绑定服务
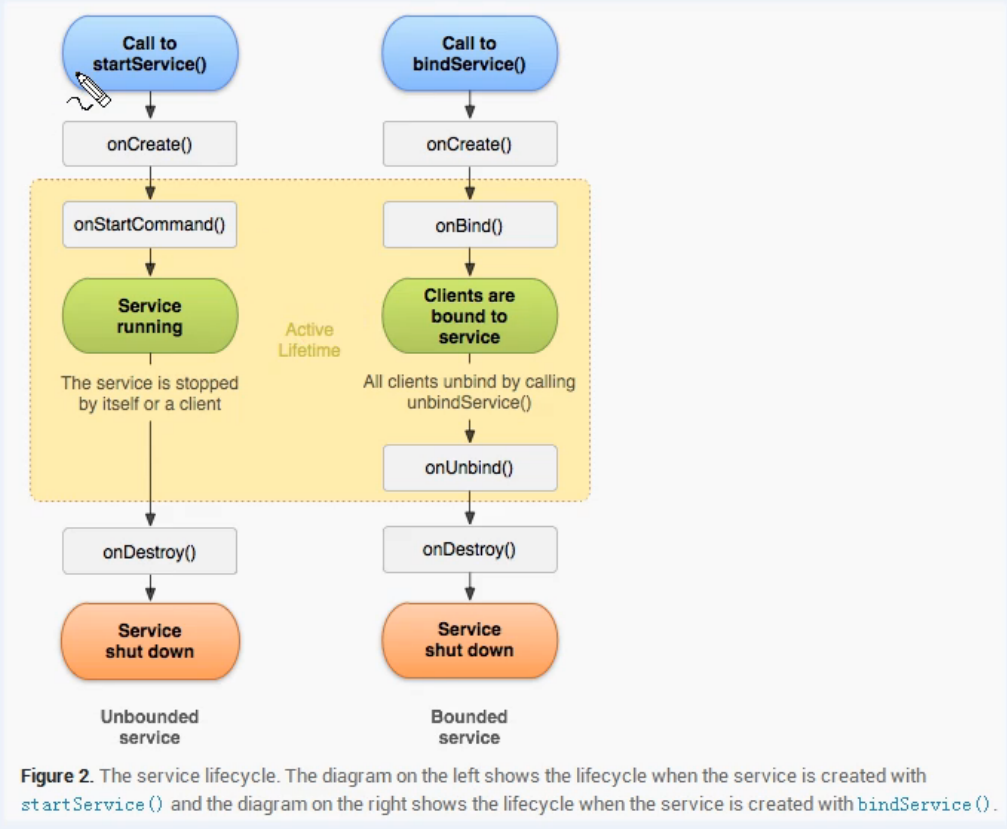
右边部分就是绑定服务的运行过程
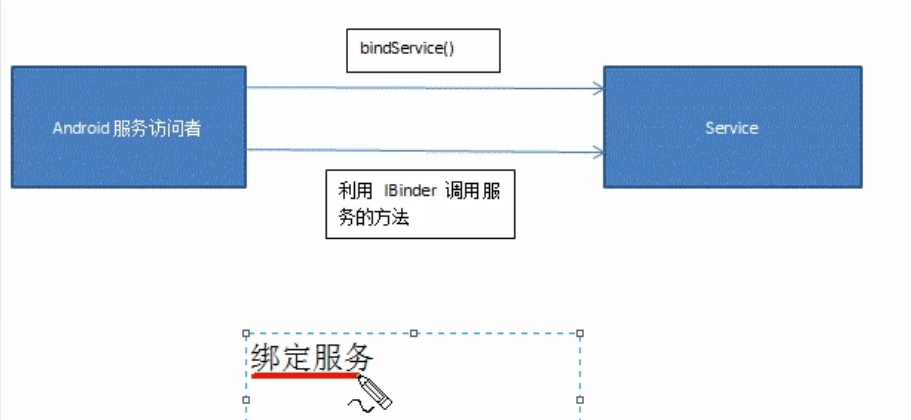
这样绑定的目的就是服务绑定者调用服务的方法,在我的样例里就是体现为服务访问者调用服务的show()方法
来张效果图吧
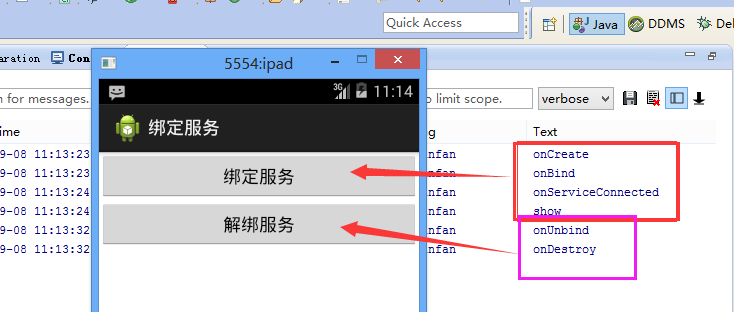
分析:
1、第一步还是继承服务类
1 package fry; 2 3 import java.io.FileDescriptor; 4 5 import android.app.Service; 6 import android.content.Intent; 7 import android.os.Binder; 8 import android.os.IBinder; 9 import android.os.IInterface; 10 import android.os.Parcel; 11 import android.os.RemoteException; 12 import android.util.Log; 13 14 public class myService extends Service{ 15 16 /** 17 * 当绑定这个服务的时候调用 18 */ 19 @Override 20 public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) { 21 Log.d("fanfan", "onBind"); 22 return new MyServiceBinder(); 23 } 24 /** 25 * 当解除绑定这个服务的时候调用 26 */ 27 @Override 28 public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) { 29 Log.d("fanfan", "onUnbind"); 30 return super.onUnbind(intent); 31 } 32 /** 33 * 当重新绑定这个服务的时候调用 34 */ 35 @Override 36 public void onRebind(Intent intent) { 37 Log.d("fanfan", "onRebind"); 38 super.onRebind(intent); 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * service被创建后调用 43 */ 44 @Override 45 public void onCreate() { 46 Log.d("fanfan", "onCreate"); 47 super.onCreate(); 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * service被start后调用 52 */ 53 @Override 54 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { 55 Log.d("fanfan", "onStartCommand"); 56 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * service被停止后调用 61 */ 62 @Override 63 public void onDestroy() { 64 Log.d("fanfan", "onDestroy"); 65 super.onDestroy(); 66 } 67 68 public void show(){ 69 Log.d("fanfan", "show"); 70 } 71 72 /** 73 * 中介 74 * @author Fry 75 * 76 */ 77 public class MyServiceBinder extends Binder{ 78 public void show(){ 79 myService.this.show(); 80 } 81 82 } 83 84 85 }
2、第二步的话就是配置服务
1 <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 package="com.example.bindservice" 3 android:versionCode="1" 4 android:versionName="1.0" > 5 6 <uses-sdk 7 android:minSdkVersion="8" 8 android:targetSdkVersion="19" /> 9 10 <application 11 android:allowBackup="true" 12 android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" 13 android:label="@string/app_name" 14 android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > 15 <activity 16 android:name="fry.MainActivity" 17 android:label="@string/app_name" > 18 <intent-filter> 19 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> 20 21 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> 22 </intent-filter> 23 </activity> 24 <activity android:name="fry.Activity01" android:exported="true"></activity> 25 26 <service android:name="fry.myService"> 27 28 </service> 29 30 </application> 31 32 </manifest>
3、第三步就是绑定服务
1 package fry; 2 3 import com.example.bindservice.R; 4 5 import fry.myService.MyServiceBinder; 6 import android.app.Activity; 7 import android.content.ComponentName; 8 import android.content.Context; 9 import android.content.Intent; 10 import android.content.ServiceConnection; 11 import android.os.Bundle; 12 import android.os.IBinder; 13 import android.util.Log; 14 import android.view.View; 15 16 public class Activity01 extends Activity{ 17 private ServiceConnection conn; 18 @Override 19 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 20 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 21 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 22 setContentView(R.layout.activity01); 23 conn=new ServiceConnection(){ 24 /** 25 * 当服务访问者与服务绑定成功后调用 26 */ 27 @Override 28 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName arg0, IBinder service) { 29 Log.d("fanfan", "onServiceConnected"); 30 MyServiceBinder binder=(MyServiceBinder)service; 31 //实现了访问者调用服务者的方法 32 binder.show(); 33 } 34 /** 35 * 当service崩溃或被系统强制杀死后调用 36 */ 37 @Override 38 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) { 39 Log.d("fanfan", "onServiceDisconnected"); 40 } 41 42 }; 43 } 44 45 public void onClick(View view){ 46 Intent intent=new Intent(); 47 intent.setClass(this, myService.class); 48 switch(view.getId()){ 49 case R.id.btn_bind://绑定服务 50 bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 51 break; 52 case R.id.btn_unbind://解绑服务 53 unbindService(conn); 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 }