图像基本操作
环境配置地址
Anaconda:https://www.anaconda.com/download/
Python_whl:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#opencv
IDE:按照自己的喜好,选择一个能debug就好
安装opencv和拓展包(opencv-python、opencv-contrib-python)这里用的3.4.1
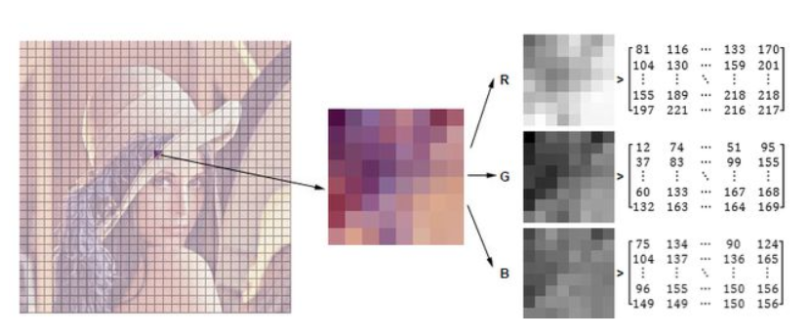
数据读取-图像
cv2.IMREAD_COLOR:彩色图像
cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE:灰度图像
import cv2 #opencv读取的格式是BGR import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np %matplotlib inline img=cv2.imread('cat.jpg') #读取图片 img
效果:
array([[[142, 151, 160], [146, 155, 164], [151, 160, 169], ..., [156, 172, 185], [155, 171, 184], [154, 170, 183]], [[107, 118, 126], [112, 123, 131], [117, 128, 136], ..., [155, 171, 184], [154, 170, 183], [153, 169, 182]], [[108, 119, 127], [112, 123, 131], [118, 129, 137], ..., [154, 170, 183], [153, 169, 182], [152, 168, 181]], ..., [[162, 186, 198], [157, 181, 193], [142, 166, 178], ..., [181, 204, 206], [170, 193, 195], [149, 172, 174]], [[140, 164, 176], [147, 171, 183], [139, 163, 175], ..., [167, 187, 188], [123, 143, 144], [104, 124, 125]], [[154, 178, 190], [154, 178, 190], [121, 145, 157], ..., [185, 198, 200], [130, 143, 145], [129, 142, 144]]], dtype=uint8)
#图像的显示,也可以创建多个窗口 cv2.imshow('image',img) # 等待时间,毫秒级,0表示任意键终止,1000表示1秒 cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
效果:

def cv_show(name,img): #函数作为后面调用 cv2.imshow(name,img) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() img.shape
效果:
(414, 500, 3)
img=cv2.imread('cat.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) #按照灰度图片读取 img img.shape
效果:
array([[153, 157, 162, ..., 174, 173, 172], [119, 124, 129, ..., 173, 172, 171], [120, 124, 130, ..., 172, 171, 170], ..., [187, 182, 167, ..., 202, 191, 170], [165, 172, 164, ..., 185, 141, 122], [179, 179, 146, ..., 197, 142, 141]], dtype=uint8) (414, 500)
#图像的显示,也可以创建多个窗口 cv2.imshow('image',img) # 等待时间,毫秒级,0表示任意键终止 cv2.waitKey(10000) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
效果:

#保存 cv2.imwrite('mycat.png',img)
效果:

type(img)
img.size
img.dtype
效果:
numpy.ndarray 207000 dtype('uint8')
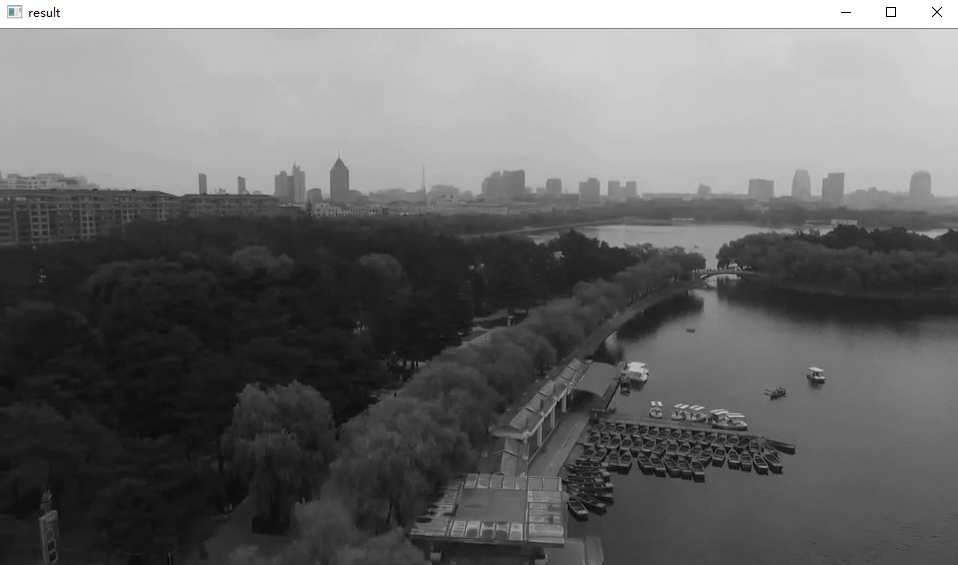
数据读取-视频
cv2.VideoCapture可以捕获摄像头,用数字来控制不同的设备,例如0,1。
如果是视频文件,直接指定好路径即可。
vc = cv2.VideoCapture('test.mp4') # 检查是否打开正确 if vc.isOpened(): open, frame = vc.read() else: open = False while open: ret, frame = vc.read() if frame is None: break if ret == True: gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) cv2.imshow('result', gray) if cv2.waitKey(100) & 0xFF == 27: break vc.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
效果:

截取部分图像数据
img=cv2.imread('cat.jpg') cat=img[0:50,0:200] cv_show('cat',cat)
效果:

颜色通道提取
b,g,r=cv2.split(img)
r
r.shape
效果:
array([[160, 164, 169, ..., 185, 184, 183], [126, 131, 136, ..., 184, 183, 182], [127, 131, 137, ..., 183, 182, 181], ..., [198, 193, 178, ..., 206, 195, 174], [176, 183, 175, ..., 188, 144, 125], (414, 500)
img=cv2.merge((b,g,r)) #将提取出的b,g,r赋值给img形成一个彩图 img.shape
效果:
(414, 500, 3)
# 只保留R cur_img = img.copy() cur_img[:,:,0] = 0 cur_img[:,:,1] = 0 cv_show('R',cur_img)
效果:

# 只保留G cur_img = img.copy() cur_img[:,:,0] = 0 cur_img[:,:,2] = 0 cv_show('G',cur_img)
效果:

# 只保留B cur_img = img.copy() cur_img[:,:,1] = 0 cur_img[:,:,2] = 0 cv_show('B',cur_img)
效果:

边界填充
BORDER_REPLICATE:复制法,也就是复制最边缘像素。
BORDER_REFLECT:反射法,对感兴趣的图像中的像素在两边进行复制例如:fedcba|abcdefgh|hgfedcb
BORDER_REFLECT_101:反射法,也就是以最边缘像素为轴,对称,gfedcb|abcdefgh|gfedcba
BORDER_WRAP:外包装法cdefgh|abcdefgh|abcdefg
BORDER_CONSTANT:常量法,常数值填充。
top_size,bottom_size,left_size,right_size = (50,50,50,50) #填充大小 # borderType指的不同类型的填充 replicate = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top_size, bottom_size, left_size, right_size, borderType=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE) reflect = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top_size, bottom_size, left_size, right_size,cv2.BORDER_REFLECT) reflect101 = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top_size, bottom_size, left_size, right_size, cv2.BORDER_REFLECT_101) wrap = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top_size, bottom_size, left_size, right_size, cv2.BORDER_WRAP) constant = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top_size, bottom_size, left_size, right_size,cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # subplot方法用于排列生成的图像,参数为坐标 plt.subplot(231), plt.imshow(img, 'gray'), plt.title('ORIGINAL') plt.subplot(232), plt.imshow(replicate, 'gray'), plt.title('REPLICATE') plt.subplot(233), plt.imshow(reflect, 'gray'), plt.title('REFLECT') plt.subplot(234), plt.imshow(reflect101, 'gray'), plt.title('REFLECT_101') plt.subplot(235), plt.imshow(wrap, 'gray'), plt.title('WRAP') plt.subplot(236), plt.imshow(constant, 'gray'), plt.title('CONSTANT') plt.show()
效果:

数值计算
img_cat=cv2.imread('cat.jpg') img_dog=cv2.imread('dog.jpg') img_cat2= img_cat +10 img_cat[:5,:,0] img_cat2[:5,:,0]
效果:
array([[142, 146, 151, ..., 156, 155, 154], [107, 112, 117, ..., 155, 154, 153], [108, 112, 118, ..., 154, 153, 152], [139, 143, 148, ..., 156, 155, 154], [153, 158, 163, ..., 160, 159, 158]], dtype=uint8) array([[152, 156, 161, ..., 166, 165, 164], [117, 122, 127, ..., 165, 164, 163], [118, 122, 128, ..., 164, 163, 162], [149, 153, 158, ..., 166, 165, 164], [163, 168, 173, ..., 170, 169, 168]], dtype=uint8)
# 相加大于255的相当于% 256 (img_cat + img_cat2)[:5,:,0]
效果:
array([[ 38, 46, 56, ..., 66, 64, 62], [224, 234, 244, ..., 64, 62, 60], [226, 234, 246, ..., 62, 60, 58], [ 32, 40, 50, ..., 66, 64, 62], [ 60, 70, 80, ..., 74, 72, 70]], dtype=uint8)
cv2.add(img_cat,img_cat2)[:5,:,0] #cv提供的add
效果:
array([[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255], [224, 234, 244, ..., 255, 255, 255], [226, 234, 246, ..., 255, 255, 255], [255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255], [255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255]], dtype=uint8) # 按照最高255处理
图像融合
img_cat + img_dog #不能直接相加
效果:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- ValueError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-34-ffa3cdc5d6b8> in <module>() ----> 1 img_cat + img_dog ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (414,500,3) (429,499,3)
img_dog = cv2.resize(img_dog, (500, 414)) #改变大小 img_dog.shape
效果:
(414, 500, 3)
res = cv2.addWeighted(img_cat, 0.4, img_dog, 0.6, 0) #大小相同后按照权重相加 plt.imshow(res)
效果:

res = cv2.resize(img, (0, 0), fx=4, fy=4) #没指定具体大小,指定倍数 plt.imshow(res)
效果:

res = cv2.resize(img, (0, 0), fx=1, fy=3)
plt.imshow(res)
效果: