第4章 并发编程
4.1~4.2并行概念
并行:并行计算是一种计算方案,它尝试使用多个执行并行算法的处理器更快速地解决问题。
顺序算法和并行算法、并发
顺序算法和并行算法的区别:
顺序算法按照所有的步骤进行单步执行。
并行算法按照指定的并行算法执行独立的任务。

理性情况下,并行算法中的所有任务都应该同时实时运行,然而在真正的并行执行只能在多核或多处理器系统中实现,在单CPU系统中,只能并发执行,即在逻辑上并行执行。
线程
线程的定义在进程之下,进程是独立的执行单元,在内核模式下,进行在唯一的地址空间上执行。而线程则是某进程统一地址空间上的独立执行单元。主线程可以创建其他线程,每个线程又可以创建更多的线程。
某进程的所有线程都在该进程的相同地址空间中执行,但每个线程都是一个独立的执行单元。
相比进程,线程好像相对更为轻量级。且线程还具有以下优点:
- 线程创建和切换速度更快:若要在某个进程中创建线程,操作系统不必为新的线程分配内存和创建页表,因为线程与进程共用同一个地址空间。所以,创建线程比创建进程更快。
- 线程的响应速度更快:一个进程只有一个执行路径。当某个进程被挂起时,帮个进程都将停止执行。相反,当某个线程被挂起时,同一进程中的其他线程可以继续执行。
- 线程更适合井行计算:并行计算的目标是使用多个执行路径更快地解决间题。基于分治原则(如二叉树查找和快速排序等)的算法经常表现出高度的并行性,可通过使用并行或并发执行来提高计算速度。
但是,线程也存在问题,需要明确的同步信息,也存在安全性问题。如果在但CPU上,处理多线程程序需要各个线程来回切换,反而增大了开销,降低了速度。
4.3~4.5 线程操作和程序实例
Linux下Pthread库提供的线程API:
pthread_create(thread, attr, function, arg): create thread
pthread_exit(status):terminate thread
pthread_cancel(thread) : cancel thread
pthread_attr_init(attr) : initialize thread attributes
pthread_attr_destroy(attr): destroy thread attribute
创建线程:使用pthread_create()来创建线程。
终止线程:线程函数结束后,线程自动终止。也可以通过调用函数int pthraad_exit {void *status)完成终止的操作。
线程连接:一个线程可以等待另一个线程的终止, 通过:int pthread_join (pthread_t thread, void **status__ptr)来完成。终止线程的退出状态以status_ptr返回。
4.6 线程同步
由于线程在进程的统一地址空间中运行,所以同一进程的所有线程都共享所有全局变量和数据结构。在多个线程都需要修改同一个变量或者是数据结构的时候就会产生竞争。要防止出现这样的问题,需要线程同步。
最简单的方法就是加锁。锁被称为互斥量。可以使用
- 静态的方法,定义互斥量m。
- 动态方法,使用
pthread_mutex_init()函数,设置互斥属性。
或者使用条件变量的方法。同样分为静态和动态两种方式。
生产者——消费者问题
一系列生产者和消费者进程共享数量有限的缓冲区。每个缓冲区每次有一个特定的项目。也称有限缓冲问题。生产者的主要作用是生成一定量的数据放到缓冲区中,然后重复此过程。与此同时,消费者也在缓冲区消耗这些数据。
信号量
在操作系统中我们学习过信号量的知识。信号量代表了一个资源的可用程度,是进程同步的一般机制。有P原语和V原语,原语都是原子操作或基本操作。
实践内容过程、问题解决过程
线程程序测试
按照教材给出的实例进行了测试。测试内容为使用线程进行快速排序。原理为:主线程先运行,然后由主线程调用qsort(&arg),让qsort()函数执行实现一个N个整数的快速排序。在qsort()中,线程会选择一个基准元素,然后进行快速排序的操作。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct{
int upperbound;
int lowerbound;
}PARM;
#define N 10
int a[N]={5,1,6,4,7,2,9,8,0,3};// unsorted data
int print(){//print current a[] contents
int i;
printf("[");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("]
");
}
void *Qsort(void *aptr){
PARM *ap, aleft, aright;
int pivot, pivotIndex,left, right,temp;
int upperbound,lowerbound;
pthread_t me,leftThread,rightThread;
me = pthread_self();
ap =(PARM *)aptr;
upperbound = ap->upperbound;
lowerbound = ap->lowerbound;
pivot = a[upperbound];//pick low pivot value
left = lowerbound - 1;//scan index from left side
right = upperbound;//scan index from right side
if(lowerbound >= upperbound)
pthread_exit (NULL);
while(left < right){//partition loop
do{left++;} while (a[left] < pivot);
do{right--;}while(a[right]>pivot);
if (left < right ) {
temp = a[left];a[left]=a[right];a[right] = temp;
}
}
print();
pivotIndex = left;//put pivot back
temp = a[pivotIndex] ;
a[pivotIndex] = pivot;
a[upperbound] = temp;
//start the "recursive threads"
aleft.upperbound = pivotIndex - 1;
aleft.lowerbound = lowerbound;
aright.upperbound = upperbound;
aright.lowerbound = pivotIndex + 1;
printf("%lu: create left and right threadsln", me) ;
pthread_create(&leftThread,NULL,Qsort,(void * )&aleft);
pthread_create(&rightThread,NULL,Qsort,(void *)&aright);
//wait for left and right threads to finish
pthread_join(leftThread,NULL);
pthread_join(rightThread, NULL);
printf("%lu: joined with left & right threads
",me);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
PARM arg;
int i, *array;
pthread_t me,thread;
me = pthread_self( );
printf("main %lu: unsorted array = ", me);
print( ) ;
arg.upperbound = N-1;
arg. lowerbound = 0 ;
printf("main %lu create a thread to do QS
" , me);
pthread_create(&thread,NULL,Qsort,(void * ) &arg);//wait for Qs thread to finish
pthread_join(thread,NULL);
printf ("main %lu sorted array = ", me);
print () ;
}
出现问题与解决办法
使用常规方法进行编译,发现无法进行编译,提示pthread相关函数未定义:
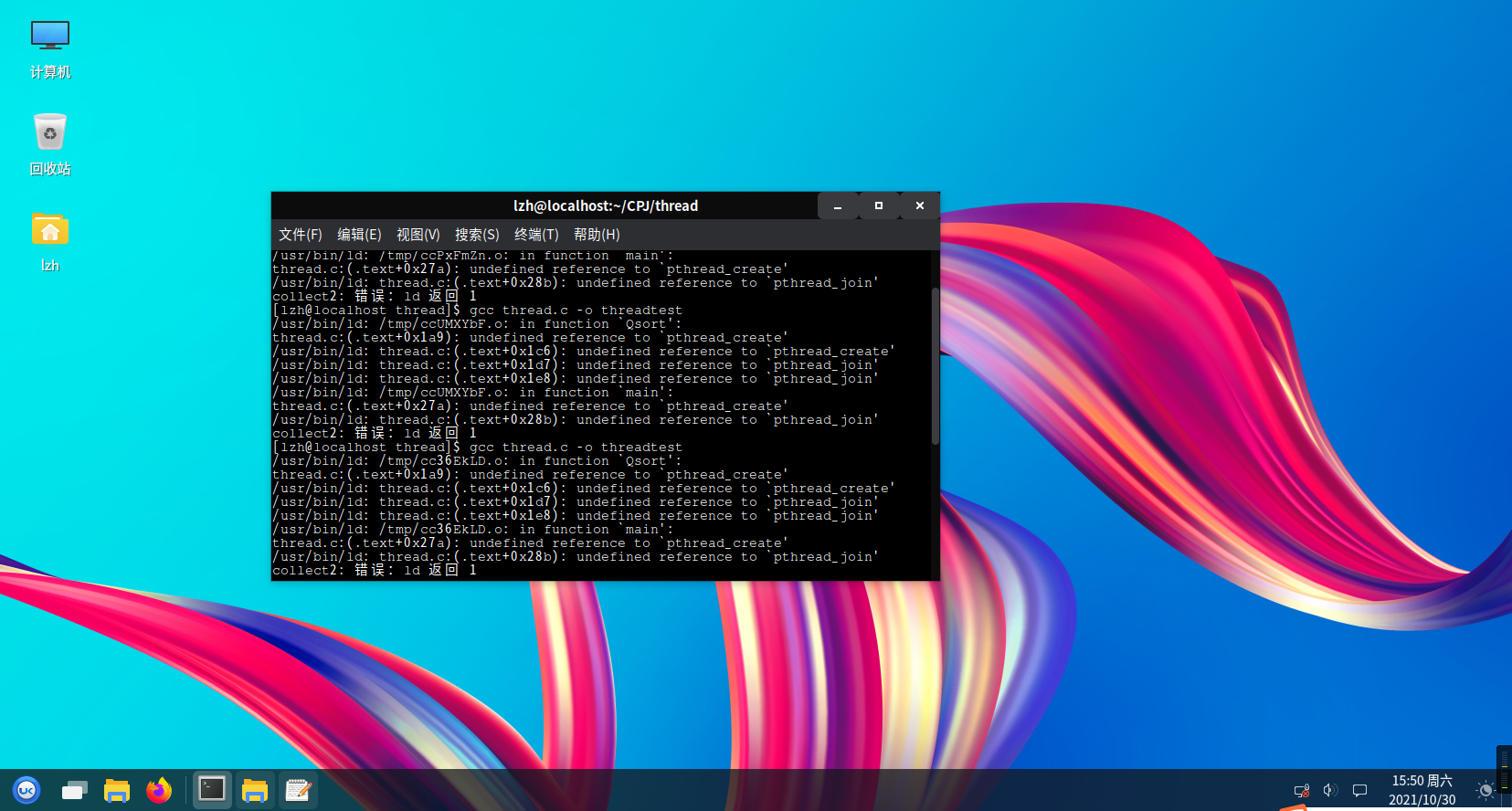
后查阅资料并仔细阅读,发现需要在编译时,在gcc命令中加入-pthread参数,如gcc thread.c -pthread才可以完成编译操作。
测试结果
在openEuler中进行测试:
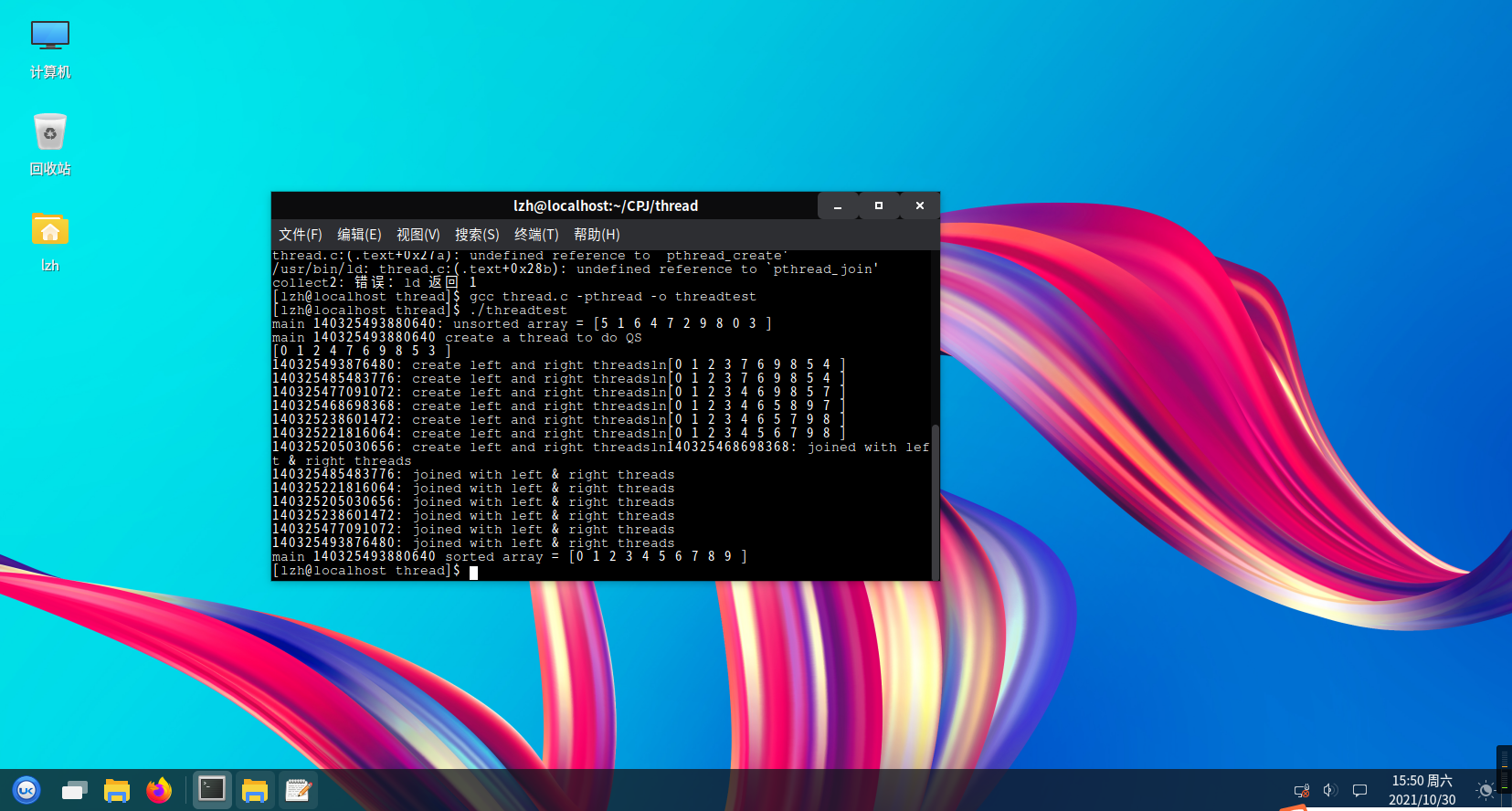
最后程序测试成功。
代码链接
代码包括一些以前的代码,在码云。链接:https://gitee.com/Ressurection20191320/code/tree/master/IS