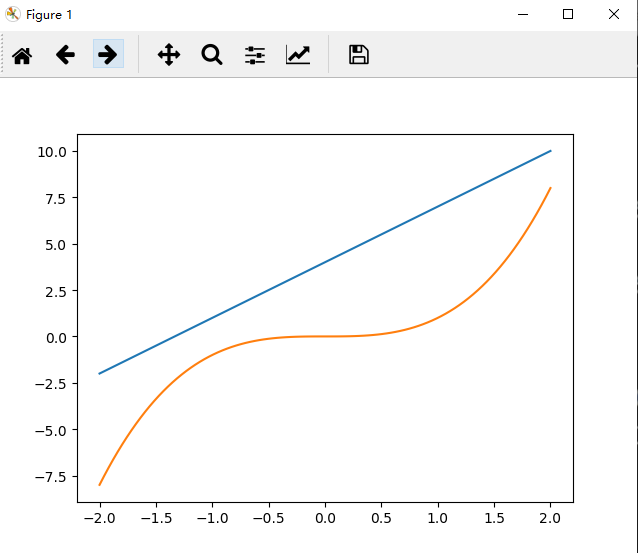
代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 引入 Matplotlib 的分模块 pyplot import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 引入 numpy import numpy as np # 创建数据 x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) #在一定范围内生成一系列点线 # y = 3 * x + 4 y1 = 3 * x + 4 y2 = x ** 3 # 创建图像 # plt.plot(x, y) plt.plot(x, y1) plt.plot(x, y2) # 显示图像 plt.show()
运行结果:
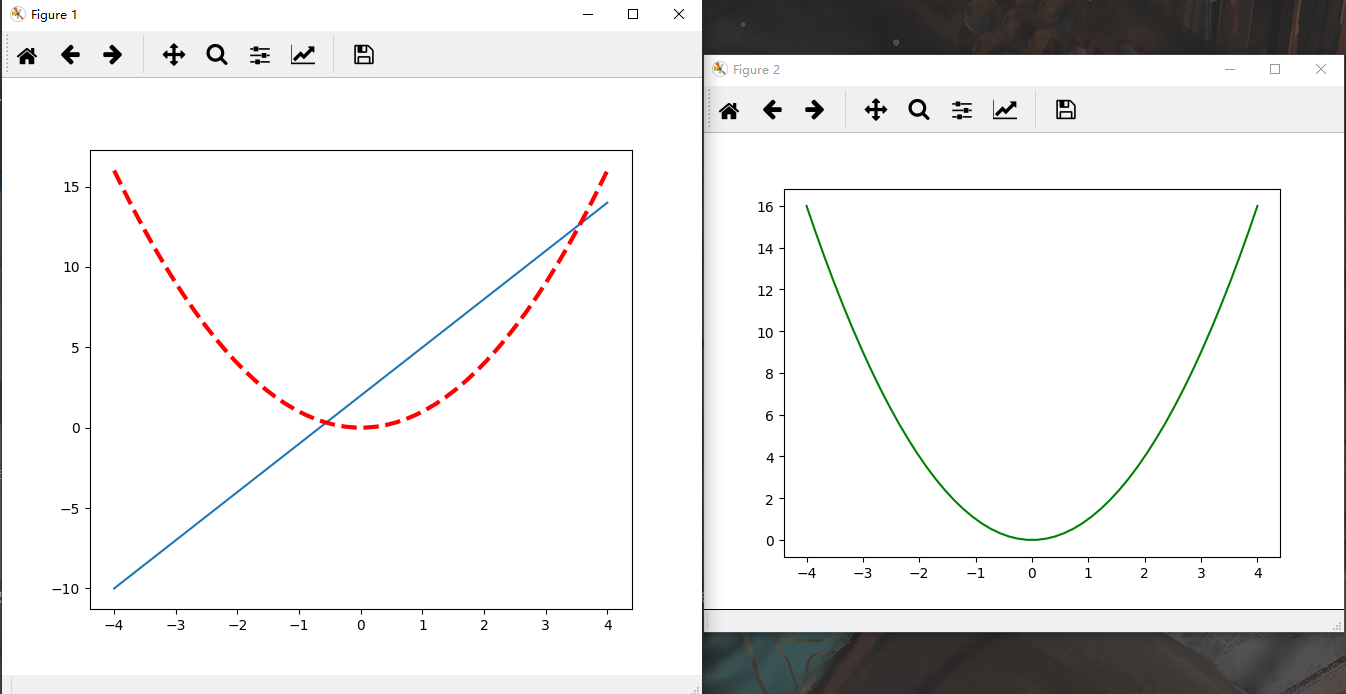
代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # 创建数据 x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 50) y1 = 3 * x + 2 y2 = x ** 2 # 第一张图 plt.figure(num=1, figsize=(7, 6)) plt.plot(x, y1) plt.plot(x, y2, color="red", linewidth=3.0, linestyle="--") # 第二张图 plt.figure(num=2) plt.plot(x, y2, color="green") # 显示所有图像 plt.show()
运行结果:
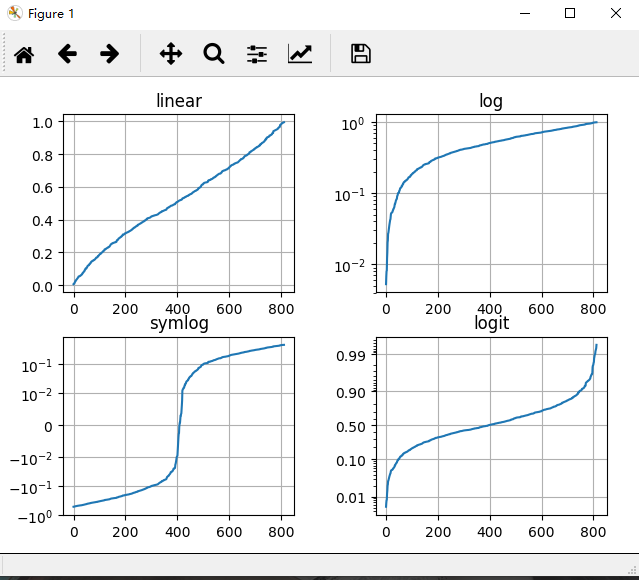
代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.ticker import NullFormatter """ 多个子图 """ # 为了能够复现 np.random.seed(1) y = np.random.normal(loc=0.5, scale=0.4, size=1000) y = y[(y > 0) & (y < 1)] y.sort() x = np.arange(len(y)) plt.figure(1) # linear plt.subplot(221) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('linear') plt.title('linear') plt.grid(True) # log plt.subplot(222) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('log') plt.title('log') plt.grid(True) # symmetric log plt.subplot(223) plt.plot(x, y - y.mean()) plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01) plt.title('symlog') plt.grid(True) # logit plt.subplot(224) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('logit') plt.title('logit') plt.grid(True) plt.gca().yaxis.set_minor_formatter(NullFormatter()) plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.92, bottom=0.08, left=0.10, right=0.95, hspace=0.25, wspace=0.35) plt.show()
运行结果:
代码:
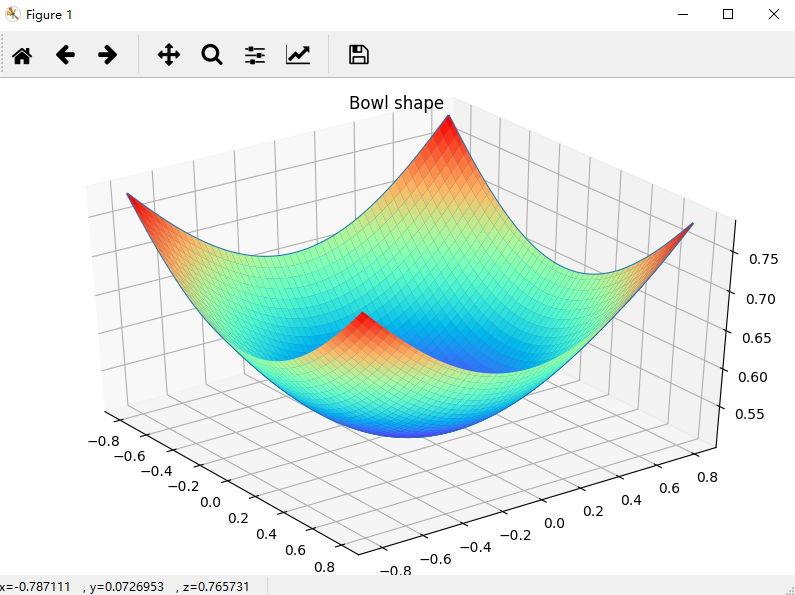
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import numpy as np """ 碗状图形 """ fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5)) ax1 = Axes3D(fig) alpha = 0.8 r = np.linspace(-alpha, alpha, 100) X, Y = np.meshgrid(r, r) l = 1. / (1 + np.exp(-(X ** 2 + Y ** 2))) ax1.plot_wireframe(X, Y, l) ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, l, cmap=plt.get_cmap("rainbow")) # 彩虹配色 ax1.set_title("Bowl shape") plt.show()
运行结果:
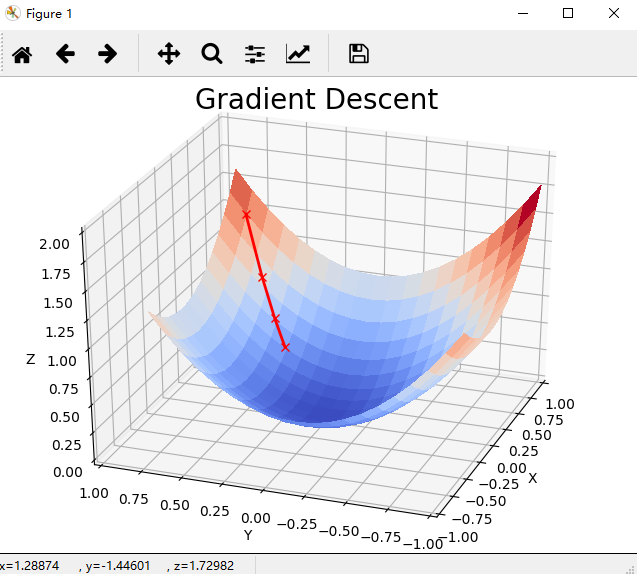
代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ Gradient Descent 的 3D 动态图示 """ import numpy as np from matplotlib import cm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as p3 import matplotlib.animation as animation nb_steps = 20 x0 = np.array([0.8, 0.8]) learning_rate = 0.1 def cost_function(x): return x[0]**2 + x[1]**2 def gradient_cost_function(x): return np.array([2*x[0], 2*x[1]]) def gen_line(): x = x0.copy() data = np.empty((3, nb_steps+1)) data[:, 0] = np.concatenate((x, [cost_function(x)])) for t in range(1, nb_steps+1): grad = gradient_cost_function(x) x -= learning_rate * grad data[:, t] = np.concatenate((x, [cost_function(x)])) return data def update_line(num, data, line): line.set_data(data[:2, :num]) line.set_3d_properties(data[2, :num]) return line fig = plt.figure() fig.suptitle("Gradient Descent", fontsize=20) ax = p3.Axes3D(fig) X = np.arange(-0.5, 1, 0.1) Y = np.arange(-1, 1, 0.1) X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) Z = cost_function((X, Y)) surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm, linewidth=0, antialiased=False) data = gen_line() line = ax.plot(data[0, 0:1], data[0, 0:1], data[0, 0:1], 'rx-', linewidth=2)[0] ax.view_init(30, -160) ax.set_xlim3d([-1.0, 1.0]) ax.set_xlabel('X') ax.set_ylim3d([-1.0, 1.0]) ax.set_ylabel('Y') ax.set_zlim3d([0.0, 2.0]) ax.set_zlabel('Z') line_ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update_line, nb_steps+1, fargs=(data, line), interval=200, blit=False) line_ani.save('gradient_descent.gif', dpi=80, writer='imagemagick') plt.show()
运行结果: