关于Sql语句的学习,选择的DBMS为SQL Server,Sql语句随着工作中的应用不断补充,不具备系统性,为个人笔记汇总,网上有很多优秀的资源,故不对每一处应用做过多细致的说明,后期会对部分篇幅较长的部分提出单独处理,暂时用到的数据表如下:
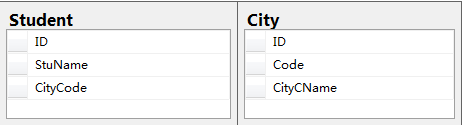
- Student表中的CityCCode对应于City表中的Code字段,为城市的英文字母缩写;
1,INSERT TO 插入语句
INSERT TO语句用于向表格中插入新的记录,如下:
1 insert into City(Code,CityCName) values('BJ','北京'); 2 insert into Student(CityCode,StuName) values('北京','SharpL');
2,DECLARE 声明表变量(后期与with as 一同提出)
Sql语句的查询中,总会涉及到多个表格的查询,会用到子查询,但是如果嵌套的层数过多,会使Sql语句难以阅读和维护,子查询Sql语句如下:
1 select Student.StuName from Student where CityCode in 2 (select Code from City where CityCName like '宁%')
上面的sql语句,在学生表中查询,所有来自'宁%'(如宁波、宁夏等)的学生姓名,同样的功能用declare语句声明如下:
1 DECLARE @t table(Code varchar(10)) 2 insert into @t(Code) (select Code from City where CityCName like '宁%') 3 select StuName from Student where CityCode in (select Code from @t)
其中@t为表变量,使用了临时表,只包括Code一列。DECLARE 声明表变量的方式在嵌套复杂时,优势才能凸显出来。
3,‘%’通配符&Like
上面的sql语句中用到了‘%’通配符,用来实现模糊查询,百分号通配符是最常使用的通配符,表示任意字符出现任意次数。如上例,‘宁%’可以表示宁波、宁夏、宁静等等。
为在搜索子句中使用通配符,就必须使用LIKE操作符。如:CityCName like '宁%'。Sql语句见2。
4,With as 添加子查询部分
在’2‘中使用了声明表变量的方法,但表变量实际上使用了临时表,增加了额外的I/O开销,SQL SERVER提供了CTE(即公共表表达式)来提高可读性与效率,如下:
with A as (select Code from City where CityCName like '宁%') select StuName from Student where CityCode in (select Code from A)
上述Sql语句可以实现与2中的Sql语句一致的效果,更具体的With as 的使用方法请参考:使用WITH AS提高性能简化嵌套SQL。
5,Except 求结果集的差
即从左查询中返回右查询中没有找到的所有非重复值。
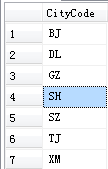
1 select CityCode from Student except 2 (select CityCode from Student where CityCode like 'N%')
注意是返回非重复值,也就是说如果Student表中存在多条来自上海的记录,返回的CityCode只会包含一条SH,结果见下图左一:

6,Case when then(后期提出)
Sql语句如下,查询的结果如上图左二:
1 select Student.StuName , 2 (case Student.CityCode 3 when 'SH' then '上海' 4 when 'BJ' then '北京' 5 when 'SZ' then '深圳' 6 when 'NB' then '宁波' 7 else '其他' 8 end)城市 9 from Student
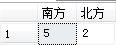
与聚合函数count组合使用,查询结果见下图,证明有5名同学来自('SZ','XM','GZ','NB','CQ')即南方。更多用法见:SQL之case when then用法
1 select 2 count(case when Student.CityCode in('SZ','XM','GZ','NB','CQ') then 1 end)南方, 3 count(case when Student.CityCode in('TJ','DL','BJ') then 1 end)北方 4 from Student
 更多实例sql语句如下:
更多实例sql语句如下:
1 select *, 2 case when ID in (select distinct ID from A) then '来自A' 3 case when ID in (select distinct ID from B) then '来自B' 4 case when ID in (select distinct ID from C) then '来自C' 5 end as 来源 6 from D