数据结构-排序(选做)
要求
在数据结构和算法中,排序是很重要的操作,要让一个类可以进行排序,有两种方法:
- 有类的源代码,针对某一成员变量排序,让类实现Comparable接口,调用Collection.sort(List)
- 没有类的源代码,或者多种排序,新建一个类,实现Comparator接口 调用Collection.sort(List, Compatator)
针对下面的Student类,使用Comparator编程完成以下功能:
- 在测试类StudentTest中新建学生列表,包括自己和学号前后各两名学生,共5名学生,给出运行结果(排序前,排序后)
- 对这5名同学分别用学号和总成绩进行增序排序,提交两个Comparator的代码
- 课下提交代码到码云
代码
Student.java
class Student{
private String id;//表示学号
private String name;//表示姓名
private int age;//表示年龄
private char sex;//表示性别
private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩
private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩
private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩
private double total_score;// 表示总成绩
private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩
public Student(String id, String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Student(String id, String name, char sex, int age,
double computer_score,double english_score,double maths_score){
this(id, name);
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.computer_score=computer_score;
this.english_score=english_score;
this.maths_score=maths_score;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}//获得当前对象的学号,
public double getComputer_score(){
return computer_score;
}//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩,
public double getMaths_score(){
return maths_score;
}//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩,
public double getEnglish_score(){
return english_score;
}//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩,
public void setId(String id){
this.id=id;
}// 设置当前对象的id值,
public void setComputer_score(double computer_score){
this.computer_score=computer_score;
}//设置当前对象的Computer_score值,
public void setEnglish_score(double english_score){
this.english_score=english_score;
}//设置当前对象的English_score值,
public void setMaths_score(double maths_score){
this.maths_score=maths_score;
}//设置当前对象的Maths_score值,
public double getTotalScore(){
return computer_score+maths_score+english_score;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。
public double getAveScore(){
return getTotalScore()/3;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。
@Override
public String toString(){
total_score=getTotalScore();
return "Student[姓名:"+name+",学号:"+id+",总成绩:"+total_score+"]";
}
}
StudentSortID.java
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentSortID {
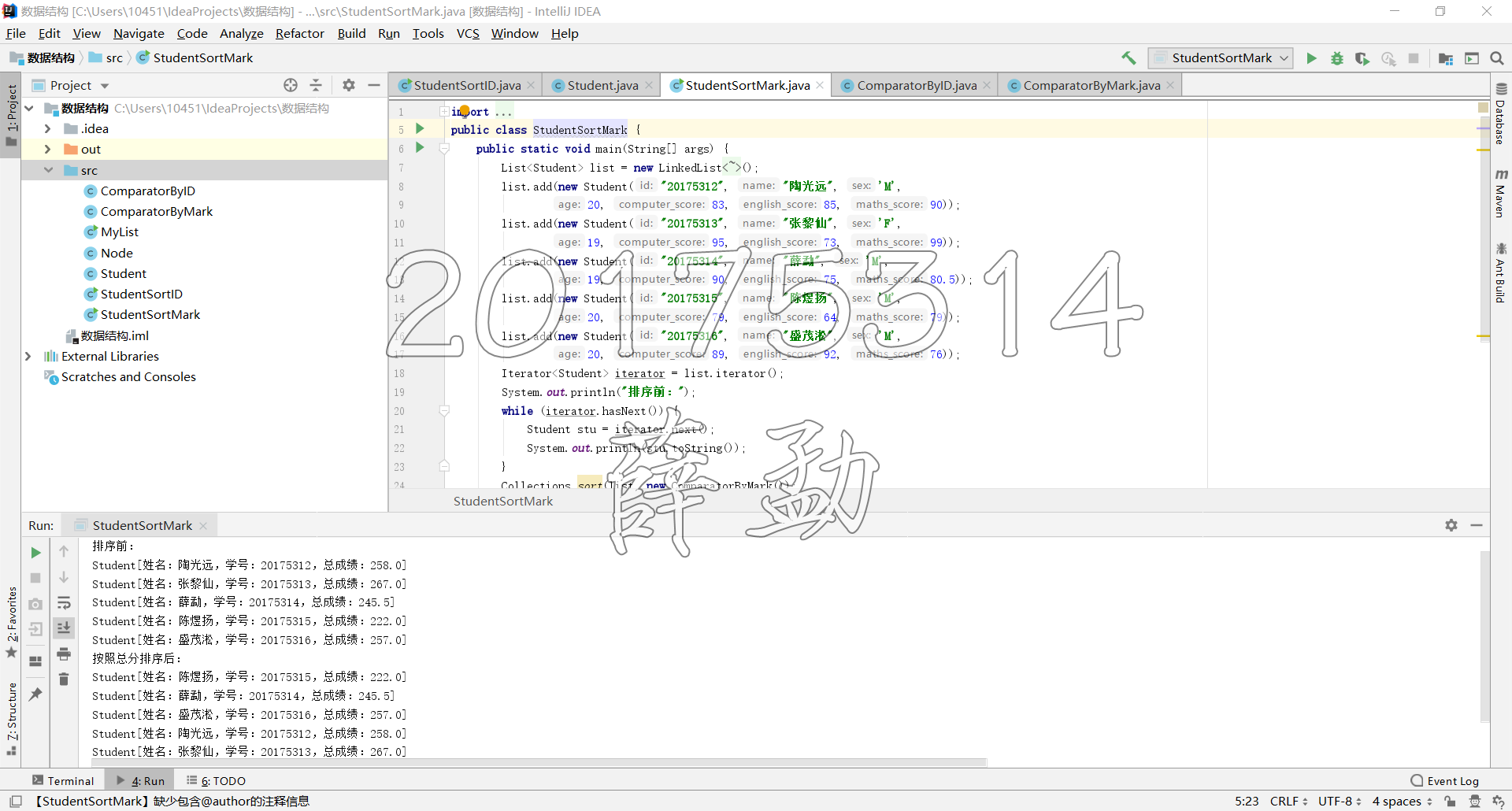
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list = new LinkedList<Student>();
list.add(new Student("20175316", "盛茂淞", 'M',
20, 89, 92, 76));
list.add(new Student("20175313", "张黎仙", 'F',
19, 95, 73, 99));
list.add(new Student("20175315", "陈煜扬", 'M',
20, 79, 64, 79));
list.add(new Student("20175314", "薛勐", 'M',
19, 90, 75, 80.5));
list.add(new Student("20175312", "陶光远", 'M',
20, 83, 85, 90));
Iterator<Student> iterator = list.iterator();
System.out.println("排序前:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student stu = iterator.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
Collections.sort(list, new ComparatorByID());
System.out.println("按照学号排序后:");
iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student stu = iterator.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
}
}
StudentSortMark.java
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentSortMark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list = new LinkedList<Student>();
list.add(new Student("20175312", "陶光远", 'M',
20, 83, 85, 90));
list.add(new Student("20175313", "张黎仙", 'F',
19, 95, 73, 99));
list.add(new Student("20175314", "薛勐", 'M',
19, 90, 75, 80.5));
list.add(new Student("20175315", "陈煜扬", 'M',
20, 79, 64, 79));
list.add(new Student("20175316", "盛茂淞", 'M',
20, 89, 92, 76));
Iterator<Student> iterator = list.iterator();
System.out.println("排序前:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student stu = iterator.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
Collections.sort(list, new ComparatorByMark());
System.out.println("按照总分排序后:");
iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student stu = iterator.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
}
}
ComparatorByID.java
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.*;
public class ComparatorByID implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2)
{
return Integer.parseInt(o1.getId()) - Integer.parseInt(o2.getId());
}
}
ComparatorByMark.java
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ComparatorByMark implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student stu1, Student stu2){
return (int)(stu1.getTotalScore()-stu2.getTotalScore());
}
}
测试结果
StudentSortID.java
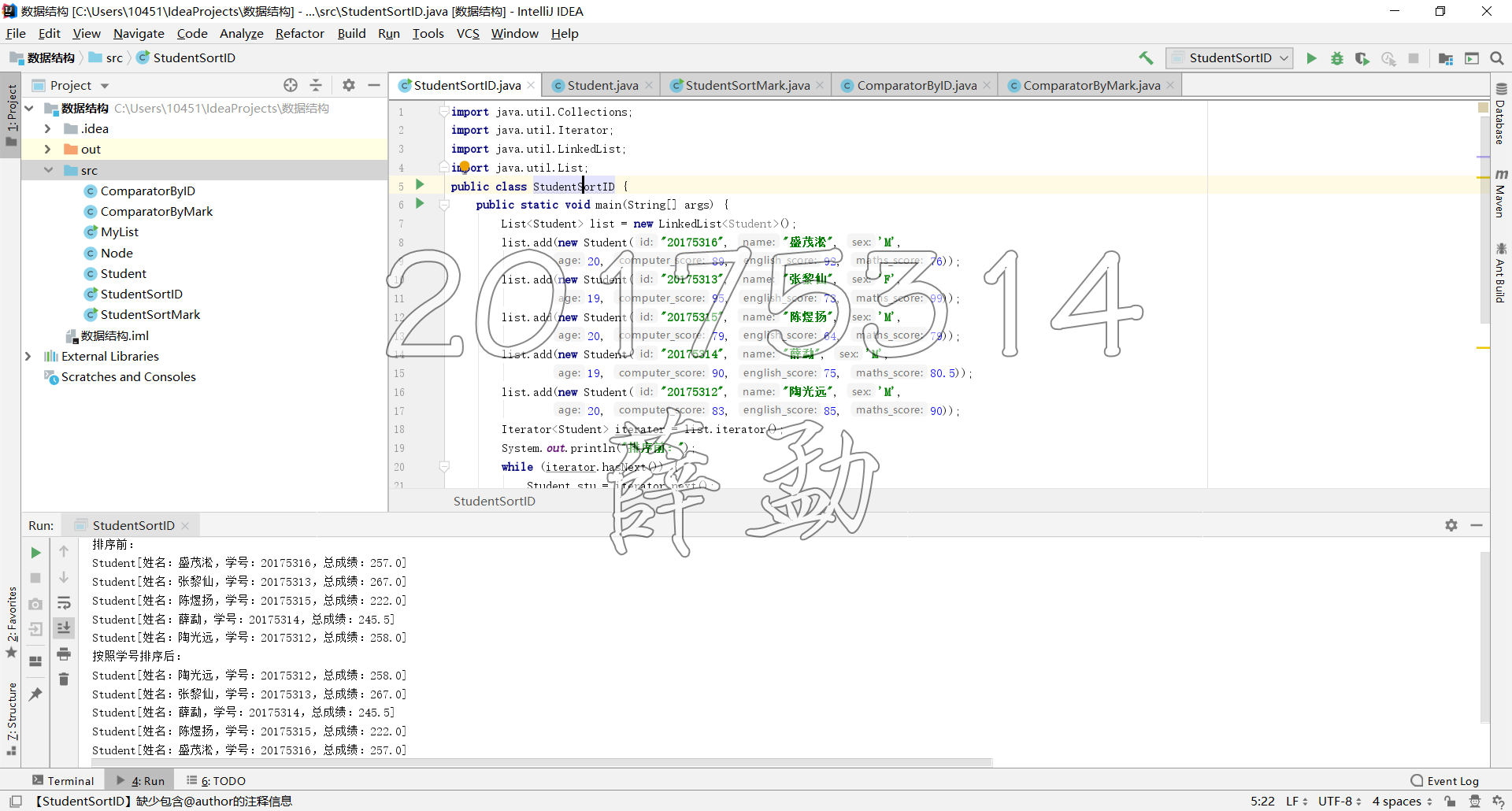
StudentSortMark.java