一.currentThread()方法
currentThread方法就是返回当前被调用的线程。
该方法为一个本地方法,原码如下:
/** * Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object. * * @return the currently executing thread. */ public static native Thread currentThread();
可以看出他返回的是一个线程对象。
下面来看一个列子:
public class CurrentThreadText extends Thread{ public CurrentThreadText(){ System.out.println("构造器被"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程调用了"); } @Override public void run(){ System.out.println("run方法被"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程调用了"); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main方法被"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程调用了"); CurrentThreadText cu=new CurrentThreadText(); cu.start(); } }
结果如下:
除了run方法是在一个被自动取名为Thread-0的线程中其他的两个都在main方法中。
但是我们不使用start方法来启动线程,我们直接调用run方法会怎么样呢?
代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main方法被"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程调用了"); CurrentThreadText cu=new CurrentThreadText(); cu.run();//我直接调用了run方法 }
结果: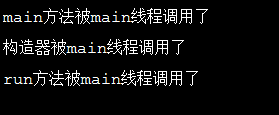
结果都是被main这个线程调用了,所以说想要启动多线程,就必须使用start方法而不是run方法。run方法就是和单线程一样按着顺序来调用,都在一个main线程中。
二.isAlive()方法
isAlive()方法人如其名意思就是“死没死啊?”,判断线程是否处于活跃状态
列子如下:
public class IsAliveText extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ System.out.print("调用run这个方法的线程为"+this.getName()); if(this.isAlive()){ System.out.println("这个线程是活跃的"); }else{ System.out.println("这个线程是不活跃的"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { IsAliveText is=new IsAliveText(); System.out.printf(String.format("开始时当前线程为%s,%s", is.getName(),is.isAlive()?("活跃"):("不活跃"))); System.out.println(); is.start(); System.out.printf(String.format("结束时当前线程为%s,%s", is.getName(),is.isAlive()?("活跃"):("不活跃"))); System.out.println(); } }
结果如下: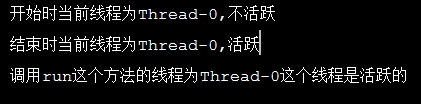
三.sleep()方法
sleep(n)方法是指让某个线程睡眠n个毫秒,比如
public class ThreadSleepText { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("当前线程为"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println("结束"); } }
程序会在5秒后结束。
四.getID()方法
过得线程的唯一标识