Python人工智能参考---线性回归(Linear Regression)
一、总结
一句话总结:
线性回归是回归问题中的一种,线性回归假设目标值与特征之间线性相关,即满足一个多元一次方程。y=wx+b
1、什么是回归分析?
a、【研究因变量和自变量之间的关系】:回归分析是一种预测性的建模技术,它研究的是因变量(目标)和自变量(预测器)之间的关系。
b、【预测分析】:这种技术通常用于预测分析,时间序列模型以及发现变量之间的因果关系。
c、【曲线拟合点】:通常使用曲线/线来拟合数据点,目标是使曲线到数据点的距离差异最小。
2、求解线性回归损失函数的两种方式?
最小二乘法(least square method):求解 w 和 b 是使损失函数最小化的过程,在统计中,称为线性回归模型的最小二乘“参数估计”(parameter estimation)。
梯度下降(gradient descent):梯度下降核心内容是对自变量进行不断的更新(针对w和b求偏导),使得目标函数不断逼近最小值的过程
3、线性回归解决问题实例?
数据可以映射到坐标轴(二维或多维)上面形成一些点,线性回归就可以用曲线来模拟这些点,从而根据曲线来预测结果
二、机器学习 | 算法笔记- 线性回归(Linear Regression)
转自或参考:机器学习 | 算法笔记- 线性回归(Linear Regression) - eo_will - 博客园
https://www.cnblogs.com/geo-will/p/10468253.html
前言
本系列为机器学习算法的总结和归纳,目的为了清晰阐述算法原理,同时附带上手代码实例,便于理解。
本章为线性回归,内容包括模型介绍及代码实现(包括自主实现和sklearn案例)。
一、算法简介
1.1 什么是回归分析
回归分析是一种预测性的建模技术,它研究的是因变量(目标)和自变量(预测器)之间的关系。这种技术通常用于预测分析,时间序列模型以及发现变量之间的因果关系。通常使用曲线/线来拟合数据点,目标是使曲线到数据点的距离差异最小。
1.2 线性回归
线性回归是回归问题中的一种,线性回归假设目标值与特征之间线性相关,即满足一个多元一次方程。通过构建损失函数,来求解损失函数最小时的参数w和b。通长我们可以表达成如下公式:
y^为预测值,自变量x和因变量y是已知的,而我们想实现的是预测新增一个x,其对应的y是多少。因此,为了构建这个函数关系,目标是通过已知数据点,求解线性模型中w和b两个参数。
1.3 目标/损失函数
求解最佳参数,需要一个标准来对结果进行衡量,为此我们需要定量化一个目标函数式,使得计算机可以在求解过程中不断地优化。
针对任何模型求解问题,都是最终都是可以得到一组预测值y^ ,对比已有的真实值 y ,数据行数为 n ,可以将损失函数定义如下:
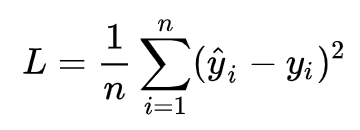
即预测值与真实值之间的平均的平方距离,统计中一般称其为MAE(mean square error)均方误差。把之前的函数式代入损失函数,并且将需要求解的参数w和b看做是函数L的自变量,可得
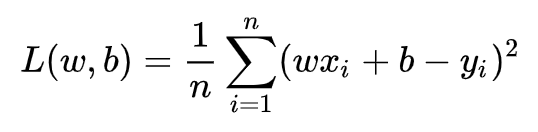
现在的任务是求解最小化L时w和b的值,
即核心目标优化式为

求解方式有两种:
1)最小二乘法(least square method)
求解 w 和 b 是使损失函数最小化的过程,在统计中,称为线性回归模型的最小二乘“参数估计”(parameter estimation)。我们可以将 L(w,b) 分别对 w 和 b 求导,得到
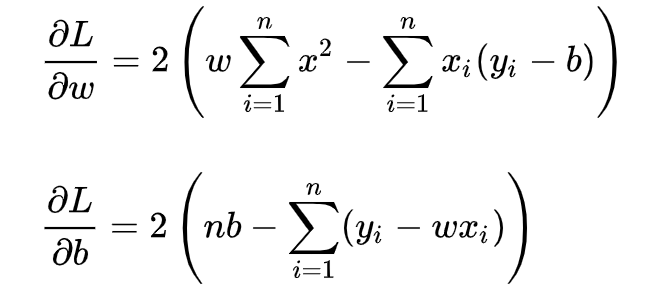
令上述两式为0,可得到 w 和 b 最优解的闭式(closed-form)解:

2)梯度下降(gradient descent)
梯度下降核心内容是对自变量进行不断的更新(针对w和b求偏导),使得目标函数不断逼近最小值的过程
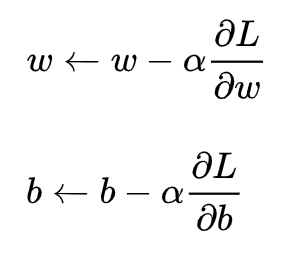
这里不做展开讲解。
二、代码实现
2.1 简单线性回归
首先建立linear_regression.py文件,用于实现线性回归的类文件,包含了线性回归内部的核心函数:
 View Code
View Code
 View Code
View Code

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np class LinerRegression(object): def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, max_iter=100, seed=None): np.random.seed(seed) self.lr = learning_rate self.max_iter = max_iter self.w = np.random.normal(1, 0.1) self.b = np.random.normal(1, 0.1) self.loss_arr = [] def fit(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y for i in range(self.max_iter): self._train_step() self.loss_arr.append(self.loss()) # print('loss: {:.3}'.format(self.loss())) # print('w: {:.3}'.format(self.w)) # print('b: {:.3}'.format(self.b)) def _f(self, x, w, b): return x * w + b def predict(self, x=None): if x is None: x = self.x y_pred = self._f(x, self.w, self.b) return y_pred def loss(self, y_true=None, y_pred=None): if y_true is None or y_pred is None: y_true = self.y y_pred = self.predict(self.x) return np.mean((y_true - y_pred)**2) def _calc_gradient(self): d_w = np.mean((self.x * self.w + self.b - self.y) * self.x) d_b = np.mean(self.x * self.w + self.b - self.y) return d_w, d_b def _train_step(self): d_w, d_b = self._calc_gradient() self.w = self.w - self.lr * d_w self.b = self.b - self.lr * d_b return self.w, self.b
建立 train.py 文件,用于生成模拟数据,并调用 liner_regression.py 中的类,完成线性回归任务:

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from liner_regression import * def show_data(x, y, w=None, b=None): plt.scatter(x, y, marker='.') if w is not None and b is not None: plt.plot(x, w*x+b, c='red') plt.show() # data generation np.random.seed(272) data_size = 100 x = np.random.uniform(low=1.0, high=10.0, size=data_size) y = x * 20 + 10 + np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=10.0, size=data_size) # plt.scatter(x, y, marker='.') # plt.show() # train / test split shuffled_index = np.random.permutation(data_size) x = x[shuffled_index] y = y[shuffled_index] split_index = int(data_size * 0.7) x_train = x[:split_index] y_train = y[:split_index] x_test = x[split_index:] y_test = y[split_index:] # visualize data # plt.scatter(x_train, y_train, marker='.') # plt.show() # plt.scatter(x_test, y_test, marker='.') # plt.show() # train the liner regression model regr = LinerRegression(learning_rate=0.01, max_iter=10, seed=314) regr.fit(x_train, y_train) print('cost: {:.3}'.format(regr.loss())) print('w: {:.3}'.format(regr.w)) print('b: {:.3}'.format(regr.b)) show_data(x, y, regr.w, regr.b) # plot the evolution of cost plt.scatter(np.arange(len(regr.loss_arr)), regr.loss_arr, marker='o', c='green') plt.show()
2.2 sklearn实现
sklearn.linear_model提供了很多线性模型,包括岭回归、贝叶斯回归、Lasso等。本文主要尝试使用岭回归Ridge,该函数一共有8个参数,详见
 View Code
View Code
岭回归是缩减法的一种,相当于对回归系数的大小施加了限制。另一种很好的缩减法是lasso。lasso难以求解,但可以使用计算简便的逐步线性回归方法求的近似解。

# -*-coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import random def scrapePage(retX, retY, inFile, yr, numPce, origPrc): """ 函数说明:从页面读取数据,生成retX和retY列表 Parameters: retX - 数据X retY - 数据Y inFile - HTML文件 yr - 年份 numPce - 乐高部件数目 origPrc - 原价 Returns: 无 """ # 打开并读取HTML文件 with open(inFile, encoding='utf-8') as f: html = f.read() soup = BeautifulSoup(html) i = 1 # 根据HTML页面结构进行解析 currentRow = soup.find_all('table', r = "%d" % i) while(len(currentRow) != 0): currentRow = soup.find_all('table', r = "%d" % i) title = currentRow[0].find_all('a')[1].text lwrTitle = title.lower() # 查找是否有全新标签 if (lwrTitle.find('new') > -1) or (lwrTitle.find('nisb') > -1): newFlag = 1.0 else: newFlag = 0.0 # 查找是否已经标志出售,我们只收集已出售的数据 soldUnicde = currentRow[0].find_all('td')[3].find_all('span') if len(soldUnicde) == 0: print("商品 #%d 没有出售" % i) else: # 解析页面获取当前价格 soldPrice = currentRow[0].find_all('td')[4] priceStr = soldPrice.text priceStr = priceStr.replace('$','') priceStr = priceStr.replace(',','') if len(soldPrice) > 1: priceStr = priceStr.replace('Free shipping', '') sellingPrice = float(priceStr) # 去掉不完整的套装价格 if sellingPrice > origPrc * 0.5: print("%d %d %d %f %f" % (yr, numPce, newFlag, origPrc, sellingPrice)) retX.append([yr, numPce, newFlag, origPrc]) retY.append(sellingPrice) i += 1 currentRow = soup.find_all('table', r = "%d" % i) def ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, lam = 0.2): """ 函数说明:岭回归 Parameters: xMat - x数据集 yMat - y数据集 lam - 缩减系数 Returns: ws - 回归系数 """ xTx = xMat.T * xMat denom = xTx + np.eye(np.shape(xMat)[1]) * lam if np.linalg.det(denom) == 0.0: print("矩阵为奇异矩阵,不能求逆") return ws = denom.I * (xMat.T * yMat) return ws def setDataCollect(retX, retY): """ 函数说明:依次读取六种乐高套装的数据,并生成数据矩阵 Parameters: 无 Returns: 无 """ scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego8288.html', 2006, 800, 49.99) #2006年的乐高8288,部件数目800,原价49.99 scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego10030.html', 2002, 3096, 269.99) #2002年的乐高10030,部件数目3096,原价269.99 scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego10179.html', 2007, 5195, 499.99) #2007年的乐高10179,部件数目5195,原价499.99 scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego10181.html', 2007, 3428, 199.99) #2007年的乐高10181,部件数目3428,原价199.99 scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego10189.html', 2008, 5922, 299.99) #2008年的乐高10189,部件数目5922,原价299.99 scrapePage(retX, retY, './lego/lego10196.html', 2009, 3263, 249.99) #2009年的乐高10196,部件数目3263,原价249.99 def regularize(xMat, yMat): """ 函数说明:数据标准化 Parameters: xMat - x数据集 yMat - y数据集 Returns: inxMat - 标准化后的x数据集 inyMat - 标准化后的y数据集 """ inxMat = xMat.copy() #数据拷贝 inyMat = yMat.copy() yMean = np.mean(yMat, 0) #行与行操作,求均值 inyMat = yMat - yMean #数据减去均值 inMeans = np.mean(inxMat, 0) #行与行操作,求均值 inVar = np.var(inxMat, 0) #行与行操作,求方差 # print(inxMat) print(inMeans) # print(inVar) inxMat = (inxMat - inMeans) / inVar #数据减去均值除以方差实现标准化 return inxMat, inyMat def rssError(yArr,yHatArr): """ 函数说明:计算平方误差 Parameters: yArr - 预测值 yHatArr - 真实值 Returns: """ return ((yArr-yHatArr)**2).sum() def standRegres(xArr,yArr): """ 函数说明:计算回归系数w Parameters: xArr - x数据集 yArr - y数据集 Returns: ws - 回归系数 """ xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T xTx = xMat.T * xMat #根据文中推导的公示计算回归系数 if np.linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0: print("矩阵为奇异矩阵,不能求逆") return ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T*yMat) return ws def crossValidation(xArr, yArr, numVal = 10): """ 函数说明:交叉验证岭回归 Parameters: xArr - x数据集 yArr - y数据集 numVal - 交叉验证次数 Returns: wMat - 回归系数矩阵 """ m = len(yArr) #统计样本个数 indexList = list(range(m)) #生成索引值列表 errorMat = np.zeros((numVal,30)) #create error mat 30columns numVal rows for i in range(numVal): #交叉验证numVal次 trainX = []; trainY = [] #训练集 testX = []; testY = [] #测试集 random.shuffle(indexList) #打乱次序 for j in range(m): #划分数据集:90%训练集,10%测试集 if j < m * 0.9: trainX.append(xArr[indexList[j]]) trainY.append(yArr[indexList[j]]) else: testX.append(xArr[indexList[j]]) testY.append(yArr[indexList[j]]) wMat = ridgeTest(trainX, trainY) #获得30个不同lambda下的岭回归系数 for k in range(30): #遍历所有的岭回归系数 matTestX = np.mat(testX); matTrainX = np.mat(trainX) #测试集 meanTrain = np.mean(matTrainX,0) #测试集均值 varTrain = np.var(matTrainX,0) #测试集方差 matTestX = (matTestX - meanTrain) / varTrain #测试集标准化 yEst = matTestX * np.mat(wMat[k,:]).T + np.mean(trainY) #根据ws预测y值 errorMat[i, k] = rssError(yEst.T.A, np.array(testY)) #统计误差 meanErrors = np.mean(errorMat,0) #计算每次交叉验证的平均误差 minMean = float(min(meanErrors)) #找到最小误差 bestWeights = wMat[np.nonzero(meanErrors == minMean)] #找到最佳回归系数 xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T meanX = np.mean(xMat,0); varX = np.var(xMat,0) unReg = bestWeights / varX #数据经过标准化,因此需要还原 print('%f%+f*年份%+f*部件数量%+f*是否为全新%+f*原价' % ((-1 * np.sum(np.multiply(meanX,unReg)) + np.mean(yMat)), unReg[0,0], unReg[0,1], unReg[0,2], unReg[0,3])) def ridgeTest(xArr, yArr): """ 函数说明:岭回归测试 Parameters: xMat - x数据集 yMat - y数据集 Returns: wMat - 回归系数矩阵 """ xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T #数据标准化 yMean = np.mean(yMat, axis = 0) #行与行操作,求均值 yMat = yMat - yMean #数据减去均值 xMeans = np.mean(xMat, axis = 0) #行与行操作,求均值 xVar = np.var(xMat, axis = 0) #行与行操作,求方差 xMat = (xMat - xMeans) / xVar #数据减去均值除以方差实现标准化 numTestPts = 30 #30个不同的lambda测试 wMat = np.zeros((numTestPts, np.shape(xMat)[1])) #初始回归系数矩阵 for i in range(numTestPts): #改变lambda计算回归系数 ws = ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, np.exp(i - 10)) #lambda以e的指数变化,最初是一个非常小的数, wMat[i, :] = ws.T #计算回归系数矩阵 return wMat def useStandRegres(): """ 函数说明:使用简单的线性回归 Parameters: 无 Returns: 无 """ lgX = [] lgY = [] setDataCollect(lgX, lgY) data_num, features_num = np.shape(lgX) lgX1 = np.mat(np.ones((data_num, features_num + 1))) lgX1[:, 1:5] = np.mat(lgX) ws = standRegres(lgX1, lgY) print('%f%+f*年份%+f*部件数量%+f*是否为全新%+f*原价' % (ws[0],ws[1],ws[2],ws[3],ws[4])) def usesklearn(): """ 函数说明:使用sklearn Parameters: 无 Returns: 无 """ from sklearn import linear_model reg = linear_model.Ridge(alpha = .5) lgX = [] lgY = [] setDataCollect(lgX, lgY) reg.fit(lgX, lgY) print('%f%+f*年份%+f*部件数量%+f*是否为全新%+f*原价' % (reg.intercept_, reg.coef_[0], reg.coef_[1], reg.coef_[2], reg.coef_[3])) if __name__ == '__main__': usesklearn()
