迷宫问题思路
根据昨天的博客,有如下几种解决方案
- 克鲁斯卡尔 ,为避免死循环,需要设定优化路径的次数。
- Prim,为避免死循环,需要设定优化路径的次数,暂定200次。
- BFS , 实现简单,无死循环。
- DFS , 实现简单,无死循环,复杂度较低。
- 动态规划,实时根据权重调整方向,目前看来最合适的解决方案。需要以数据证明。
综上,本次优先选择BFS,首先不存在死循环的风险,其次算法复杂度较低,容易理解且实现。适合初步练手。
一. 思路及程序算法
首先建立迷宫,将其看作点位矩阵,先把墙堆起来,剩下的就是路。
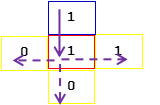
而每个点都有四个方向(上、下、左、有),每个方向上都对应一个点。在这四个点中,有一个点是当前站立点的“上一个点”,另外三个点是当前站立点的“下一个点”,如图1.1所示,红色框为当前站立点,蓝色框为“上一个点”,黄色框为三个“下一个点”。
图1.1站立点的四个方向
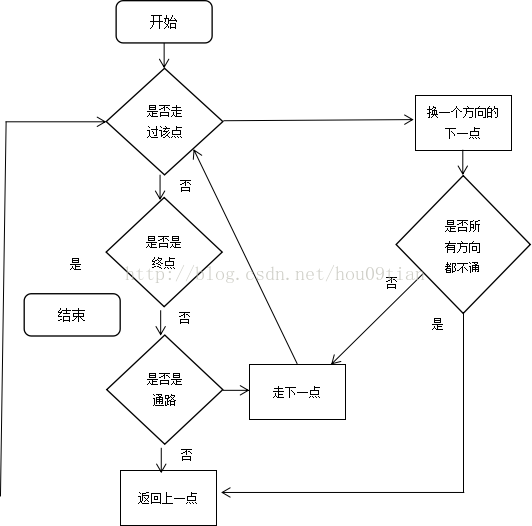
当前站立点有三种状态,分别是“终点”、“通路”和“死路”。如果当前站立点是“终点”,则停止搜索;如果当前站立点是“通路”,则向下继续走;如果当前站立点是“死路”,则要向回走,然后搜索其它路径。其流程如图1.2所示。
图1.2判断迷宫路径流程图
二. 实现
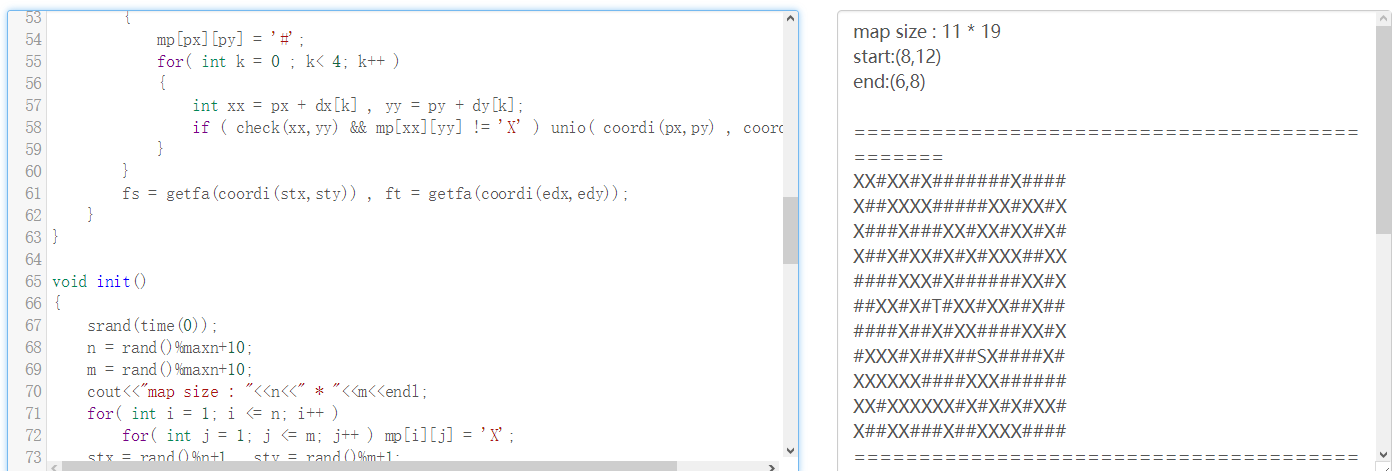
实现效果如图2.1所示:
图2.1 BFS迷宫求解实现图
BFS迷宫求解实现代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define coordi(x,y) ( m*(x-1)+y )
const int maxn = 30;
const int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1};
const int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0};
int mp[maxn+10][maxn+10];
int nxtx[maxn+10][maxn+10];
int nxty[maxn+10][maxn+10];
bool vis[maxn+10][maxn+10];
int fa[(maxn+10)*(maxn+10)];
int n , m;
int stx , sty , edx , edy;
inline int check( int x , int y )
{
return 1<=x && x<=n && 1<=y && y<=m;
}
inline void print_map()
{
puts("
==============================================");
for( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
{
for( int j = 1; j <= m; j++ )
printf("%c",mp[i][j]);
putchar('
');
}
puts("==============================================");
}
// 并查集
int getfa( int x )
{
return x==fa[x]?x:fa[x] = getfa(fa[x]);
}
void unio( int a , int b )
{
int fx = getfa(a) , fy = getfa(b);
if ( fx != fy ) fa[fx] = fy;
}
// 并查集
void connect()
{
int t = n*m/3*2;
for( int i = 1; i <= n*m; i++ ) fa[i] = i;
int fs = getfa(coordi(stx,sty)) , ft = getfa(coordi(edx,edy));
while( fs != ft || t > 0 )
{
t--;
int px = rand()%n+1 , py = rand()%m+1;
if ( mp[px][py] == 'X' )
{
mp[px][py] = '.';
for( int k = 0 ; k< 4; k++ )
{
int xx = px + dx[k] , yy = py + dy[k];
if ( check(xx,yy) && mp[xx][yy] != 'X' ) unio( coordi(px,py) , coordi(xx,yy) );
}
}
fs = getfa(coordi(stx,sty)) , ft = getfa(coordi(edx,edy));
}
}
void init()
{
srand(time(0));
n = rand()%maxn+10;
m = rand()%maxn+10;
cout<<"map size : "<<n<<" * "<<m<<endl;
for( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for( int j = 1; j <= m; j++ ) mp[i][j] = 'X';
stx = rand()%n+1 , sty = rand()%m+1;
edx = rand()%n+1 , edy = rand()%m+1;
while( abs(edx-stx) + abs(edy-sty) <= 1 ) edx = rand()%n+1 , edy = rand()%m+1;
mp[stx][sty] = 'S' , mp[edx][edy] = 'T';
cout<<"start:("<<stx<<","<<sty<<")"<<endl;
cout<<"end:("<<edx<<","<<edy<<")"<<endl;
connect();
print_map();
}
void print_path() // path = '*' st = S , ed = T , road = . , wall = X
{
int x = edx , y = edy;
while( !( x == stx && y == sty ) )
{
mp[x][y] = '*';
int tx = nxtx[x][y];
y = nxty[x][y];
x = tx;
}
mp[edx][edy] = 'T';
print_map();
}
void bfs()
{
queue< pair<int,int> > q;
q.push( make_pair(stx,sty) );
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[stx][sty] = true;
while( !q.empty() )
{
pair<int,int> temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if ( temp.first == edx && temp.second == edy )
{
print_path();
return;
}
for( int k = 0; k < 4; k++ )
{
int xx = temp.first + dx[k] , yy = temp.second + dy[k];
if ( !check(xx,yy) || vis[xx][yy] || mp[xx][yy] == 'X' ) continue;
vis[xx][yy] = 1 , nxtx[xx][yy] = temp.first , nxty[xx][yy] = temp.second;
q.push( make_pair(xx,yy) );
}
}
}
int main()
{
init();
bfs();
return 0;
}