前言:
一直以来,对于多线程的理解总是赶在前一秒翻书时回忆起,后一秒放下书即忘。甚是可恼!今晚对多线程总结一下,也好有个了断~
概念引入:
首先,我们想了解的是:什么是线程,跟进程有什么关联?
其实是这样的:线程是程序执行流的最小单元。其一般有3种状态:就绪,执行和阻塞(因本文注重实例,就不对概念作过多的解释~)。在计算机中,一个代码块(block)运行时产生一个或多个进程(process),而每一个进程又对应一至多个线程(thread),每一个线程又可以分为一至多个任务(task).
因此,以上的关系我们可以通过下面一张图进行理解。
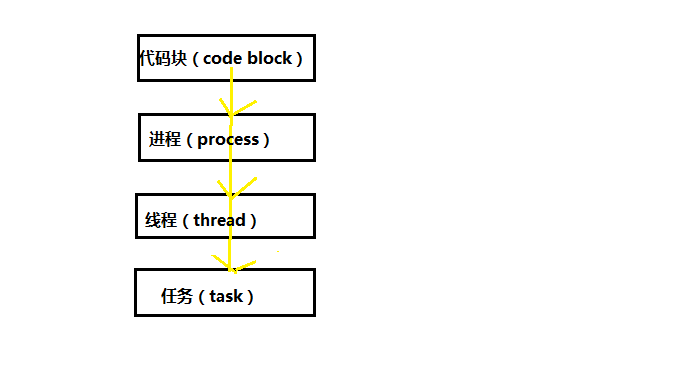
-
1.创建线程的两种实现方式:
1)继承Thread类
2)实现Runnable接口
1 package com.gdufe.thread; 2 3 public class ThreadTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new TaskA(),"thread1"); 8 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new TaskB('a',100),"thread2"); 9 Thread thread3 = new Thread(new TaskB('b',100),"thread3"); 10 11 thread1.start();; 12 thread2.start(); 13 thread3.start(); 14 System.out.println("--End--"); 15 16 17 } 18 19 /* 20 * 任务A通过实现Runnable接口创建任务 21 */ 22 private static class TaskA implements Runnable{ 23 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ 27 System.out.print(i+" "); 28 } 29 } 30 31 } 32 /* 33 * 任务B通过继承Thread类并重写run()方法来创建任务 34 */ 35 private static class TaskB extends Thread{ 36 37 private char ch; 38 private int times; 39 40 public TaskB(char ch,int times){ 41 this.ch=ch; 42 this.times=times; 43 } 44 @Override 45 public void run() { 46 for(int i=0;i<times;i++){ 47 System.out.print(ch+" "); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 }
输出结果:
-
2.线程池thread-pool
线程池指的是不需要每个任务用一个线程来存储,而是初始就给出一个“池”。线程池首先会初始池的大小,即可供同时进入的“任务”的数量,这样的话每当来一个新任务就直接往线程池里面扔,不需要再单独创建一个个线程。
-
3.线程不安全
【不安全实例代码】
1 package com.gdufe.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 6 public class ThreadNotSafe { 7 static Account account = new Account(); 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 12 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 13 executor.execute(new Deposit()); 14 } 15 executor.shutdown(); 16 while (!executor.isTerminated()) { 17 } 18 System.out.println("Finally, the account get the total balance:" 19 + account.getBalance()); 20 } 21 /* 22 * 存钱操作,每次存入1 23 */ 24 static class Deposit implements Runnable { 25 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 account.deposit(1); 29 } 30 } 31 32 static class Account { 33 private int balance = 0; 34 35 public int getBalance() { 36 return balance; 37 } 38 39 public void deposit(int value) { 40 int newBalance = balance + value; 41 try { 42 Thread.sleep(5); //故意将原有的简单操作拆分两步,并且中间延迟5毫秒 43 } catch (Exception e) { 44 } 45 balance = newBalance; 46 } 47 } 48 49 }
输出结果:
Finally, the account get the total balance:3
(注意:执行多次的结果不一样)
分析:
上述实例进行100个任务,每个任务都是往账号里面存“1”,正确的结果应该输出“100”,那为什么最终的结果好像“不正确”。原因是,当多个任务同时访问一个资源时,就出现了所谓的资源“竞争”。
解决方法:
1)使用关键字“synchronized”对资源进行封锁,此方式称作“隐式加锁”;
2)采用java内部工具类“Lock”进行“显式加锁”。
【方式1-代码修改部分】:
1 static class Account { 2 private int balance = 0; 3 4 public int getBalance() { 5 return balance; 6 } 7 /* 8 * 增加关键字‘synchronized’,方法未执行完时,仅限一个任务访问该方法 9 */ 10 public synchronized void deposit(int value) { 11 int newBalance = balance + value; 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(5); //故意延迟5毫秒 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 } 16 balance = newBalance; 17 } 18 }
【方式2-代码修改部分】:
1 static class Account { 2 private int balance = 0; 3 private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 4 5 public int getBalance() { 6 return balance; 7 } 8 /* 9 * 采用显示加锁,方法开始执行时加锁,执行结束前解锁 10 */ 11 public void deposit(int value) { 12 lock.lock(); //加锁 13 int newBalance = balance + value; 14 try { 15 Thread.sleep(5); //故意延迟5毫秒 16 balance = newBalance; 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 19 }finally{ 20 lock.unlock(); //解锁 21 } 22 } 23 }
输出结果:
Finally, the account get the total balance:100
(多次执行,输出结果总是100)
-
4.线程协作实例:
实例情境:
假如现在要对一个银行账号(Account)进行存(Deposit)取(Withdraw)钱操作。故确定了2个线程,这里的协作需要注意一点的是当银行账号的余额不足时,取钱操作必须等待。因此,除了前面设定的锁之外,我们还得加一个信号量signal。信号量的作用是当取钱的数量大于当前账号余额时,停止该操作,发出等待的信号量signal;存钱时,有多少即存多少就是了。不过,每进行一次存钱操作,都必须发出信号提醒还在等待的取钱操作,不然取钱操作将一直等下去...
代码实现:
1 package com.gdufe.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 7 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 8 9 public class ThreadCooperation { 10 private static Account account = new Account(); 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 //开启大小为2线程池的,依次加入任务 14 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); 15 executor.execute(new DepositTask()); 16 executor.execute(new WithdrawTask()); 17 //关闭线程池入口 18 executor.shutdown(); 19 System.out.println("Operation------Balance"); 20 } 21 //从账号取出钱 22 static class WithdrawTask implements Runnable { 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 try { 26 while (true) { 27 account.withdraw((int) (Math.random() * 10)); 28 } 29 } catch (Exception e) { 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 //往账号存钱 34 static class DepositTask implements Runnable { 35 @Override 36 public void run() { 37 try{ 38 while (true) { 39 account.deposit((int) (Math.random() * 10)); 40 Thread.sleep(1000); 41 } 42 }catch(Exception e){ 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 //内部类,只有‘balance’属性 48 static class Account { 49 private int balance = 0; 50 private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 51 private static Condition signal = lock.newCondition(); 52 53 public int getBalance() { 54 return balance; 55 } 56 //前后加锁,解锁 57 public void deposit(int amount) { 58 lock.lock(); 59 try { 60 balance += amount; 61 System.out.println("deposit "+amount+"----total:" + account.getBalance()); 62 signal.signalAll(); //not 'notifyAll()' 63 } finally { 64 lock.unlock(); 65 } 66 } 67 //同样加锁,解锁 68 public void withdraw(int amount) { 69 lock.lock(); 70 try { 71 while (balance < amount) { 72 signal.await(); 73 System.out.println("signal await..."); 74 } 75 balance -= amount; 76 System.out.println("whthdraw "+amount+"----total:" + account.getBalance()); 77 } catch (Exception e) { 78 e.printStackTrace(); 79 } finally { 80 lock.unlock(); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 }
输出结果:

-
5.经典生产者消费者问题
(抱歉,时间关系!后续补上关于生产者消费者的实例,敬请关注~~)