使用React 开发程序的时候,组件中的数据共享是通过数据提升,变成父组件中的属性,然后再把属性向下传递给子组件来实现的。但当程序越来越复杂,需要共享的数据也越来越多,最后可能就把共享数据直接提升到最外层的组件,这时子组件再想获取到共享数据就有点麻烦了,需要向下传递好多层才能到达想要数据的子组件,这就很容易产生了一个问题,由于经过的这些层(组件)可能不需要这个数据,向下传递的过程中,有可能就忘记写共享属性了,程序就会出错,并且还不好调试。有没有一种方法,可以穿透组件,想要数据的子组件直接就能获取到共享数据, 这就是React context。
Context就是上下文,环境的意思,React 的context 就是提供了一个上下文或环境,在这个环境中,有context提供者和context消费者,提供者(provider) 提供共享数据,消费者(consumer) 消费这些共享数据。所以使用React Context 的Api时,首先要先创建一个context, 假设是proContext, 创建成功后,这个proContext 就有两个属性provider和consumer,它们是两个组件,分别就是提供者和消费者,提供者提供数据是通过组件的value属性实现的, 消费者消费数据是通过函数实现了, 消费者怎么获取到提供者提供的数据呢?都是组件吗,只要消费者是提供者的子组件,它就是能获取到数据,这也就避免了层层传递。
说起来,可能不好说,写一下代码就清楚了。打开cmd命令窗口, create-react-app react-context,创建项目 react-context,项目很非常简单,如下所示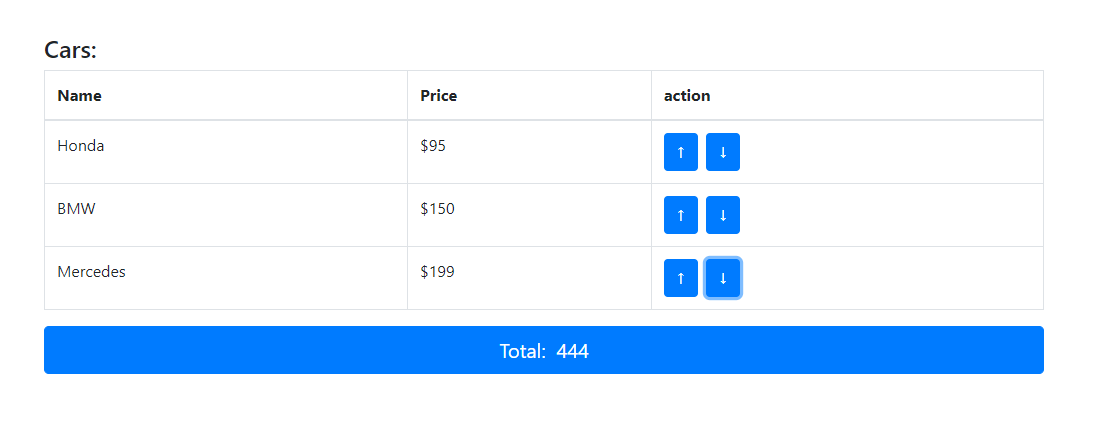
点击每个项目的上下箭头,改变total, 为了更能体现context 的用法,我把列表中的数据做成了共享数据,放到了最外层的父组件中。 项目要使用boostrap 提供样式,cd react-context && npm install bootstrap --save, 安装它。使用vs code 编辑器打开项目, 在index.js中引入bootstrap css 样式
import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import './index.css'; import App from './App'; import * as serviceWorker from './serviceWorker'; import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css'; // 添加bootstrap 样式 ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
先不用context,把它实现一下,在src 目录下建Cars.js, ProductList.js和 Total.js 文件
import React, { Fragment } from "react";
export const Cars = props => (
<Fragment>
<h4>Cars:</h4>
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Price</th>
<th scope="col">action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{/* Finally we can use data */}
{Object.keys(props.cars).map(carID => (
<tr key={carID}>
<td>{props.cars[carID].name}</td>
<td>${props.cars[carID].price}</td>
<td>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => props.incrementCarPrice(carID)}>↑</button>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => props.decrementCarPrice(carID)}>↓</button>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Fragment>
);
import React from "react"; import { Cars } from "./Cars"; export const ProductList = props => ( <Cars cars={props.cars} incrementCarPrice={props.incrementCarPrice} decrementCarPrice={props.decrementCarPrice} /> );
import React from 'react'; export const Total = props => { const { cars } = props; return ( <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg btn-block"> Total: { Object.keys(cars).reduce((sum, car) => { return sum + cars[car].price }, 0) } </button> ) }
把App.js 修改如下
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { ProductList } from "./ProductList";
import { Total } from "./Total";
export default class App extends Component {
state = {
cars: {
car001: { name: 'Honda', price: 100 },
car002: { name: 'BMW', price: 150 },
car003: { name: 'Mercedes', price: 200 }
}
};
incrementCarPrice = (selectedID) => {
const cars = Object.assign({}, this.state.cars);
cars[selectedID].price = cars[selectedID].price + 1;
this.setState({
cars
});
}
decrementCarPrice = (selectedID) => {
const cars = Object.assign({}, this.state.cars);
cars[selectedID].price = cars[selectedID].price - 1;
this.setState({
cars
});
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ '1000px', margin: '50px auto'}}>
<ProductList
cars={this.state.cars}
incrementCarPrice={this.incrementCarPrice}
decrementCarPrice={this.decrementCarPrice}
/>
<Total cars={this.state.cars}></Total>
</div>
);
}
}
可以看到真正使用App组件中共享state的是组件Cars,ProductList组件根本没有使用。但是由于Cars 组件不是App组件的子组件,所以需要经过ProductList 组件进行传递,ProductList 组件也不得不接收和传递它自己不需要的属性,造成了代码的冗余。这正是Context 解决的问题。现在使用context 解决一下。
按照上面所说,首先要创建一个context, 使用的是React.createContext() 方法,它接受一个可选的参数,就是共享内容的默认值,我们要共享什么,就在这里定义好,提供默认值,当然也可以不传,直接调用.createContext() 方法。不过,建议写上参数,把它看作是共享内容的格式定义,一看到这个context, 就知道要共享什么。那创建的context 放在什么地方呢?context 可以定义在任意位置,在src 目录下新建一个文件CarContext.js 来存放context.
import React from 'react'; // 共享的数据是一个对象,有一个属性cars, 默认值是空对象 export const CarContext = React.createContext({ cars: {} })
创建一个provider 来提供真正的共享数据,使用的是CarContext.Provider 组件。它放到什么地方呢?因为共享的数据是App中的state, 而且需要消费数据的是ProductList 组件中的Car, 所以要在App.js 中引入CarContext, 并使用CarContext.Provider 把ProductList 组件包起来,这样ProductList 及其子组件就是获取到共享数据, 共享数据又是怎么提供呢?CarContext.Provider 有一个value 属性,所有共享的内容都放到value属性中。这样productList 就可以不用传递cars 属性了,把它去掉
import { CarContext } from "./CarContext"; // app.js 顶部引入
....
// render 内容修改如下
<div style={{ '1000px', margin: '50px auto'}}>
<CarContext.Provider value={{cars: this.state.cars}}>
<ProductList
incrementCarPrice={this.incrementCarPrice}
decrementCarPrice={this.decrementCarPrice}
/>
</CarContext.Provider>
<Total cars={this.state.cars}></Total>
</div>
最后就是修改Cars组件来消费共享数据,使用Consumer 组件。相比Provider 组件,它的使用稍微有一点麻烦,它不是把Cars组件原来的内容包起来,而是使用函数表达式。Consumer 组件的内容是一个函数表达式,函数的参数,就是Consumer 组件帮我们注入到Cars组件中的共享数据,返回的内容就是Cars 原有的内容,它这时就可以直接使用共享数据了。
import React, { Fragment } from "react";
import { CarContext } from "./CarContext";
export const Cars = props => (
<CarContext.Consumer>
{/* contextData 就是共享数据 */}
{contextData => {
const {cars} = contextData;
return <Fragment>
<h4>Cars:</h4>
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Price</th>
<th scope="col">action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{/* Finally we can use data */}
{Object.keys(cars).map(carID => (
<tr key={carID}>
<td>{cars[carID].name}</td>
<td>${cars[carID].price}</td>
<td>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => props.incrementCarPrice(carID)}>↑</button>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => props.decrementCarPrice(carID)}>↓</button>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Fragment>
}}
</CarContext.Consumer>
);
有时候,修改共享数据的方法也需要共享,假设在Total 中也可以更改app的state,那么incrementCarPrice 和decrementCarPrice 就要共享, 那么 CarContext.Provider 组件的value 属性就要包含这两个方法
<div style={{ '1000px', margin: '50px auto'}}>
<CarContext.Provider value={
{cars: this.state.cars, incrementCarPrice: this.incrementCarPrice, decrementCarPrice: this.decrementCarPrice}
}>
<ProductList/>
</CarContext.Provider>
<Total cars={this.state.cars}></Total>
</div>
最好也在carCotext 中提供这两个方法的默认实现,carContext.js 修改如下:
export const CarContext = React.createContext({ cars: {}, incrementCarPrice: () => {}, decrementCarPrice: () => {} })
Cars 消费组件,调用incrementCarPrice 和decrementCarPrice, 就要从共享数据contextData 中获取
import React, { Fragment } from "react";
import { CarContext } from "./CarContext";
export const Cars = props => (
<CarContext.Consumer>
{/* contextData 就是共享数据 */}
{contextData => {
const {cars, incrementCarPrice, decrementCarPrice} = contextData;
return <Fragment>
<h4>Cars:</h4>
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Price</th>
<th scope="col">action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{/* Finally we can use data */}
{Object.keys(cars).map(carID => (
<tr key={carID}>
<td>{cars[carID].name}</td>
<td>${cars[carID].price}</td>
<td>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => incrementCarPrice(carID)}>↑</button>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => decrementCarPrice(carID)}>↓</button>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Fragment>
}}
</CarContext.Consumer>
);
由于Consumer 组件使用起来相对麻烦一点,所以React也提供了简便方法,可以给消费组件设一个静态属性contextType, 值为CarContext , 然后组件内就可以通过this.context 来获取到context 共享数据,而不用使用Consumer 组件包括。 静态属性,可以直接给消费组件类赋值一个属性,Car.contextType = CarContext , 或者在类中使用static 修饰 static contextType = CarContext , 这时要把组件变成类组件
import React, { Fragment } from "react";
import { CarContext } from "./CarContext";
export class Cars extends React.Component{
static contextType = CarContext;
render() {
const {cars, incrementCarPrice, decrementCarPrice} = this.context;
return (
<Fragment>
<h4>Cars:</h4>
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Price</th>
<th scope="col">action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{/* Finally we can use data */}
{Object.keys(cars).map(carID => (
<tr key={carID}>
<td>{cars[carID].name}</td>
<td>${cars[carID].price}</td>
<td>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => incrementCarPrice(carID)}>↑</button>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => decrementCarPrice(carID)}>↓</button>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Fragment>
)
}
}
但为了这一个context ,改成类组件,也不是很爽,如果你的React 版本是16.8 及以上,你可以使用React Hook, useContext
import React, { Fragment, useContext } from "react";
import { CarContext } from "./CarContext";
export const Cars = () => {
const {cars, incrementCarPrice, decrementCarPrice} = useContext(CarContext);
return <Fragment>
<h4>Cars:</h4>
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Price</th>
<th scope="col">action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{/* Finally we can use data */}
{Object.keys(cars).map(carID => (
<tr key={carID}>
<td>{cars[carID].name}</td>
<td>${cars[carID].price}</td>
<td>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => incrementCarPrice(carID)}>↑</button>
<button className="btn btn-primary" onClick={() => decrementCarPrice(carID)}>↓</button>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Fragment>
};
这时ProductList 组件就可以不用传递任何数据了
export const ProductList = props => ( <Cars/> );
但如果仅仅是为了不想层层伟递数据,就使用context,那没有必要,那可以传递组件。在父组件中声明要传递的组件,直接把组件传递过去。经过的子组件以数据并没有感知。