal) path.astar() path.smooth(weight_data, weight_smooth) return run(grid, goal, path.spath, [p_gain, d_gain]) # ------------------------------------------------ # # input data and parameters grid = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]] init = [0, 0] goal = [len(grid)-1, len(grid[0])-1] #以下这些参数可以调着玩,特别是p、d的权重,用优化函数可能得不到返回,自己尝试出好的值 steering_noise = 0.1 distance_noise = 0.03 measurement_noise = 0.3 weight_data = 0.1 weight_smooth = 0.2 p_gain = 2.0 d_gain = 6.0 print main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, weight_data, weight_smooth, p_gain, d_gain) #---------------------------------------- # 参数优化 def twiddle(init_params): n_params = len(init_params) dparams = [1.0 for row in range(n_params)] params = [0.0 for row in range(n_params)] K = 10 for i in range(n_params): params[i] = init_params[i] best_error = 0.0; for k in range(K): ret = main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3]) if ret[0]: best_error += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2] else: best_error += 99999 best_error = float(best_error) / float(k+1) print best_error n = 0 while sum(dparams) > 0.0000001: for i in range(len(params)): params[i] += dparams[i] err = 0 for k in range(K): ret = main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3], best_error) if ret[0]: err += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2] else: err += 99999 print float(err) / float(k+1) if err < best_error: best_error = float(err) / float(k+1) dparams[i] *= 1.1 else: params[i] -= 2.0 * dparams[i] err = 0 for k in range(K): ret = main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3], best_error) if ret[0]: err += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2] else: err += 99999 print float(err) / float(k+1) if err < best_error: best_error = float(err) / float(k+1) dparams[i] *= 1.1 else: params[i] += dparams[i] dparams[i] *= 0.5 n += 1 print 'Twiddle #', n, params, ' -> ', best_error print ' ' return params #twiddle([weight_data, weight_smooth, p_gain, d_gain])
SLAM是一种建图方法,是同时定位和建图的总称。
当移动机器人在环境中建图时,因为移动的不确定性迫使我们去定位。比如一个机器人从X0(0,0)沿x轴运动10个单位到X1,不能以X1=X0+10去表示移动后机器人的位置,而是用关于两个参数的高斯分布来表示,y方向同样。这两个高斯函数就成了约束条件,Graph SLAM就是利用一系列这样的约束来定义概率。(这是相对约束)
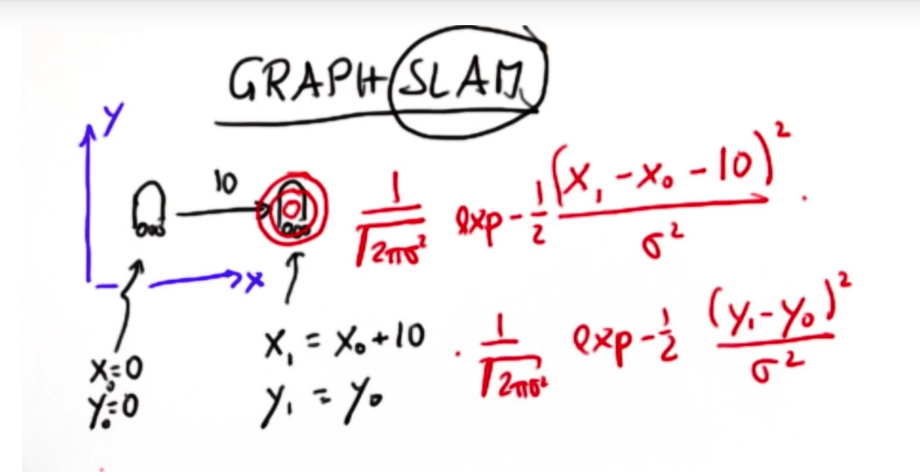
一个机器人的移动过程,每个点X1~X4都是(x,y,orientation)的三维向量,每个点时刻都会测量一次与地标的距离(测量结果z用高斯表示),这样会有三个约束出现:初始位置约束、相对约束(两点之间的相对位置)、相对地标位置约束。
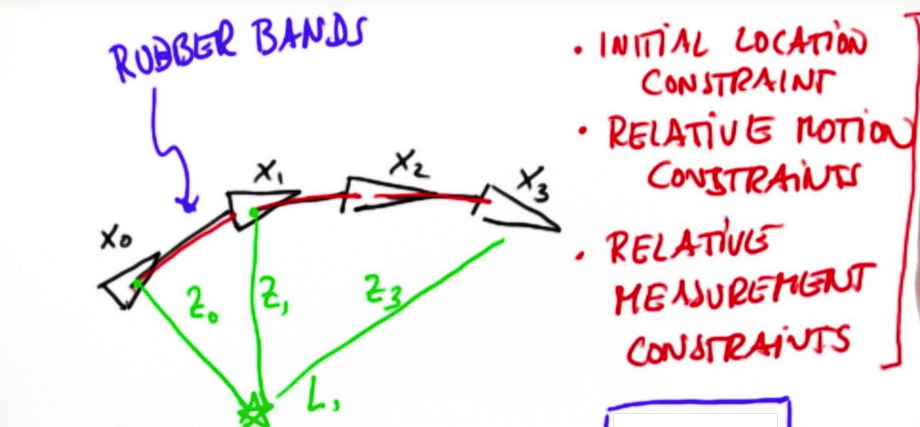
完成Graph SLAM
为了完成Graph SLAM,一个矩阵和一个向量被引入,要把所有的姿势坐标和地标都填到这个二维矩阵里,
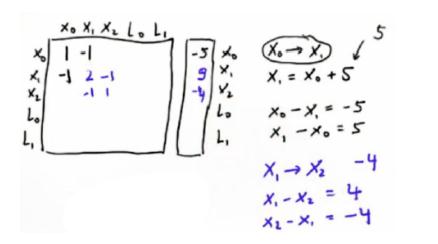
x0—>x1 5,那么x0+5=x1,x0+(-1*x1)=-5,就是第一行。然后反过来x1+(-1*x0)=5,就是第二行。
举一反三,倒回,x2—>x1 -4 ,x1-4=x2,x2+(-x1)=-4,这就是第三行。然后x1+(-x2)=4,加到第二行,最后结果如图,以此类推填充矩阵。
同理填入地标格子,没测地标的检测点空(x与L对应的空格),临近的两个检测点才测互相的空格。
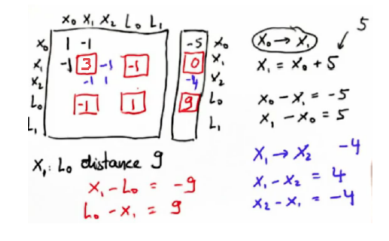
Ω和§
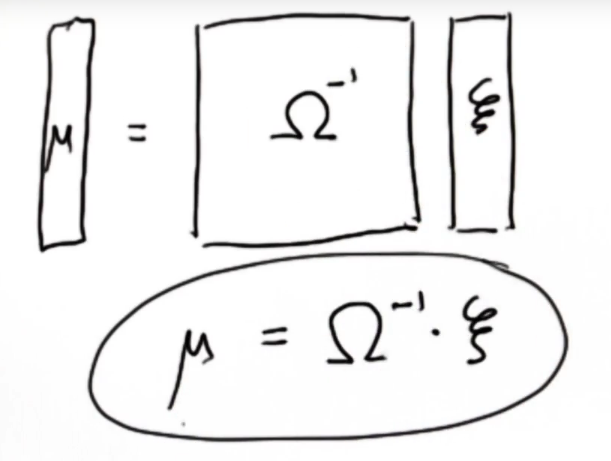
然后将这两个矩阵经过简单的数学运算就能找到所有世界坐标的最佳解,即最好估计值μ。
这就是SLAM Graph方法,只要每次看到约束的时候就把这些数字填到这两个矩阵当中,然后只需一个简单的运算,机器人的位置最佳坐标就出来了。
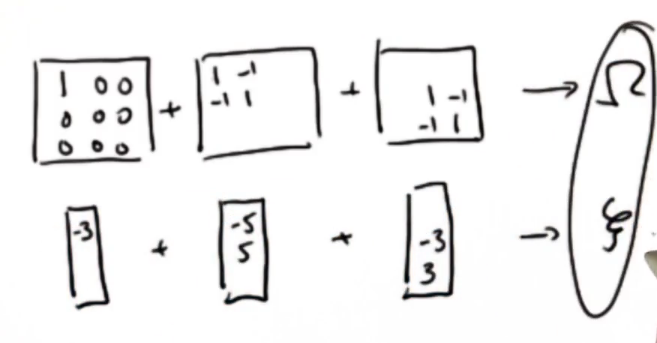
1 # ----------- 2 # 写一个函数doit, 输入初始机器人的位置、move1、move2 3 # 这个函数能计算出Omega矩阵和Xi向量,并且返回mu向量 4 5 from math import * 6 import random 7 8 9 # ------------------------------------------------ 10 # 11 # 这是一个矩阵的类,它能让收集约束和计算结果更容易, 12 # 尽管效率低下 13 14 class matrix: 15 # 包含矩阵基本运算的类 16 17 # ------------ 18 # 初始化 19 20 def __init__(self, value = [[]]): 21 self.value = value 22 self.dimx = len(value) 23 self.dimy = len(value[0]) 24 if value == [[]]: 25 self.dimx = 0 26 27 # ------------ 28 # 设置矩阵(向量?)尺寸并使每个元素为0 29 30 def zero(self, dimx, dimy = 0): 31 if dimy == 0: 32 dimy = dimx 33 # check if valid dimensions 34 if dimx < 1 or dimy < 1: 35 raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix" 36 else: 37 self.dimx = dimx 38 self.dimy = dimy 39 self.value = [[0.0 for row in range(dimy)] for col in range(dimx)] 40 41 # ------------ 42 # 设置等长宽的矩阵并全设1 43 44 def identity(self, dim): 45 # check if valid dimension 46 if dim < 1: 47 raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix" 48 else: 49 self.dimx = dim 50 self.dimy = dim 51 self.value = [[0.0 for row in range(dim)] for col in range(dim)] 52 for i in range(dim): 53 self.value[i][i] = 1.0 54 55 # ------------ 56 # 输出矩阵值 57 58 def show(self, txt = ''): 59 for i in range(len(self.value)): 60 print txt + '['+ ', '.join('%.3f'%x for x in self.value[i]) + ']' 61 print ' ' 62 63 # ------------ 64 # 同规模的两矩阵相加 65 66 def __add__(self, other): 67 # check if correct dimensions 68 if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimx != other.dimx: 69 raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimension to add" 70 else: 71 # add if correct dimensions 72 res = matrix() 73 res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy) 74 for i in range(self.dimx): 75 for j in range(self.dimy): 76 res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] + other.value[i][j] 77 return res 78 79 # ------------ 80 # 同规模矩阵相减 81 82 def __sub__(self, other): 83 # check if correct dimensions 84 if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimx != other.dimx: 85 raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimension to subtract" 86 else: 87 # subtract if correct dimensions 88 res = matrix() 89 res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy) 90 for i in range(self.dimx): 91 for j in range(self.dimy): 92 res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] - other.value[i][j] 93 return res 94 95 # ------------ 96 # 等规模矩阵相乘 97 98 def __mul__(self, other): 99 # check if correct dimensions 100 if self.dimy != other.dimx: 101 raise ValueError, "Matrices must be m*n and n*p to multiply" 102 else: 103 # multiply if correct dimensions 104 res = matrix() 105 res.zero(self.dimx, other.dimy) 106 for i in range(self.dimx): 107 for j in range(other.dimy): 108 for k in range(self.dimy): 109 res.value[i][j] += self.value[i][k] * other.value[k][j] 110 return res 111 112 # ------------ 113 # 矩阵转置 114 115 def transpose(self): 116 # compute transpose 117 res = matrix() 118 res.zero(self.dimy, self.dimx) 119 for i in range(self.dimx): 120 for j in range(self.dimy): 121 res.value[j][i] = self.value[i][j] 122 return res 123 124 125 # ------------ 126 # 从现有的矩阵元素中提取一个新的矩阵 127 # 例如 ([0, 2], [0, 2, 3])即提取第0行和第3行的第0、2、3个元素 128 129 def take(self, list1, list2 = []): 130 if list2 == []: 131 list2 = list1 132 if len(list1) > self.dimx or len(list2) > self.dimy: 133 raise ValueError, "list invalid in take()" 134 135 res = matrix() 136 res.zero(len(list1), len(list2)) 137 for i in range(len(list1)): 138 for j in range(len(list2)): 139 res.value[i][j] = self.value[list1[i]][list2[j]] 140 return res 141 142 # ------------ 143 # 从现有的矩阵元素中提取扩张一个新的矩阵 144 # 例如 (3, 5, [0, 2], [0, 2, 3]),结果是3行5列,结果中第1/3行 145 # 的1、3、4列是初始矩阵按顺序分布,其余0补充 146 def expand(self, dimx, dimy, list1, list2 = []): 147 if list2 == []: 148 list2 = list1 149 if len(list1) > self.dimx or len(list2) > self.dimy: 150 raise ValueError, "list invalid in expand()" 151 152 res = matrix() 153 res.zero(dimx, dimy) 154 for i in range(len(list1)): 155 for j in range(len(list2)): 156 res.value[list1[i]][list2[j]] = self.value[i][j] 157 return res 158 159 # ------------ 160 # 计算正定矩阵的上三角Cholesky分解 161 def Cholesky(self, ztol= 1.0e-5): 162 res = matrix() 163 res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx) 164 165 for i in range(self.dimx): 166 S = sum([(res.value[k][i])**2 for k in range(i)]) 167 d = self.value[i][i] - S 168 if abs(d) < ztol: 169 res.value[i][i] = 0.0 170 else: 171 if d < 0.0: 172 raise ValueError, "Matrix not positive-definite" 173 res.value[i][i] = sqrt(d) 174 for j in range(i+1, self.dimx): 175 S = sum([res.value[k][i] * res.value[k][j] for k in range(i)]) 176 if abs(S) < ztol: 177 S = 0.0 178 res.value[i][j] = (self.value[i][j] - S)/res.value[i][i] 179 return res 180 181 # ------------ 182 # 计算矩阵的Cholesky上三角分解矩阵的逆矩阵 183 184 def CholeskyInverse(self): 185 res = matrix() 186 res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx) 187 188 # Backward step for inverse. 189 for j in reversed(range(self.dimx)): 190 tjj = self.value[j][j] 191 S = sum([self.value[j][k]*res.value[j][k] for k in range(j+1, self.dimx)]) 192 res.value[j][j] = 1.0/ tjj**2 - S/ tjj 193 for i in reversed(range(j)): 194 res.value[j][i] = res.value[i][j] = 195 -sum([self.value[i][k]*res.value[k][j] for k in 196 range(i+1,self.dimx)])/self.value[i][i] 197 return res 198 199 # ------------ 200 # 计算返回矩形矩阵的逆置 201 202 def inverse(self): 203 aux = self.Cholesky() 204 res = aux.CholeskyInverse() 205 return res 206 207 #-------------- 208 #打印矩阵 209 210 def __repr__(self): 211 return repr(self.value) 212 213 214 # ################################ 215 """下面这个粒子调用(-3,5,3),-3初始位置,5 move1,3 move2 216 应返回向量结果[[-3.0], 217 [2.0], 218 [5.0]] 219 """ 220 def doit(initial_pos, move1, move2): 221 Omega = [[1,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]] #x0=-3 222 Xi = [[initial_pos],[0],[0]] 223 224 Omega += [[1,-1,0],[-1,1,0],[0,0,0]] #x0+5=x1 225 Xi += [[-move1],[move1],[0]] 226 227 Omega += [[0,0,0],[0,1,-1],[0,-1,1]] #x1+3=x2 228 Xi += [[0],[-move2],[move2]] 229
230 Omega.show('Omegs: ')
231 Xi.show('Xi: ') 232 mu = Omega.inverse()*Xi 233 mu.show('mu: ')
234 235 return mu 236 237 doit(-3, 5, 3)
加入一个地标,从3*3变成4*4,代码添加
Omega = Omega.expand(4, 4, [0,1,2], [0,1,2]) Xi = Xi.expand(4, 1, [0, 1, 2], [0]) Omega += matrix([[1., 0., 0., -1.],[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.,0.],[ -1., 0., 0., 1.]]) Xi += matrix([[-Z0], [0.], [0.], [Z0]]) Omega += matrix([[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 1., 0., -1.],[0., 0., 0.,0.],[0.,-1., 0., 1.]]) Xi += matrix([[0.], [-Z1], [0.], [Z1]]) Omega += matrix([[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 1.,-1.],[0.,0., -1., 1.]]) Xi += matrix([[0.], [0.], [-Z2], [Z2]])
引入噪音
噪音使得测量地标距离不精准, 假设有两个机器人位置,第二个在第一个右边10,并伴有高斯噪音,情况和高斯噪音如下:
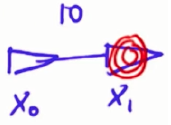
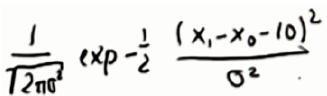
假设最后一个点测量的地标距离是1(本来是2),总概率是两者的乘积,最后结果类似 x1/σ+x0/σ=10/σ ,1/σ代表信度,要想这个乘积更大,几个技巧:1.去掉常数;2.如果能把乘积编程加法,去掉指数3.甚至可以去掉-1/2
修改代码,使得最后的测量具有非常高的置信度,系数为5.您应该得到[3,2.179,5.714,6.821]作为答案。 从这个结果中可以看出,最后一点与地标的差异非常接近1.0的测量差异,因为与其他测量和运动相比,这个置信度相对较高。
Omega += matrix([[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0.,5., -5.],[0., 0., -5., 5.]]) Xi += matrix([[0.], [0.], [-Z2*5], [Z2*5]])
完成SLAM编程
每一时刻都有一组约束(初始位置,移动或者地标测量),把他们装入矩阵Omega和向量Xi,两个thing相乘,结果就是路径和地图,强度因数1/σ表示信度。
下面是将SLAM适用于广义环境设置的参数和调用输出结果:
num_landmarks = 5 # 地标数量 N = 20 # time steps world_size = 100.0 # 世界的尺寸 measurement_range = 50.0 # 能检测到地标的检测范围 motion_noise = 2.0 measurement_noise = 2.0 distance = 20.0 # 机器人打算移动的距离
data = make_data(N,num_landmarks,world_size,measurement_range,motion_noise,measurement_noise,distance)
result = slam(data,N,num_landmarks,motion_noise,measurement_noise)
print_result(N,num_landmarks,result)
make_data(),装入环境参数,返回一个运动序列和一个测量序列,即将写的函数slam()装入这两个数据序列和以上这些参数设置,返回一个机器人路径表和估计的地标位置。
初始位置设置在[50,50],这个世界的中心。
取所有的输入参数,并设置矩阵Ω和矢量Xi的维数。 维度是路径的长度加上地标数量的两倍,因为在相同的数据结构中为每一个空格都建立了x与y。然后,为Ω创建一个矩阵,为Xi创建一个向量,给它适当的尺寸,然后引入一个约束条件,即初始位置必须是world_size / 2.0,强度值为1.0。这对最终解决方案没有影响,因为这是唯一的绝对约束。 但是你可以看到矩阵的主对角线是1,x是1,y是1,Xi向量一样。
dim = 2* (N + num_landmarks) Omega = matrix() Omega.zero(dim,dim) Omega.value[0][0] = 1.0 Omega.value[1][1] = 1.0 Xi = matrix() Xi.zero(dim, 1) Xi.value[0][0] = world_size / 2 Xi.value[1][0] = world_size / 2
S标识位置,L标识坐标,每个格子有x和y组成。以下编写SLAM代码。
from math import *
import random
#这里引入矩阵操作的类和机器人的类
def make_data(N, num_landmarks, world_size, measurement_range, motion_noise, measurement_noise, distance)
complete = False
while not complete:
data = []
# make robot and landmarks
r = robot(world_size, measurement_range, motion_noise, measurement_noise)
r.make_landmarks(num_landmarks)
seen = [False for row in range(num_landmarks)]
# guess an initial motion
orientation = random.random() * 2.0 * pi
dx = cos(orientation) * distance
dy = sin(orientation) * distance
for k in range(N-1):
# sense
Z = r.sense()
# check off all landmarks that were observed
for i in range(len(Z)):
seen[Z[i][0]] = True
# move
while not r.move(dx, dy):
# if we'd be leaving the robot world, pick instead a new direction
orientation = random.random() * 2.0 * pi
dx = cos(orientation) * distance
dy = sin(orientation) * distance
# memorize data
data.append([Z, [dx, dy]])
# we are done when all landmarks were observed; otherwise re-run
complete = (sum(seen) == num_landmarks)
print ' '
print 'Landmarks: ', r.landmarks
print r
return data
def print_result(N, num_landmarks, result):
print 'Estimated Pose(s):'
for i in range(N):
print ' ['+ ', '.join('%.3f'%x for x in result.value[2*i]) + ', '
+ ', '.join('%.3f'%x for x in result.value[2*i+1]) +']'
print 'Estimated Landmarks:'
for i in range(num_landmarks):
print ' ['+ ', '.join('%.3f'%x for x in result.value[2*(N+i)]) + ', '
+ ', '.join('%.3f'%x for x in result.value[2*(N+i)+1]) +']'
def slam(data, N, num_landmarks, motion_noise, measurement_noise): #set the dimension of the filter dim = 2 * (N + num_landmarks) #make the constraint information matrix and vector Omega = matrix() Omega.zero(dim,dim) Omega.value[0][0] = 1.0 Omega.value[1][1] = 1.0 Xi = matrix() Xi.zero(dim, 1) Xi.value[0][0] = world_size / 2 Xi.value[1][0] = world_size / 2 for k in range(len(data)): #n is the index of the robots pose in the matrix/vector n = k * 2 measurement = data[k][0] motion = data[k][1] # integrate measurements for i in range(len(measurement)): #m is the index of the landmark coordinate in the #matrix/vector m = 2 * (N + measurement[i][0]) # update the information matrix according to measurement for b in range(2): Omega.value[n+b][n+b] += 1.0 / measurement_noise Omega.value[m+b][m+b] += 1.0 / measurement_noise Omega.value[n+b][m+b] += 1.0 / measurement_noise Omega.value[m+b][n+b] += 1.0 / measurement_noise Xi.value[ n + b ][ 0 ] += measurement[i][1+b] / measurement_noise Xi.value[m+b][0] += measurement[i][1+b] / measurement_noise # update the information matrix according to motion for b in range(4): Omega.value[n+b][n+b] += 1.0 / motion_noise for b in range(2): Omega.value[n+b][n+b+2] += 1.0 / motion_noise Omega.value[n+b+2][n+b ] += 1.0 / motion_noise Xi.value[n+b][0] += motion[b] / motion_noise Xi.value[n+b+2][0] += motion[b] / motion_noise mu = Omega.inverse() * Xi return mu
#这里调用这节的第一个编程(参数设置及调用输出)
输入起始位置和所有地标测量位置,得出每次机器人的估计坐标位置(即路径)和所有地标的位置估计
两个月零八天,蒙特卡洛定位——>卡尔曼追踪定位——>粒子滤波定位——>路径规划——>PID控制——>SLAM
How far is self car~