本项目Github地址
https://github.com/SSSGLQ/WordCount
PSP表格分析
| 预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 180 | 200 |
| ·Estimate | ·估计这个任务需要多上时间 | 180 | 200 |
| Development | 开发 | 1560 | 1800 |
| ·Analysis | ·需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 90 | 100 |
| ·Design Spec | ·生成设计文档 | 90 | 100 |
| ·Design Review | ·设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) | 60 | 80 |
| ·Coding Standard | ·代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 80 |
| ·Design | ·具体设计 | 180 | 200 |
| ·Coding | ·具体编码 | 720 | 800 |
| ·Code Review | ·代码复审 | 120 | 150 |
| ·Testing | ·测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 240 | 290 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 240 | 300 |
| ·Test Report | ·测试报告 | 100 | 120 |
| ·Size Measurement | ·计算工作量 | 40 | 60 |
| ·Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | ·事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 100 | 120 |
| 合计 | 1980 | 2300 | |
| PSP表格的填写参考了邹欣老师的博客现代软件工程讲义 2 工程师的能力评估和发展[1] |
解题思路
首先来看WordCount的需求:
对程序设计语言源文件统计字符数、单词数、行数,统计结果以指定格式输出到默认文件中,以及其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
可执行程序命名为:wc.exe,该程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [input_file_name]
存储统计结果的文件默认为result.txt,放在与wc.exe相同的目录下。
从命令行的参数可知要对文件进行处理,故要用到文件读写的方法,我参考了博客Java读取文件的几种方法[2]学习java按字符读取文件和按行读取文件以及在文件末尾添加内容。
对于基本功能
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
只要按字符读取文件并技术即可得到文件的字符数。
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的单词总数
只要跳过空格或 , 不处理剩下的就是单词并计数即可得到单词数。
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的总行数
对于这个功能既可以按字符读取文件然后记下' '的个数得到行数,也可以按行读取文件并计数得到行数。
wc.exe -o outputFile.txt //将结果输出到指定文件outputFile.txt
只要把结果追加到文件末尾即可。
对于拓展功能
wc.exe -s //递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
我参考了博客java递归读取目录下的所有文件[3]对递归读取指定目录下文件的方法实现该功能。
wc.exe -a file.c //返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)
我是按照把注释行和空行统计出来再用总行数减去这两项得到代码行的方法实现该功能。
wc.exe -e stopList.txt // 停用词表,统计文件单词总数时,不统计该表中的单词
对于该功能的实现我把stopList.txt的单词添加到动态数组,然后要统计单词数的文件的单词也放到动态数组,两个数组进行对比得到不用统计的单词数,再用总单词数减去得到剩下的单词数。
为了进行项目源代码管理,把源代码提交到Github,我参考了Git教程-廖雪峰的官方网站[4]的教程。
因为项目源代码是用java写的,但最后要的是exe可执行文件,所以要将Java代码打包为jar文件,并转为exe可执行文件,我参考了博客手把手教你如何把jar文件,打包成jar文件以及转换为exe可执行文件[5]的方法。
程序设计实现
我在IntelliJ IDEA中开发本项目,创建了项目WordCount,设计了BasicFunc类、AppendToFile类、ExtendedFunc类、WordCount类,在BasicFunc类中写实现四个基本功能的方法,包括统计文件字符数的方法numOfChar()、统计文件单词数的方法numOfWord()(该方法返回一个包含文件所有单词的字符串数组)、统计文件行数的方法numOfLine()、将统计的信息输出到result.txt或指定文件的方法output(),output()方法调用AppendToFile类的将传入的字符串参数追加至相应文件末尾的方法appendMethod(),在ExtendedFunc类写实现三个拓展功能的方法,包括返回传入目录参数下符合条件的文件的路径的字符串数组的方法getAllFilePath()、统计文件代码行/空行/注释行的方法numOfSeveralLines()、返回停用单词文件的单词的字符串数组的方法countStopList()、统计文件中包含停用单词的数量的方法numOfStopWord(),WordCount类只有一个main()方法,对从命令行传入的参数进行判断,如果有某个参数,则调用相应的方法实现命令行要求的功能。
关键方法流程图
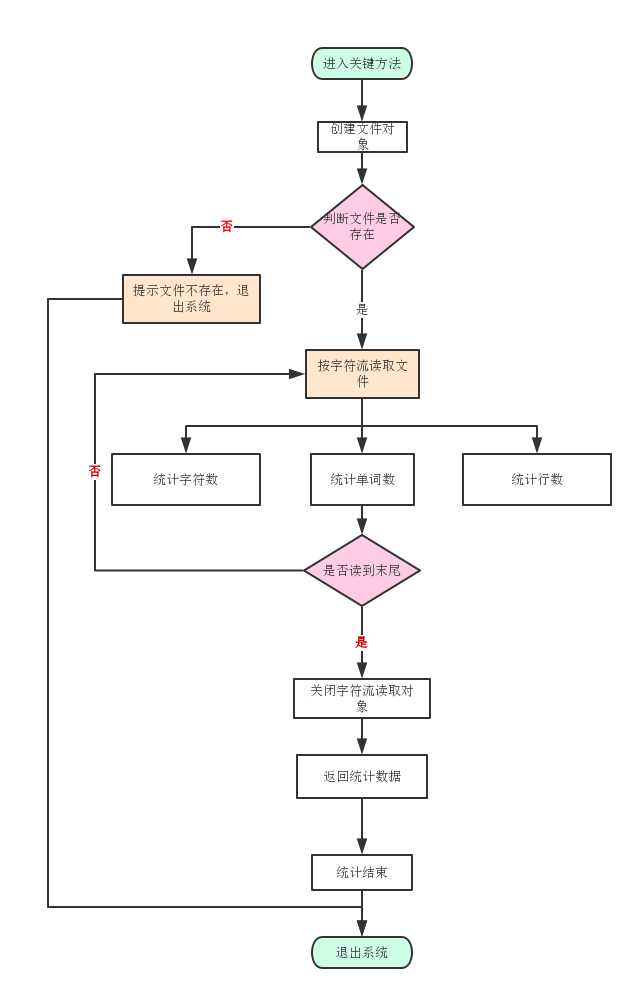
代码说明
调用numOfChar()方法返回字符数
/**
* 统计字符数
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static int numOfChar(String fileName){
int numOfChar=0;
File file = new File(fileName);//创建输入文件名的File对象,其他地方同理
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
Reader reader = null;
try {
// 一次读一个字符,其他地方同理
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
while ( reader.read() != -1) {
++numOfChar;//字符数自增
}
reader.close();//关闭输入流读取
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return numOfChar;
}
调用numOfWord()方法返回一个存放文件所有单词的动态数组,动态数组的大小即为单词数
/**
* 统计单词数
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> numOfWord(String fileName){
String str="";
List<String> wordList=new ArrayList<>();//创建一个字符串动态数组用于存放单词
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
Reader reader = null;
try {
// 一次读一个字符
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
int tempchar;
boolean isTheHeadOfLine=true;//该布尔型变量用于标记当前字符是否位于行首
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
if((char)tempchar==' '){
if(!isTheHeadOfLine){
wordList.add(str);
str="";
}
while((tempchar=reader.read())==' ');//循环读取字符,当前字符为空格时不做任何处理
}
if((char)tempchar==',') {
if(!isTheHeadOfLine) {
wordList.add(str);
str="";
}
while((tempchar=reader.read())==',');//循环读取字符,当前字符为','时不做任何处理
}
if((char)tempchar=='
') {
wordList.add(str);
str="";
isTheHeadOfLine=true;
continue;
}
str+=(char)tempchar;
if(isTheHeadOfLine){
isTheHeadOfLine=false;
}
}
reader.close();
if(numOfChar(fileName)!=0){
wordList.add(str);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return wordList;//返回存放了文件所有单词的动态数组
}
调用numOfLine()方法返回行数
/**
* 统计行数
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static int numOfLine(String fileName){
int numOfLine=1;
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
Reader reader = null;
try {
// 一次读一个字符
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
if((char)tempchar=='
') {
++numOfLine;//当前字符为换行符时行数增加
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return numOfLine;
}
调用output()方法将把统计结果输出到默认result.txt或指定文件
/**
* 输出结果到result.txt或指定的输出文件
* @param fileName
* @param str
*/
public static void output(String fileName,String str){
AppendToFile.appendMethod(fileName, str);
}
调用getAllFilePath()方法递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
/**
* 获取某目录及其子目录下所有指定后缀文件的路径
* @param fileDir
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getAllFilePath(String fileDir) {
List<String> fileList=new ArrayList<>();//创建一个存放某目录或子目录下所有指定后缀文件的路径
File file = new File(fileDir);
File[] files = file.listFiles();// 获取目录下的所有文件或文件夹
if (files == null) {// 如果目录为空,直接退出
System.exit(0);
}
// 遍历,目录下的所有文件
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isFile()) {
String fstr=f.getName();
if(fstr.substring(fstr.lastIndexOf(".")+1).equals("c")) {
fileList.add(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
} else if (f.isDirectory()) {
getAllFilePath(f.getAbsolutePath());//用到递归
}
}
return fileList;
}
调用numOfSeveralLines()方法返回文件注释行/空行/代码行
/**
* 统计文件的代码行/空行/注释行
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static String numOfSeveralLines(String fileName){
int lineOfCode,lineOfEmpty=0,lineOfComments=0;
boolean isInComment=false,lineIsEmpty=true;//前者用于标记当前是否处于注释中,后者用于标记当前行是否为空
String str=",代码行/空行/注释行:";
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
// 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 显示行号
if(tempString.indexOf("{")==0||tempString.indexOf("}")==0
||tempString.indexOf(" ")==0||tempString.indexOf("
")==0
||tempString.indexOf(" ")==0||tempString.indexOf("")==0){
for(int i=1;i<tempString.length()-1;++i){
if(tempString.charAt(i)!=' '||tempString.charAt(i)!=' '){
lineIsEmpty=false;
}
}
if(lineIsEmpty){
++lineOfEmpty;//空行数自增
}
lineIsEmpty=true;
}
if(tempString.contains("//")&&!isInComment){
++lineOfComments;//注释行数自增
}
if(tempString.contains("/*")){
isInComment=true;//当前处于注释中
++lineOfComments;
continue;
}else if(isInComment&&!tempString.contains("*/")){
++lineOfComments;
}
if(isInComment&&tempString.contains("*/")){
++lineOfComments;
isInComment=false;
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
lineOfCode=BasicFunc.numOfLine(fileName)-lineOfEmpty-lineOfComments;//计算代码行数
return str+lineOfCode+"/"+lineOfEmpty+"/"+lineOfComments+"
";
}
调用countStopList()方法和numOfStopWord()方法来获取文件中包含的停用单词数
/**
* 返回存放停用单词的动态数组
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
private static List<String> countStopList(String fileName){
List<String> stopList=new ArrayList<>();//创建一个存放停用单词的动态数组
String str="";
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
// 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
for(int i=0;i<tempString.length()-1;++i){
while(tempString.charAt(i)==' ')
++i;
str+=tempString.charAt(i);
if(tempString.charAt(i+1)==' '||tempString.charAt(i+1)=='�'){
stopList.add(str);//往动态数组中添加停用单词
str="";
}
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
return stopList;
}
/**
* 统计文件中包含的停用单词数
* @param fileName
* @param stopFileName
* @return
*/
public static int numOfStopWord(String fileName,String stopFileName){
int numOfStopWord=0;
List<String> stopList=countStopList(stopFileName);
List<String> wordList=BasicFunc.numOfWord(fileName);
for(String str1:stopList){
for(String str2:wordList){
if(str1.equals(str2))
++numOfStopWord;
}
}
return numOfStopWord;
}
测试设计过程
我用白盒测试测试用例设计方法设计测试用例,测试用例要求覆盖项目的所有功能。
| 输入 | ||
|---|---|---|
| wc.exe –c char.c | char.c, 字符数: 30 | char.c,字符数:30 |
| wc.exe –c charwithspace.c | charwithspace.c, 字符数: 33 | charwithspace.c,字符数:34 |
| wc.exe –w –l wordtest.c | wordtest.c, 单词数: 16 wordtest.c, 行数: 4 |
wordtest.c,单词数:16 wordtest.c,行数:4 |
| wc.exe -l helloworld.c | helloworld.c,行数:4 | helloworld.c,行数:4 |
| wc.exe –a atest.c | atest.c, 代码行/空行/注释行: 10/3/9 | atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 |
| wc.exe –w stoptest.c –e stoplist.txt | stoptest.c, 单词数: 15 | stoptest.c,单词数:15 |
| wc.exe -s -a –w *.c | atest.c,单词数:31 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,单词数:16 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,单词数:21 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,单词数:21 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,单词数:16 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
atest.c,单词数:31 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,单词数:16 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,单词数:21 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,单词数:21 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,单词数:16 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
| wc.exe -s -a –c -w *.c –e stop.txt –o output.txt | atest.c,字符数:412 atest.c,单词数:28 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,字符数:30 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,字符数:34 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:13 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,字符数:176 stoptest.c,单词数:15 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,字符数:176 testFile.c,单词数:15 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,字符数:189 wordtest.c,单词数:13 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
atest.c,字符数:412 atest.c,单词数:28 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,字符数:30 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,字符数:34 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:13 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,字符数:176 stoptest.c,单词数:15 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,字符数:176 testFile.c,单词数:15 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,字符数:189 wordtest.c,单词数:13 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
| wc.exe -c -w -l helloworld.c -o output.txt | helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:16 helloworld.c,行数:4 |
helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:16 helloworld.c,行数:4 |
| wc.exe -c -w -l -s -a *.c -e stoplist.txt -o output.txt | atest.c,字符数:412 atest.c,单词数:28 atest.c,行数:22 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,字符数:30 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,行数:1 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,字符数:34 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,行数:2 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:13 helloworld.c,行数:4 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,字符数:176 stoptest.c,单词数:15 stoptest.c,行数:9 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,字符数:176 testFile.c,单词数:15 testFile.c,行数:9 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,字符数:189 wordtest.c,单词数:13 wordtest.c,行数:4 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
atest.c,字符数:412 atest.c,单词数:28 atest.c,行数:22 atest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:9/3/10 char.c,字符数:30 char.c,单词数:2 char.c,行数:1 char.c,代码行/空行/注释行:1/0/0 charwithspace.c,字符数:34 charwithspace.c,单词数:4 charwithspace.c,行数:2 charwithspace.c,代码行/空行/注释行:2/0/0 helloworld.c,字符数:189 helloworld.c,单词数:13 helloworld.c,行数:4 helloworld.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 stoptest.c,字符数:176 stoptest.c,单词数:15 stoptest.c,行数:9 stoptest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 testFile.c,字符数:176 testFile.c,单词数:15 testFile.c,行数:9 testFile.c,代码行/空行/注释行:8/1/0 wordtest.c,字符数:189 wordtest.c,单词数:13 wordtest.c,行数:4 wordtest.c,代码行/空行/注释行:4/0/0 |
参考文献链接
[1] http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/10/22/2220872.html
[2] http://blog.csdn.net/u013063153/article/details/70237241
[3] http://blog.csdn.net/chaoyueygw/article/details/53466887
[4] https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0013739516305929606dd18361248578c67b8067c8c017b000/
[5] http://blog.csdn.net/sunkun2013/article/details/13167099