CSS不像其它高级语言一样支持算术运算、变量、流程控制与面向对象特性,所以CSS样式较多时会引起一些问题,如修改复杂,冗余,某些别的语言很简单的功能实现不了等。而javascript则是一种半面向对象的动态语言,有java的影子,有C的味道,中间有比其它语言多的糟粕,使用预处理办法可以解决这些问题。其中Less[les]与Sass是CSS的预处理技术,而CoffeeScript、TypeScript则是javascript的预处理技术。

一、Less
1.1、概要
Less是一种动态样式语言,Less 是一门 CSS 预处理语言,它扩展了 CSS 语言,增加了变量、Mixin、函数等特性,使 CSS 更易维护和扩展。
Less 将 CSS 赋予了动态语言的特性,如 变量, 继承, 运算, 函数。LESS 既可以在 客户端 上运行 (支持IE 6+, Webkit, Firefox),也可以借助Node.js或者Rhino在服务端运行。 Less是一个JS库,所以他可以在客户端运行,相对Sass则必须在服务端借助Ruby运行
中文网站: http://www.lesscss.net/
英文官网: http://lesscss.org
less源码: https://github.com/cloudhead/less.js
github地址: https://github.com/less/less.js
1.2、变量
语法:@变量名:值;
1)、以@作为变量的起始标识,变量名由字母、数字、_和-组成
2)、没有先定义后使用的规定;
3)、以最后定义的值为最终值;
4)、可用于rule值、rule属性、rule属性部件、选择器、选择器部件、字符串拼接;
5)、定义时 "@变量名: 变量值;" 的形式;引用时采用 "@变量名" 或 "@{变量名}" 的形式;
6)、存在作用域,局部作用域优先级高于全局作用域。
@color: #4d926f; #header { color: @color; } #header { color: #4d926f; } @color: #253636; @color: #ff3636; //覆盖第一次的定义 #header {color: @color;} //多次反复解析 #header {color: #ff3636;}
编译后:
#header { color: #ff3636; } #header { color: #4d926f; } #header { color: #ff3636; } #header { color: #ff3636; }
1.3、解析Less
1.3.1、在线处理
页面中直接引用less的源码,使用javascript动态翻译,这样在开发阶段非常方便,但是在运行阶段会影响效率,建议在开发阶段使用less.js在线处理,项目稳定运行时将less文件预处理。
步骤一:
下载到less.js动态处理.less文件的javascript脚本,下载地址: https://github.com/less/less.js
步骤二:
在页面中引入样式与less.js文件,如下:
<link rel="stylesheet/less" type="text/css" href="styles.less"> <script src="less.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
测试运行
示例代码:
style1.less
/*1定义变量*/ @color:red; @bgColor:lightgreen; /*定义变量color,值为red*/ .cls11{ color: @color; } @color:lightblue; /*重新定义,覆盖前面的定义,后定义的起作用*/ .cls12 { background: @bgColor; border: 2px solid @color; }
de2.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Less</title> <link rel="stylesheet/less" type="text/css" href="css/style1.less"> <script src="js/less/less.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="cls12"> Hello Less </div> </body> </html>
运行效果:
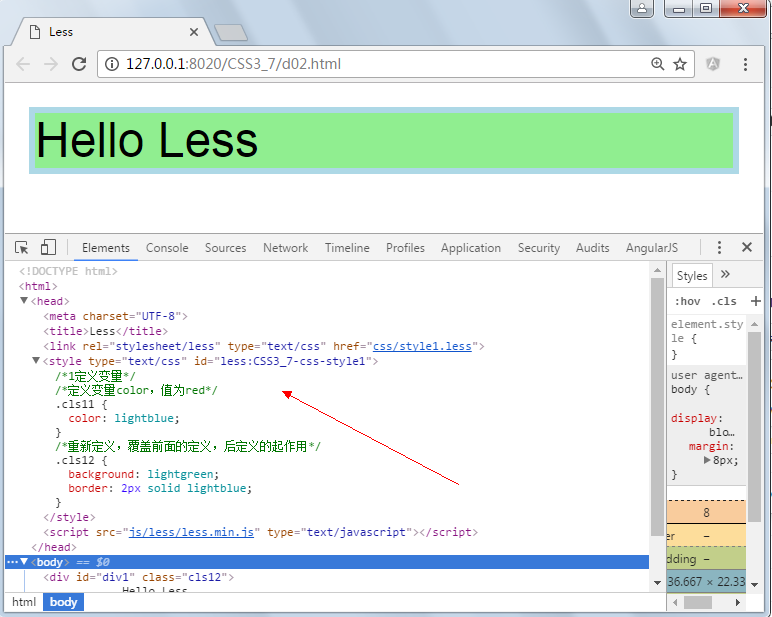
从上图可以看出less.js将style1.less文件翻译后变成了一个标准的CSS内部样式表。
1.3.2、预处理
在线处理的效率低,预处理就是将less文件先翻译成标准的CSS文件,再引入到项目中,处理的办法有许多:
方法一:使用lessc
a)、请先在电脑上安装node.js,下载地址: https://nodejs.org/en/

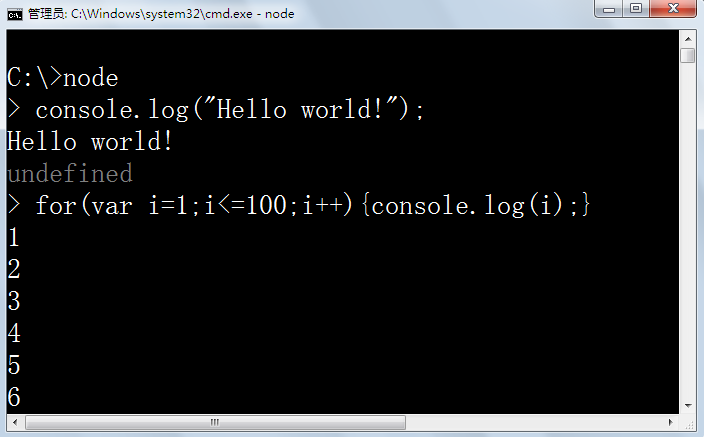
a)、安装lessc
使用npm(node.js package management)node.js包管理器
在命令行模式下输入安装指令:npm install less -g

使用lessc翻译less文件为css文件:
lessc styles.less 显示
lessc styles.less > styles.css 生成文件
参数 –x 普通压缩
参数 -h 帮助
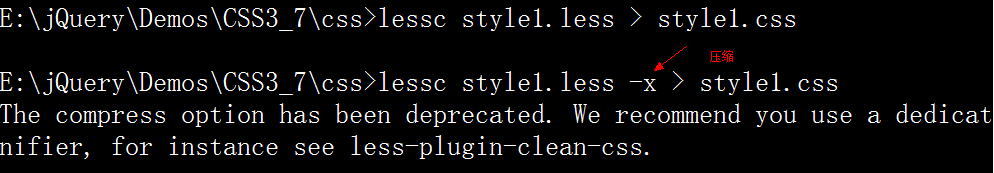
-x的压缩方法已经被弃用,建议使用清理插件。
方法二:使用工具软件
能够翻译Less的工具软件有不少,这里介绍:Koala
Koala是一个开源的预处理语言图形编译工具,目前已支持Less、Sass、Compass与CoffeeScript。
功能特性:
多语言支持: 支持Less、Sass、Compass与CoffeeScript。
实时监听与编译: 在后台监听文件的变动,检测到文件被修改后将自动进行编译。
编译选项支持: 可以设置与自定义你需要的编译选项。
压缩支持: Less、Sass可直接编译生成压缩后的css代码。
错误提示: 编译中如果遇到错误,Koala将在右下角提示并显示出具体的出错地方,方便开发者快速定位。
跨平台: Windows、Mac、Linux完美支持。
安装Koala
在Koala官网根据你的系统平台下载对应的版本。Linux系统要求已安装好ruby运行环境。
下载地址: http://koala-app.com/
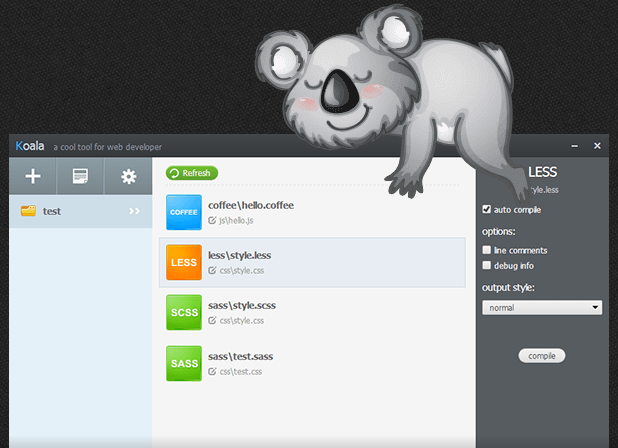
注意:路径中不要使用中文,切记!
方法三:使用IDE插件
如果使用Eclipse,Hbuilder,Visual Studio等开发工具可以安装插件完成自动翻译功能,这里使用HBuilder,在工具->插件下可以选择安装,如下图所示:
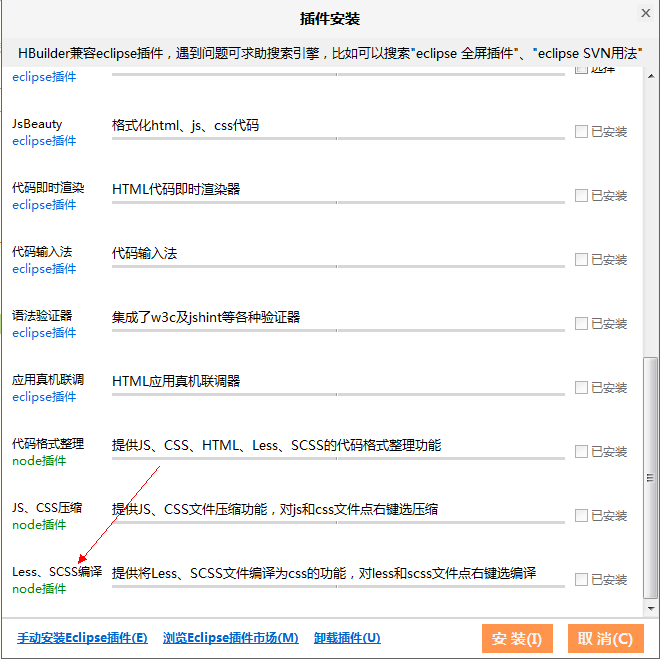
使用方法:
新建Less文件,保存后会自己生成对应的CSS文件。
1.4、混入(Mixins)
类似函数或宏
定义函数,@radius是参数,3px是默认值
.borderRadius(@radius:3px){
-moz-border-radius: @radius;
-webkit-border-radius: @radius;
border-radius: @radius;
}
使用函数,带参数
#header { .borderRadius(10px); }
不带参数使用默认参数
.btn { .borderRadius}
注意:
a)、可以不使用参数 .wrap(){…} .pre{ .wrap },也可以使用多个参数
b)、内置变量@arguments代表所有参数(运行时)的值 .boxShadow(@x:0,@y:0,@blur:1px,@color:#000){ box-shadow: @arguments; }
注意,在参数没有默认值的前提下使用@arguments调用时必须赋值,否则会导致整个页面内的less语法出错而失效。
c)、Mixins必须使用ID或者类,即#xx或.xx,否则无效。
Less示例代码:
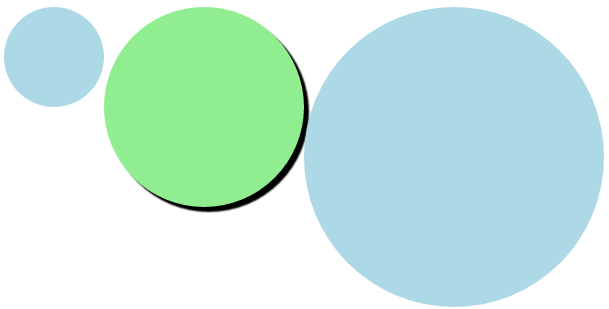
/*混入(Mixins)*/ /*定义*/ .circle(@100px, @color:lightblue) { width: @width; height: @width; background: @color; border-radius: @width/2; float: left; } .boxShadow(@x:0, @y:0, @blur:1px, @color:#000) { box-shadow: @arguments; } /*调用*/ .cls21 { .circle(); /*默认值*/ } .cls22 { .circle(200px,lightgreen); /*带参数*/ .boxShadow(5px,5px); } .cls23 { .circle(300px); /*带一个参数*/ }
HTML页面:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Less</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/style2.css" /> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="cls21"> </div> <div id="div1" class="cls22"> </div> <div id="div1" class="cls23"> </div> </body> </html>
翻译结果:
/*调用*/ .cls21 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: lightblue; border-radius: 50px; float: left;/*默认值*/ } .cls22 { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: lightgreen; border-radius: 100px; float: left; /*带参数*/ box-shadow: 5px 5px 1px #000; } .cls23 { width: 300px; height: 300px; background: lightblue; border-radius: 150px; float: left;/*带一个参数*/ } /*# sourceMappingURL=style2.css.map */
运行效果:
1.5、嵌套
允许将多个CSS选择器嵌套在一起,&表示当前选择器的父选择器
#header {
&.fl{ float: left; }
.mln { margin-left: 0; }
}
生成
#header.fl{float: left;}
#header .mln {margin-left: 0;}
示例:
/*嵌套*/ #parent { color: red; .sub11 { background: green; } &.sub12 { width: 100px; } .sub13 { height: 200px; .sub131 { font-size: 10px; } } }
结果:
/*嵌套*/ #parent { color: red; } #parent .sub11 { background: green; } #parent.sub12 { width: 100px; } #parent .sub13 { height: 200px; } #parent .sub13 .sub131 { font-size: 10px; }
1.6、运算
运算主要是针对任何数字、颜色、变量的操作,支持加、减、乘、除、()或者更复杂的综合运算;
@init: #111111;
@transition: @init*2;
.switchColor { color: @transition; }
算术运算示例:
/*运算*/ @base: 5%; @filler: @base * 2; @other: @base + @filler; @base-color:lightblue; .cls41{ color: #888 / 4; background-color: @base-color + #111; height: 100% / 2 + @filler; }
运行结果:
.cls41 { color: #222222; background-color: #bee9f7; height: 60%; }
1.7、函数
Less 提供了许多用于转换颜色,处理字符串和进行算术运算的函数
.lightColor{lighten(@color, 10%); }
更多函数: http://www.lesscss.net/functions/
示例:
/*函数*/ .cls51 { /*将一个资源内嵌到样式文件,如果开启了ieCompat选项,而且资源文件的体积过大,或者是在浏览器中使用,则会使用url()进行回退。如果没有指定MIME,则Node.js会使用MIME包来决定正确的MIME。*/ background: data-uri('../img/yes.gif') no-repeat; height: 20px; } .cls52 { /*增加一定数值的颜色亮度。*/ background: lighten(blue,20%); }
翻译结果:
/*函数*/ .cls51 { /*将一个资源内嵌到样式文件,如果开启了ieCompat选项,而且资源文件的体积过大,或者是在浏览器中使用,则会使用url()进行回退。如果没有指定MIME,则Node.js会使用MIME包来决定正确的MIME。*/ background: url("data:null;base64,R0lGODlhDAAMAKIAAMznjyJ6Gu732TKGFq7ZTF+nDI7JBf///yH5BAAAAAAALAAAAAAMAAwAAAM8eCdAZgQItdy7RAlXyhidBhjdEAQD1ZDHGVDQUyivMlws1d6xR6EFyKi06xgkHA8oSJhscI8mhWGJTA4JADs=") no-repeat; height: 20px; } .cls52 { /*增加一定数值的颜色亮度。*/ background: #6666ff; }
运行效果:
1.8、继承
示例代码:
/*继承*/ .animal { background-color: black; color: white; } .bear { &:extend(.animal); background-color: brown; } .mouse{ &:extend(.animal); }
翻译结果:
/*继承*/ .animal, .bear, .mouse { background-color: black; color: white; } .bear { background-color: brown; }
1.9、作用域
同一级的变量后者覆盖前者,内部变量优先级高于外部变量,变量只在同一个文件中生效。
示例:
/*作用域*/ @len:10px; .cls61{ @len:20px; height:@len; } .cls62{ width:@len; } @len:30px; .cls63{ height: @len; }
结果:
.cls61 { height: 20px; } .cls62 { width: 30px; } .cls63 { height: 30px; }
1.10、注释
示例:
/*注释*/ .cls71{ width: 100px; //单行注释,CSS中不允许单行注释,Less允许 height:100px; /* 多行注释,CSS与Less都允许 */ }
结果:
/*注释*/ .cls71 { width: 100px; height: 100px;/* 多行注释,CSS与Less都允许 */ }
二、Sass
Sass与Less类似类似也是一种CSS的预编译语言,他出现的更晚,但功能更加强大,Sass 有两种语法。 第一种被称为 SCSS (Sassy CSS),是一个 CSS3 语法的扩充版本;第二种比较老的语法成为缩排语法(或者就称为 "Sass"), 提供了一种更简洁的 CSS 书写方式特点如下:
特点:
1)、不能直接在页面中解析,需要使用ruby预先翻译成css文件,而Less可以在线动态翻译。
2)、Sass功能更加强大,拥有流控语句等Less不具备的功能
3)、完全兼容 CSS3,在 CSS 语言基础上添加了扩展功能,比如变量、嵌套 (nesting)、混合 (mixin)
在使用时Sass的后缀名为scss,本文全部使用scss的语法,可以安装Koala直接解析,不需要去搭建ruby环境,Koala已封装好。
下载地址: http://koala-app.com/
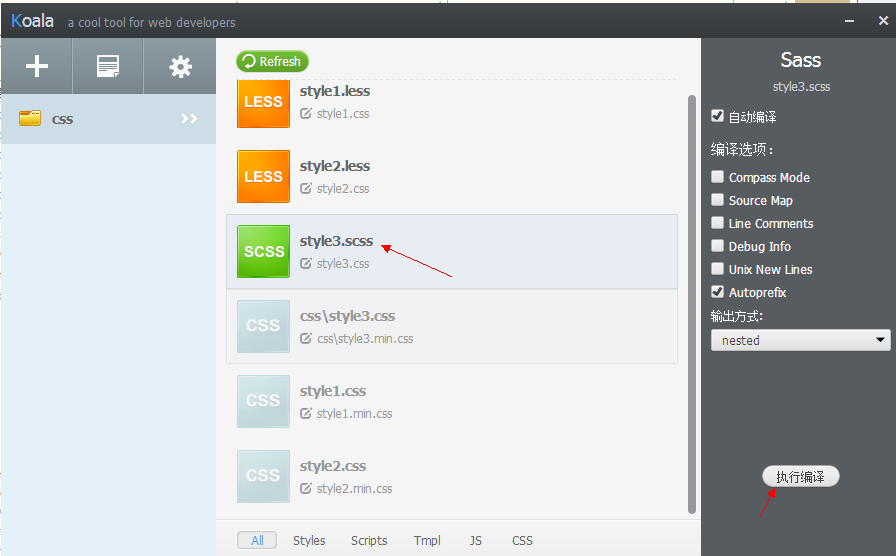
2.1、变量
sass中可以定义变量,方便统一修改和维护
Sass代码:
/*变量*/ $1004px; $color:blue; .cls11 { width: $width; height: $width/2; background: $color; } $100px; $color:red; .cls12 { $color:green; width: $width; height: $width/2; background: $color; }
CSS代码:
.cls11 { width: 1004px; height: 502px; background: blue; } .cls12 { width: 100px; height: 50px; background: green; }
2.2、嵌套
sass可以进行选择器的嵌套,表示层级关系,看起来很优雅整齐。
Sass代码:
.cls21 { width: 100px; .cls22{ height: 200px; } .cls23 { color:blue; } }
CSS代码:
.cls21 { width: 100px; } .cls21 .cls22 { height: 200px; } .cls21 .cls23 { color: blue; }
2.3、导入
sass中如导入其他sass文件,最后编译为一个css文件,优于纯css的@import
reset.scss
$zero:0; $PI:3.14; * { margin: $zero; padding: $zero; } body,html{ height: 100%; }
Sass代码:
@import "reset"; .cls31 { /*height: zero; */ /*error*/ }
CSS代码:
* { margin: 0; padding: 0; } body, html { height: 100%; } .cls31 { /*height: zero; */ /*error*/ }
2.4、mixin 混入
sass中可用mixin定义一些代码片段,且可传参数,方便日后根据需求调用。从此处理css3的前缀兼容轻松便捷。定义时使用关键字@mixin,调用时使用@include
SCSS样式:
@mixin circle($size:100px,$color:lightblue){ width: $size; height: $size; border-radius: $size/2; background: $color; } .cls41{ @include circle(); } .cls42{ @include circle(150px); } .cls43{ @include circle(200px,lightgreen); }
CSS样式:
.cls41 { width: 100px; height: 100px; border-radius: 50px; background: lightblue; } .cls42 { width: 150px; height: 150px; border-radius: 75px; background: lightblue; } .cls43 { width: 200px; height: 200px; border-radius: 100px; background: lightgreen; }
2.5、扩展/继承
sass可通过@extend来实现代码组合声明,使代码更加优越简洁。
SCSS样式:
.state { background: blue; border: 1px solid lightblue; } .success{ @extend .state; background: green; } .error { @extend .state; border: 2px solid red; }
CSS样式:
.state, .success, .error { background: blue; border: 1px solid lightblue; } .success { background: green; } .error { border: 2px solid red; }
2.6、运算
SCSS样式:
.cls61 { width: (100px+10px)/2-20px%7px+1px*8; }
CSS样式:
.cls61 { width: 57px; }
2.7、函数
sass中集成了大量的颜色函数,让变换颜色更加简单。
SCSS样式:
$pcolor: #999ccc; .cls71 a { color: $pcolor; &:hover { background: darken($pcolor,15%); /*变暗15%*/ color: lighten($pcolor,5%); /*变亮5%*/ }
CSS样式:
.cls71 a { color: #999ccc; } .cls71 a:hover { background: #666bb3; color: #aaacd5; }
2.8、流程控制
sass中和其它程序语言一样也拥有流程控制语句,如if,for,each,while,指令,函数等。
SCSS样式:
$blur: lightblue; @for $i from 1 through 10 { .font-#{$i} { /*计算字体大小*/ font-size: 12px+$i*2px; /*颜色变暗*/ color: darken($blur,$i*2); /*如果i是3的倍数,则下划线*/ @if $i%3==0 { text-decoration: underline; } } }
CSS样式:
/*8*/ .font-1 { font-size: 14px; color: #a5d4e4; } .font-2 { font-size: 16px; color: #9dd1e1; } .font-3 { font-size: 18px; color: #96cddf; text-decoration: underline; } .font-4 { font-size: 20px; color: #8ec9dc; } .font-5 { font-size: 22px; color: #86c5da; } .font-6 { font-size: 24px; color: #7ec2d8; text-decoration: underline; } .font-7 { font-size: 26px; color: #76bed5; } .font-8 { font-size: 28px; color: #6ebad3; } .font-9 { font-size: 30px; color: #67b7d1; text-decoration: underline; } .font-10 { font-size: 32px; color: #5fb3ce; }
HTML页面:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/style3.css" /> </head> <body style="padding: 10px;"> <div class="font-1">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-2">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-3">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-4">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-5">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-6">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-7">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-8">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-9">Hello SASS!</div> <div class="font-10">Hello SASS!</div> </body> </html>
运行效果:

更多内容请参考:http://www.sass-zh.com/
三、CoffeeScript
javascript变得日益重要,但有很多明显的缺点,借助一种中间语言转译出优雅的javascript是解决这些问题的方法。如CoffeeScript,TypeScript。
Coffee Script是JavaScript的转译语言。了解JavaScript的发展历程:https://news.cnblogs.com/n/558565/。
Coffee的特点:
CoffeeScript语法类似 Ruby ,可以被编译成 JavaScript
CoffeeScript取JavaScript之精华,而抛弃了诸如全局变量声明、with等容易出错的部分
CoffeeScript是JavaScript与程序员之间的桥梁,程序员看到的是优雅的CoffeeScript接口,使得编程更简洁,写法更随意
更少,更紧凑,和更清晰的代码
通过规避和改变对JavaScript中不良部分的使用,只留下精华,让代码减少出错率,更容易维护
在很多常用模式的实现上采用了JavaScript中的最佳实践
CoffeeScript生成的JavaScript代码都可以完全通过JSLint的检测

中文网: http://coffee-script.org/
源码:https://github.com/coffee-js/coffee-script
3.1、安装
CoffeeScript 编译器本身是 CoffeeScript 写的, 使用了 Jison parser generator. 命令行版本的coffee是一个实用的 Node.js 工具。
安装前你需要最新稳定版 Node.js, 和 npm (Node Package Manager)。借助 npm 可以安装 CoffeeScript:
npm install -g coffee-script
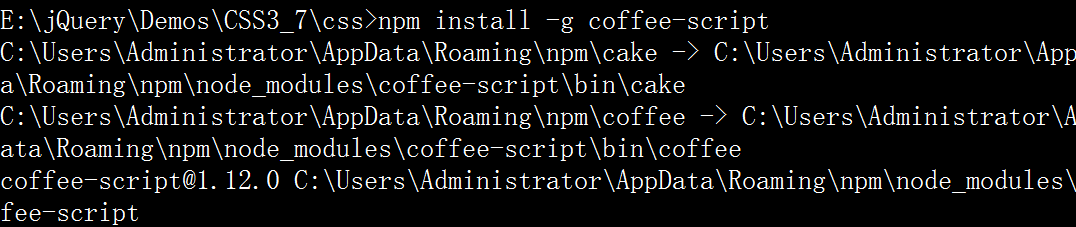
安装之后, 你应该可以运行 coffee 命令以执行脚本, 编译 .coffee 文件到 .js 文件, 和提供一个交互式的 REPL. coffee 命令有下列参数:
-c, --compile 编译一个 .coffee 脚本到一个同名的 .js 文件.
-m, --map 随 JavaScript 文件一起生成 source maps. 并且在 JavaScript 里加上 sourceMappingURL 指令.
-i, --interactive 启动一个交互式的 CoffeeScript 会话用来尝试一些代码片段. 等同于执行 coffee 而不加参数.
-o, --output [DIR] 将所有编译后的 JavaScript 文件写到指定文件夹. 与 --compile 或 --watch 搭配使用.
-j, --join [FILE] 编译之前, 按参数传入顺序连接所有脚本到一起, 编译后写到指定的文件. 对于编译大型项目有用.
-w, --watch 监视文件改变, 任何文件更新时重新执行命令.
-p, --print JavaScript 直接打印到 stdout 而不是写到一个文件.
-s, --stdio 将 CoffeeScript 传递到 STDIN 后从 STDOUT 获取 JavaScript. 对其他语言写的进程有好处. 比如:
cat src/cake.coffee | coffee -sc
-l, --literate 将代码作为 Literate CoffeeScript 解析. 只会在从 stdio 直接传入代码或者处理某些没有后缀的文件名需要写明这点.
-e, --eval 直接从命令行编译和打印一小段 CoffeeScript. 比如:
coffee -e "console.log num for num in [10..1]"
-b, --bare 编译到 JavaScript 时去掉顶层函数的包裹.
-t, --tokens 不对 CoffeeScript 进行解析, 仅仅进行 lex, 打印出 token stream: [IDENTIFIER square] [ASSIGN =] [PARAM_START (] ...
-n, --nodes 不对 CoffeeScript 进行编译, 仅仅 lex 和解析, 打印 parse tree:
--nodejs node 命令有一些实用的参数, 比如
--debug, --debug-brk, --max-stack-size, 和 --expose-gc. 用这个参数直接把参数转发到 Node.js. 重复使用 --nodejs 来传递多个参数.
3.2、使用
1、编辑coffee脚本,后缀为coffee,代码如下:
# 赋值: number = 42 opposite = true # 条件: number = -42 if opposite # 函数: square = (x) -> x * x # 数组: list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # 对象: math = root: Math.sqrt square: square cube: (x) -> x * square x # Splats: race = (winner, runners...) -> print winner, runners # 存在性: alert "I knew it!" if elvis? # 数组 推导(comprehensions): cubes = (math.cube num for num in list)
将coffeescript翻译成javascript的方法如下:
a)、使用IDE插件直接翻译
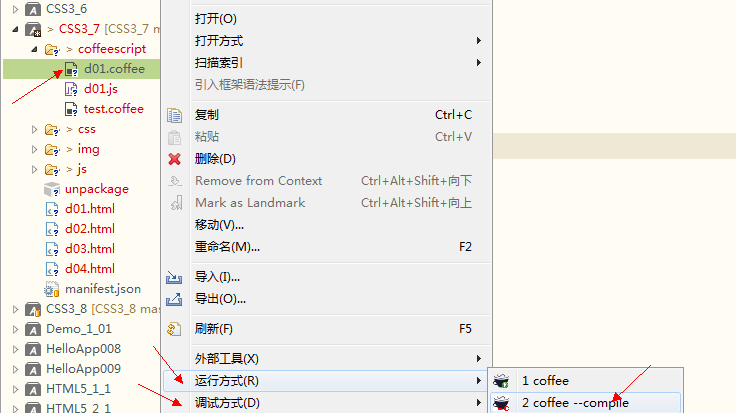
翻译成javascript后的脚本如下:
(function() { var cubes, list, math, num, number, opposite, race, square, slice = [].slice; number = 42; opposite = true; if (opposite) { number = -42; } square = function(x) { return x * x; }; list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; math = { root: Math.sqrt, square: square, cube: function(x) { return x * square(x); } }; race = function() { var runners, winner; winner = arguments[0], runners = 2 <= arguments.length ? slice.call(arguments, 1) : []; return print(winner, runners); }; if (typeof elvis !== "undefined" && elvis !== null) { alert("I knew it!"); } cubes = (function() { var i, len, results; results = []; for (i = 0, len = list.length; i < len; i++) { num = list[i]; results.push(math.cube(num)); } return results; })(); }).call(this);
b)、命令行翻译
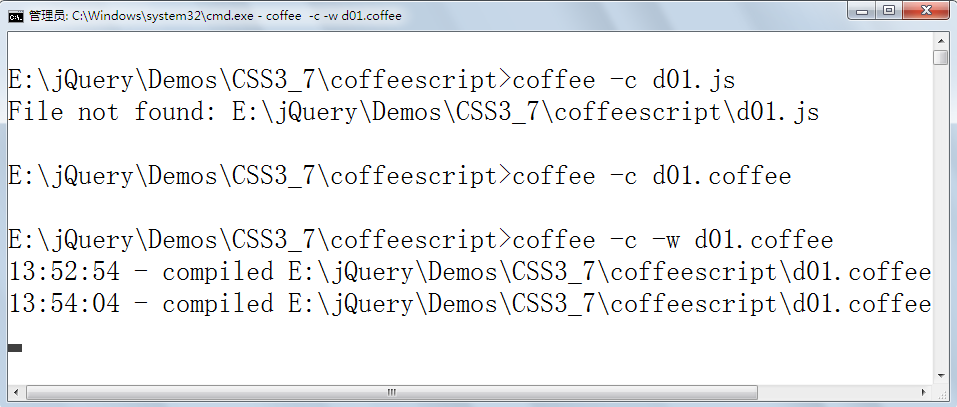
翻译后的结果与上文相同,-c是参数表示编译的意思,-w是监听文件的变化,文件发生变化后将立即编译。
面向对象示例:
class Animal constructor: (@name) -> move: (meters) -> alert @name + " moved #{meters}m." class Snake extends Animal move: -> alert "Slithering..." super 5 class Horse extends Animal move: -> alert "Galloping..." super 45 sam = new Snake "Sammy the Python" tom = new Horse "Tommy the Palomino" sam.move() tom.move()
翻译后的javascript:
(function() { var Animal, Horse, Snake, sam, tom, extend = function(child, parent) { for(var key in parent) { if(hasProp.call(parent, key)) child[key] = parent[key]; } function ctor() { this.constructor = child; } ctor.prototype = parent.prototype; child.prototype = new ctor(); child.__super__ = parent.prototype; return child; }, hasProp = {}.hasOwnProperty; Animal = (function() { function Animal(name) { this.name = name; } Animal.prototype.move = function(meters) { return alert(this.name + (" moved " + meters + "m.")); }; return Animal; })(); Snake = (function(superClass) { extend(Snake, superClass); function Snake() { return Snake.__super__.constructor.apply(this, arguments); } Snake.prototype.move = function() { alert("Slithering..."); return Snake.__super__.move.call(this, 5); }; return Snake; })(Animal); Horse = (function(superClass) { extend(Horse, superClass); function Horse() { return Horse.__super__.constructor.apply(this, arguments); } Horse.prototype.move = function() { alert("Galloping..."); return Horse.__super__.move.call(this, 45); }; return Horse; })(Animal); sam = new Snake("Sammy the Python"); tom = new Horse("Tommy the Palomino"); sam.move(); tom.move(); }).call(this);
四、TypeScript
TypeScript是一种由微软开发的自由和开源的编程语言,它是JavaScript的一个超集,扩展了JavaScript的语法,而且本质上向这个语言添加了可选的静态类型和基于类的面向对象编程。安德斯·海尔斯伯格,C#的首席架构师,工作于TypeScript的开发。
官网:http://www.typescriptlang.org/
github:https://github.com/Microsoft/TypeScript
4.1、安装
a)、在node.js环境下安装typescript,npm install -g typescript
b)、使用Microsoft指定的编辑器或IDE如,VS与微软Visual Studio Code 免费跨平台代码编辑器,安装相应的插件。

4.2、使用typescript
编写typescript源代码,greeter.ts:
class Greeter { constructor(public greeting: string) { } greet() { return "<h1>" + this.greeting + "</h1>"; } }; var greeter = new Greeter("Hello, world!"); document.body.innerHTML = greeter.greet();
使用tsc greeter.ts编译生成javascript greeter.js脚本:
var Greeter = (function () { function Greeter(greeting) { this.greeting = greeting; } Greeter.prototype.greet = function () { return "<h1>" + this.greeting + "</h1>"; }; return Greeter; }()); ; var greeter = new Greeter("Hello, world!"); document.body.innerHTML = greeter.greet();
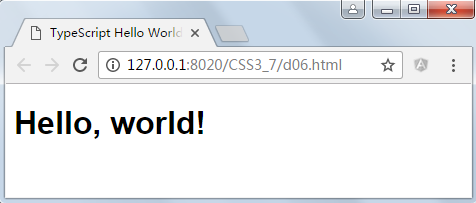
新建一个页面测试:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TypeScript Hello World!</title> </head> <body> <script src="typescript/greeter.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </body> </html>
运行结果:
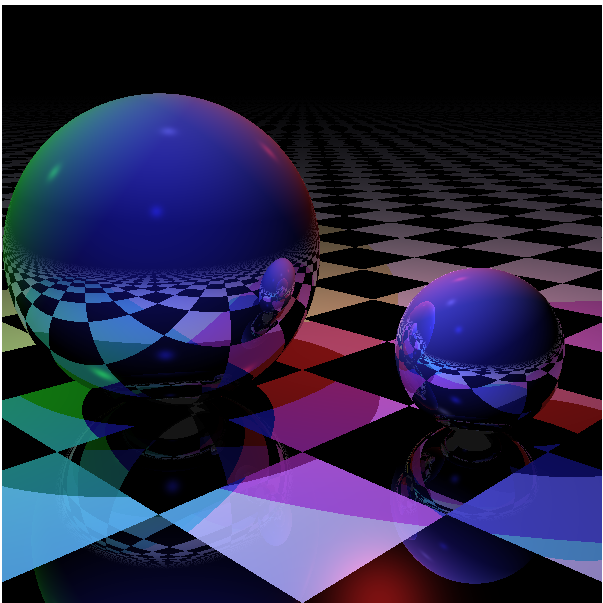
示例2,raytracer.ts代码:

class Vector { constructor(public x: number, public y: number, public z: number) { } static times(k: number, v: Vector) { return new Vector(k * v.x, k * v.y, k * v.z); } static minus(v1: Vector, v2: Vector) { return new Vector(v1.x - v2.x, v1.y - v2.y, v1.z - v2.z); } static plus(v1: Vector, v2: Vector) { return new Vector(v1.x + v2.x, v1.y + v2.y, v1.z + v2.z); } static dot(v1: Vector, v2: Vector) { return v1.x * v2.x + v1.y * v2.y + v1.z * v2.z; } static mag(v: Vector) { return Math.sqrt(v.x * v.x + v.y * v.y + v.z * v.z); } static norm(v: Vector) { var mag = Vector.mag(v); var div = (mag === 0) ? Infinity : 1.0 / mag; return Vector.times(div, v); } static cross(v1: Vector, v2: Vector) { return new Vector(v1.y * v2.z - v1.z * v2.y, v1.z * v2.x - v1.x * v2.z, v1.x * v2.y - v1.y * v2.x); } } class Color { constructor(public r: number, public g: number, public b: number) { } static scale(k: number, v: Color) { return new Color(k * v.r, k * v.g, k * v.b); } static plus(v1: Color, v2: Color) { return new Color(v1.r + v2.r, v1.g + v2.g, v1.b + v2.b); } static times(v1: Color, v2: Color) { return new Color(v1.r * v2.r, v1.g * v2.g, v1.b * v2.b); } static white = new Color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); static grey = new Color(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); static black = new Color(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); static background = Color.black; static defaultColor = Color.black; static toDrawingColor(c: Color) { var legalize = d => d > 1 ? 1 : d; return { r: Math.floor(legalize(c.r) * 255), g: Math.floor(legalize(c.g) * 255), b: Math.floor(legalize(c.b) * 255) } } } class Camera { public forward: Vector; public right: Vector; public up: Vector; constructor(public pos: Vector, lookAt: Vector) { var down = new Vector(0.0, -1.0, 0.0); this.forward = Vector.norm(Vector.minus(lookAt, this.pos)); this.right = Vector.times(1.5, Vector.norm(Vector.cross(this.forward, down))); this.up = Vector.times(1.5, Vector.norm(Vector.cross(this.forward, this.right))); } } interface Ray { start: Vector; dir: Vector; } interface Intersection { thing: Thing; ray: Ray; dist: number; } interface Surface { diffuse: (pos: Vector) => Color; specular: (pos: Vector) => Color; reflect: (pos: Vector) => number; roughness: number; } interface Thing { intersect: (ray: Ray) => Intersection; normal: (pos: Vector) => Vector; surface: Surface; } interface Light { pos: Vector; color: Color; } interface Scene { things: Thing[]; lights: Light[]; camera: Camera; } class Sphere implements Thing { public radius2: number; constructor(public center: Vector, radius: number, public surface: Surface) { this.radius2 = radius * radius; } normal(pos: Vector): Vector { return Vector.norm(Vector.minus(pos, this.center)); } intersect(ray: Ray) { var eo = Vector.minus(this.center, ray.start); var v = Vector.dot(eo, ray.dir); var dist = 0; if (v >= 0) { var disc = this.radius2 - (Vector.dot(eo, eo) - v * v); if (disc >= 0) { dist = v - Math.sqrt(disc); } } if (dist === 0) { return null; } else { return { thing: this, ray: ray, dist: dist }; } } } class Plane implements Thing { public normal: (pos: Vector) =>Vector; public intersect: (ray: Ray) =>Intersection; constructor(norm: Vector, offset: number, public surface: Surface) { this.normal = function(pos: Vector) { return norm; } this.intersect = function(ray: Ray): Intersection { var denom = Vector.dot(norm, ray.dir); if (denom > 0) { return null; } else { var dist = (Vector.dot(norm, ray.start) + offset) / (-denom); return { thing: this, ray: ray, dist: dist }; } } } } module Surfaces { export var shiny: Surface = { diffuse: function(pos) { return Color.white; }, specular: function(pos) { return Color.grey; }, reflect: function(pos) { return 0.7; }, roughness: 250 } export var checkerboard: Surface = { diffuse: function(pos) { if ((Math.floor(pos.z) + Math.floor(pos.x)) % 2 !== 0) { return Color.white; } else { return Color.black; } }, specular: function(pos) { return Color.white; }, reflect: function(pos) { if ((Math.floor(pos.z) + Math.floor(pos.x)) % 2 !== 0) { return 0.1; } else { return 0.7; } }, roughness: 150 } } class RayTracer { private maxDepth = 5; private intersections(ray: Ray, scene: Scene) { var closest = +Infinity; var closestInter: Intersection = undefined; for (var i in scene.things) { var inter = scene.things[i].intersect(ray); if (inter != null && inter.dist < closest) { closestInter = inter; closest = inter.dist; } } return closestInter; } private testRay(ray: Ray, scene: Scene) { var isect = this.intersections(ray, scene); if (isect != null) { return isect.dist; } else { return undefined; } } private traceRay(ray: Ray, scene: Scene, depth: number): Color { var isect = this.intersections(ray, scene); if (isect === undefined) { return Color.background; } else { return this.shade(isect, scene, depth); } } private shade(isect: Intersection, scene: Scene, depth: number) { var d = isect.ray.dir; var pos = Vector.plus(Vector.times(isect.dist, d), isect.ray.start); var normal = isect.thing.normal(pos); var reflectDir = Vector.minus(d, Vector.times(2, Vector.times(Vector.dot(normal, d), normal))); var naturalColor = Color.plus(Color.background, this.getNaturalColor(isect.thing, pos, normal, reflectDir, scene)); var reflectedColor = (depth >= this.maxDepth) ? Color.grey : this.getReflectionColor(isect.thing, pos, normal, reflectDir, scene, depth); return Color.plus(naturalColor, reflectedColor); } private getReflectionColor(thing: Thing, pos: Vector, normal: Vector, rd: Vector, scene: Scene, depth: number) { return Color.scale(thing.surface.reflect(pos), this.traceRay({ start: pos, dir: rd }, scene, depth + 1)); } private getNaturalColor(thing: Thing, pos: Vector, norm: Vector, rd: Vector, scene: Scene) { var addLight = (col, light) => { var ldis = Vector.minus(light.pos, pos); var livec = Vector.norm(ldis); var neatIsect = this.testRay({ start: pos, dir: livec }, scene); var isInShadow = (neatIsect === undefined) ? false : (neatIsect <= Vector.mag(ldis)); if (isInShadow) { return col; } else { var illum = Vector.dot(livec, norm); var lcolor = (illum > 0) ? Color.scale(illum, light.color) : Color.defaultColor; var specular = Vector.dot(livec, Vector.norm(rd)); var scolor = (specular > 0) ? Color.scale(Math.pow(specular, thing.surface.roughness), light.color) : Color.defaultColor; return Color.plus(col, Color.plus(Color.times(thing.surface.diffuse(pos), lcolor), Color.times(thing.surface.specular(pos), scolor))); } } return scene.lights.reduce(addLight, Color.defaultColor); } render(scene, ctx, screenWidth, screenHeight) { var getPoint = (x, y, camera) => { var recenterX = x =>(x - (screenWidth / 2.0)) / 2.0 / screenWidth; var recenterY = y => - (y - (screenHeight / 2.0)) / 2.0 / screenHeight; return Vector.norm(Vector.plus(camera.forward, Vector.plus(Vector.times(recenterX(x), camera.right), Vector.times(recenterY(y), camera.up)))); } for (var y = 0; y < screenHeight; y++) { for (var x = 0; x < screenWidth; x++) { var color = this.traceRay({ start: scene.camera.pos, dir: getPoint(x, y, scene.camera) }, scene, 0); var c = Color.toDrawingColor(color); ctx.fillStyle = "rgb(" + String(c.r) + ", " + String(c.g) + ", " + String(c.b) + ")"; ctx.fillRect(x, y, x + 1, y + 1); } } } } function defaultScene(): Scene { return { things: [new Plane(new Vector(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), 0.0, Surfaces.checkerboard), new Sphere(new Vector(0.0, 1.0, -0.25), 1.0, Surfaces.shiny), new Sphere(new Vector(-1.0, 0.5, 1.5), 0.5, Surfaces.shiny)], lights: [{ pos: new Vector(-2.0, 2.5, 0.0), color: new Color(0.49, 0.07, 0.07) }, { pos: new Vector(1.5, 2.5, 1.5), color: new Color(0.07, 0.07, 0.49) }, { pos: new Vector(1.5, 2.5, -1.5), color: new Color(0.07, 0.49, 0.071) }, { pos: new Vector(0.0, 3.5, 0.0), color: new Color(0.21, 0.21, 0.35) }], camera: new Camera(new Vector(3.0, 2.0, 4.0), new Vector(-1.0, 0.5, 0.0)) }; } function exec() { var canv = document.createElement("canvas"); canv.width = 256; canv.height = 256; document.body.appendChild(canv); var ctx = canv.getContext("2d"); var rayTracer = new RayTracer(); return rayTracer.render(defaultScene(), ctx, canv.width, canv.height); } exec();
编译生成后的raytracer.js代码:

var Vector = (function() { function Vector(x, y, z) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; } Vector.times = function(k, v) { return new Vector(k * v.x, k * v.y, k * v.z); }; Vector.minus = function(v1, v2) { return new Vector(v1.x - v2.x, v1.y - v2.y, v1.z - v2.z); }; Vector.plus = function(v1, v2) { return new Vector(v1.x + v2.x, v1.y + v2.y, v1.z + v2.z); }; Vector.dot = function(v1, v2) { return v1.x * v2.x + v1.y * v2.y + v1.z * v2.z; }; Vector.mag = function(v) { return Math.sqrt(v.x * v.x + v.y * v.y + v.z * v.z); }; Vector.norm = function(v) { var mag = Vector.mag(v); var div = (mag === 0) ? Infinity : 1.0 / mag; return Vector.times(div, v); }; Vector.cross = function(v1, v2) { return new Vector(v1.y * v2.z - v1.z * v2.y, v1.z * v2.x - v1.x * v2.z, v1.x * v2.y - v1.y * v2.x); }; return Vector; }()); var Color = (function() { function Color(r, g, b) { this.r = r; this.g = g; this.b = b; } Color.scale = function(k, v) { return new Color(k * v.r, k * v.g, k * v.b); }; Color.plus = function(v1, v2) { return new Color(v1.r + v2.r, v1.g + v2.g, v1.b + v2.b); }; Color.times = function(v1, v2) { return new Color(v1.r * v2.r, v1.g * v2.g, v1.b * v2.b); }; Color.toDrawingColor = function(c) { var legalize = function(d) { return d > 1 ? 1 : d; }; return { r: Math.floor(legalize(c.r) * 255), g: Math.floor(legalize(c.g) * 255), b: Math.floor(legalize(c.b) * 255) }; }; return Color; }()); Color.white = new Color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); Color.grey = new Color(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); Color.black = new Color(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); Color.background = Color.black; Color.defaultColor = Color.black; var Camera = (function() { function Camera(pos, lookAt) { this.pos = pos; var down = new Vector(0.0, -1.0, 0.0); this.forward = Vector.norm(Vector.minus(lookAt, this.pos)); this.right = Vector.times(1.5, Vector.norm(Vector.cross(this.forward, down))); this.up = Vector.times(1.5, Vector.norm(Vector.cross(this.forward, this.right))); } return Camera; }()); var Sphere = (function() { function Sphere(center, radius, surface) { this.center = center; this.surface = surface; this.radius2 = radius * radius; } Sphere.prototype.normal = function(pos) { return Vector.norm(Vector.minus(pos, this.center)); }; Sphere.prototype.intersect = function(ray) { var eo = Vector.minus(this.center, ray.start); var v = Vector.dot(eo, ray.dir); var dist = 0; if(v >= 0) { var disc = this.radius2 - (Vector.dot(eo, eo) - v * v); if(disc >= 0) { dist = v - Math.sqrt(disc); } } if(dist === 0) { return null; } else { return { thing: this, ray: ray, dist: dist }; } }; return Sphere; }()); var Plane = (function() { function Plane(norm, offset, surface) { this.surface = surface; this.normal = function(pos) { return norm; }; this.intersect = function(ray) { var denom = Vector.dot(norm, ray.dir); if(denom > 0) { return null; } else { var dist = (Vector.dot(norm, ray.start) + offset) / (-denom); return { thing: this, ray: ray, dist: dist }; } }; } return Plane; }()); var Surfaces; (function(Surfaces) { Surfaces.shiny = { diffuse: function(pos) { return Color.white; }, specular: function(pos) { return Color.grey; }, reflect: function(pos) { return 0.7; }, roughness: 250 }; Surfaces.checkerboard = { diffuse: function(pos) { if((Math.floor(pos.z) + Math.floor(pos.x)) % 2 !== 0) { return Color.white; } else { return Color.black; } }, specular: function(pos) { return Color.white; }, reflect: function(pos) { if((Math.floor(pos.z) + Math.floor(pos.x)) % 2 !== 0) { return 0.1; } else { return 0.7; } }, roughness: 150 }; })(Surfaces || (Surfaces = {})); var RayTracer = (function() { function RayTracer() { this.maxDepth = 5; } RayTracer.prototype.intersections = function(ray, scene) { var closest = +Infinity; var closestInter = undefined; for(var i in scene.things) { var inter = scene.things[i].intersect(ray); if(inter != null && inter.dist < closest) { closestInter = inter; closest = inter.dist; } } return closestInter; }; RayTracer.prototype.testRay = function(ray, scene) { var isect = this.intersections(ray, scene); if(isect != null) { return isect.dist; } else { return undefined; } }; RayTracer.prototype.traceRay = function(ray, scene, depth) { var isect = this.intersections(ray, scene); if(isect === undefined) { return Color.background; } else { return this.shade(isect, scene, depth); } }; RayTracer.prototype.shade = function(isect, scene, depth) { var d = isect.ray.dir; var pos = Vector.plus(Vector.times(isect.dist, d), isect.ray.start); var normal = isect.thing.normal(pos); var reflectDir = Vector.minus(d, Vector.times(2, Vector.times(Vector.dot(normal, d), normal))); var naturalColor = Color.plus(Color.background, this.getNaturalColor(isect.thing, pos, normal, reflectDir, scene)); var reflectedColor = (depth >= this.maxDepth) ? Color.grey : this.getReflectionColor(isect.thing, pos, normal, reflectDir, scene, depth); return Color.plus(naturalColor, reflectedColor); }; RayTracer.prototype.getReflectionColor = function(thing, pos, normal, rd, scene, depth) { return Color.scale(thing.surface.reflect(pos), this.traceRay({ start: pos, dir: rd }, scene, depth + 1)); }; RayTracer.prototype.getNaturalColor = function(thing, pos, norm, rd, scene) { var _this = this; var addLight = function(col, light) { var ldis = Vector.minus(light.pos, pos); var livec = Vector.norm(ldis); var neatIsect = _this.testRay({ start: pos, dir: livec }, scene); var isInShadow = (neatIsect === undefined) ? false : (neatIsect <= Vector.mag(ldis)); if(isInShadow) { return col; } else { var illum = Vector.dot(livec, norm); var lcolor = (illum > 0) ? Color.scale(illum, light.color) : Color.defaultColor; var specular = Vector.dot(livec, Vector.norm(rd)); var scolor = (specular > 0) ? Color.scale(Math.pow(specular, thing.surface.roughness), light.color) : Color.defaultColor; return Color.plus(col, Color.plus(Color.times(thing.surface.diffuse(pos), lcolor), Color.times(thing.surface.specular(pos), scolor))); } }; return scene.lights.reduce(addLight, Color.defaultColor); }; RayTracer.prototype.render = function(scene, ctx, screenWidth, screenHeight) { var getPoint = function(x, y, camera) { var recenterX = function(x) { return(x - (screenWidth / 2.0)) / 2.0 / screenWidth; }; var recenterY = function(y) { return -(y - (screenHeight / 2.0)) / 2.0 / screenHeight; }; return Vector.norm(Vector.plus(camera.forward, Vector.plus(Vector.times(recenterX(x), camera.right), Vector.times(recenterY(y), camera.up)))); }; for(var y = 0; y < screenHeight; y++) { for(var x = 0; x < screenWidth; x++) { var color = this.traceRay({ start: scene.camera.pos, dir: getPoint(x, y, scene.camera) }, scene, 0); var c = Color.toDrawingColor(color); ctx.fillStyle = "rgb(" + String(c.r) + ", " + String(c.g) + ", " + String(c.b) + ")"; ctx.fillRect(x, y, x + 1, y + 1); } } }; return RayTracer; }()); function defaultScene() { return { things: [new Plane(new Vector(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), 0.0, Surfaces.checkerboard), new Sphere(new Vector(0.0, 1.0, -0.25), 1.0, Surfaces.shiny), new Sphere(new Vector(-1.0, 0.5, 1.5), 0.5, Surfaces.shiny) ], lights: [{ pos: new Vector(-2.0, 2.5, 0.0), color: new Color(0.49, 0.07, 0.07) }, { pos: new Vector(1.5, 2.5, 1.5), color: new Color(0.07, 0.07, 0.49) }, { pos: new Vector(1.5, 2.5, -1.5), color: new Color(0.07, 0.49, 0.071) }, { pos: new Vector(0.0, 3.5, 0.0), color: new Color(0.21, 0.21, 0.35) }], camera: new Camera(new Vector(3.0, 2.0, 4.0), new Vector(-1.0, 0.5, 0.0)) }; } function exec() { var canv = document.createElement("canvas"); canv.width = 600; canv.height = 600; document.body.appendChild(canv); var ctx = canv.getContext("2d"); var rayTracer = new RayTracer(); return rayTracer.render(defaultScene(), ctx, canv.width, canv.height); } exec();
运行效果:
五、总结
coffeescript已经过去了,除非你对它非常熟悉,否则建选择typescript。
因为ECMAScript6的出现,javascript比以前要完善一些,但浏览器的支持度还是不够,但是有一天当JavaScript变得足够完善时这些中间语言就没有太多市场了。
上面提到的4种预处理工具都可以加快开发速度,某些程度上可以提高代码质量。
至于学习的方法我认为官网有详细的帮助。
总的来说要选择:Coffeescript、TypeScript或ES6都有争议。
六、示例下载
https://github.com/zhangguo5/CSS3_7.git
参照:http://www.cnblogs.com/best

