Java基础之:OOP——继承
面向对象编程OOP(Object Oriented Programming)的三大特征之二:继承
首先看一个案例,分别创建小学生与研究生类,输出他们的信息:
小学生类:
public class Pupil { //小学生类
String name;
double score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void testing() {
System.out.println("小学生考语文...");
}
public void showScore() {
System.out.println("学生名" + name + " 成绩=" + score);
}
}
研究生类:
public class Graduate { //研究生
String name;
double score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void testing() {
System.out.println("研究生考的是微积分...");
}
public void showScore() {
System.out.println("学生名 " + name + " 成绩=" + score);
}
}
可以看到 在小学生类与研究生类中 ,有大量的内容是重复的,只有 testing() 方法不同。所以我们可以将它们两个类中共同的属性或方法抽象出来创建一个Student类,再继承Student。
继承介绍
继承可以解决代码的复用性问题,让编程更解决我们人类的思维逻辑,多个类出现相同的属性/方法时,可以将这些属性/方法抽象出来,放在一个父类中来定义,所有的子类都不需要再定义这些属性/方法,只需要继承(extends)父类即可。
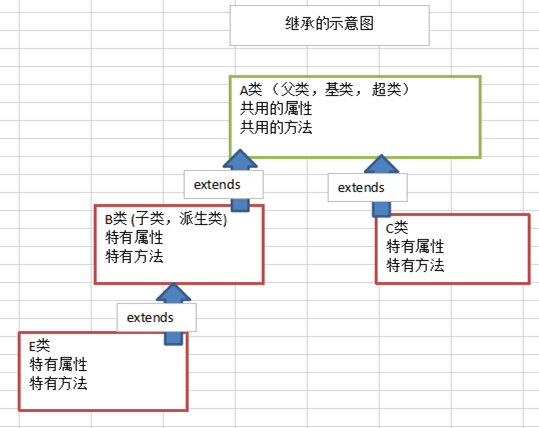
继承语法
class 子类名 extends 父类名 {}
说明:
1) 子类就会自动拥有父类定义的属性和方法
2) 父类又叫 超类,基类。
3) 子类又叫派生类。
简单案例
对上面的小学生类和研究生类进行改进。
Student类:
public class Student { //父类
String name;
double score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void showScore() {
System.out.println("学生名 " + name + " 成绩=" + score);
}
}
Pupil类:
public class Pupil extends Student { //小学生类, 子类
public void testing() {
System.out.println("小学生考语文...");
}
}
Graduate类:
public class Graduate extends Student{ //研究生 子类
public void testing() {
System.out.println("研究生考的是微积分...");
}
}
继承优点
-
代码复用性提高了。
-
代码的扩展性和维护性提高了。
继承使用细节与注意事项
-
子类继承了所有的属性和方法,只是私有的属性不能直接访问,需要通过公共方法进行访问。(封装的体现)
-
子类没有继承父类的构造器,但在子类的构造器中必须调用父类的构造器,完成父类的初始化。(例:肯定是先有爷爷再有爸爸最后有儿子)
-
当创建子类时,不管你使用子类的哪个构造方法,默认情况下总会去调用父类的无参构造函数,如果父类没有提供无参构造函数,则必须在子类的构造函数中用 super 去指定使用父类的哪个构造函数完成对父类的初始化工作,否则,编译不会通过。
-
如果希望指定调用父类的某个构造方法,需要使用super关键字显式调用。
-
无参构造器:super();
-
有一个参数:super(参数);
-
要注意super在使用时,需要放在方法体的第一句位置。
-
-
super() 和 this() 都只能放在构造方法句首,因此这两个方法不能共存在一个方法中
-
java中所有的类都是Object类的子类
-
子类最多只能有一个直接父类,也就是只能继承一个父类。(若需要A类继承B类和C类,则A继承B,B继承C)。
-
父类构造器的调用不限于直接父类!将一直往上追溯直到Object类。同样的,若子类调用父类提供的方法,也不限于直接父类。

简单案例
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ExtendsDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BB bb = new BB();
bb.m1();
}
}
class DD {
public DD() {
System.out.println("DD() 被调用");
}
}
// 子类继承了所有的属性和方法,只是私有的属性不能直接访问,需要通过公共的方法去访问
class AA extends DD {
// 属性
public int n1 = 10;
protected int n2 = 20;
int n3 = 30;
private int n4 = 40;
public int getN4() {
return n4;
}
// public AA() {
// System.out.println("AA() 构造器..");
// }
public AA(String name) {
}
public AA() {
}
public AA(int num) {
//super();
}
}
//类的BB继承 ctrl+t
class BB extends AA { //子类BB 继承 AA
public void m1() {
System.out.println(n1 + " " + n2 + " " + n3 + " " /*+ n4 */);
System.out.println(getN4());
}
//子类没有继承父类的构造器,但必须调用父类的构造器, 完成父类的初始化.
//至于调用父类的哪个构造器,无所谓,但是一定要调用一个
public BB() {
//默认有一句话 super(), 父类的无参构造器
//如果希望指定去调用父类的某个构造方法,则显示的调用一下
//super在使用时,需要放在方法体的第一句位置
//super() 和 this() 都只能放在构造方法句首,因此这两个方法不能共存在一个方法中
super(10);
System.out.println("BB() 构造器..");
}
}
内存分析案例
public class ClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
son son = new son();
}
}
class Guandpa {
private String name;
public Guandpa(String name) {
super(); //指向 Object();
this.name = name;
}
public Guandpa() {
//默认存在super(); 即使不显式的写出
this.name = "爷爷";
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("Guandpa:" + name);
}
}
class father extends Guandpa{
private String name;
public father(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public father() {
super();// 指向 Guandpa();
this.name = "父亲";
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("father"+name);
}
}
class son extends father{
private String name;
public son(String name) {
super();
//默认存在super();即使不显式的写出。
//当我们在father类中 无参构造方法被覆盖时, son子类的构造方法就会报错。
//因为son子类在构造时 ,会首先调用super();
this.name = name;
}
public son() {
super(); //指向 father();
this.name = "儿子";
}
public void f1() {
show();
}
}
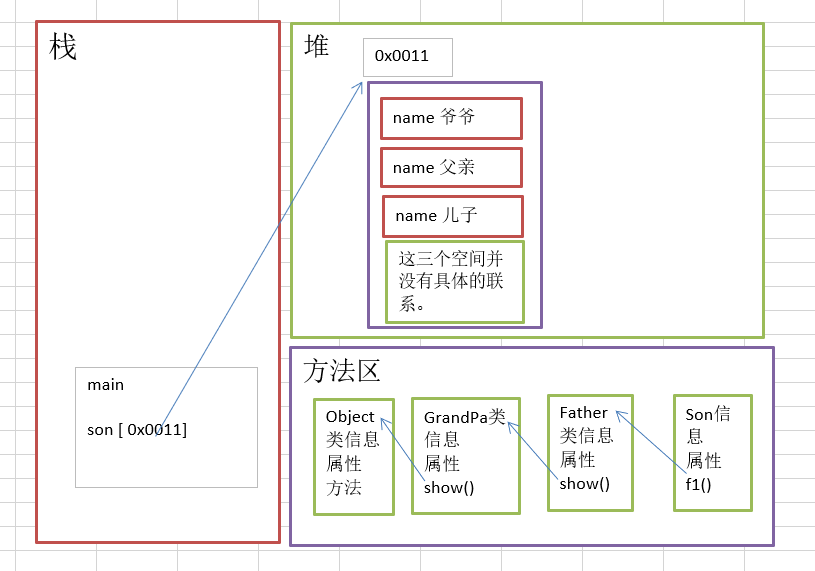
super关键字
super代表父类的引用,用于访问父类的属性、方法、构造器
基本语法
-
访问父类的属性 , 不能访问父类的private属性 [案例] super.属性名;
-
访问父类的方法,不能访问父类的private方法
super.方法名(参数列表);
-
访问父类的构造器(只能访问非私有的父类构造器):
super(参数列表); 构造器的调用只能放在构造器中,且一定在第一行。
细节说明
-
调用父类的构造器 (分工明确, 父类属性由父类初始化,子类的属性由子类初始化)
-
当子类中有和父类中的成员(属性和方法)重名时,为了访问父类的成员,必须通过super。如果没有重名,使用super、this、直接访问是一样的效果!
-
super的访问不限于直接父类,如果爷爷类和本类中有同名的成员,也可以使用super去访问爷爷类的成员;如果多个基类中都有同名的成员,使用super访问遵循就近原则。A->B->C
简单案例
public class SuperTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BB bb = new BB();
bb.m1();
}
}
class AA {
public int n1 = 10;
protected int n2 = 20;
int n3 = 30;
private int n4 = 40;
public void run() {
}
protected void eat() {
}
void sleep() {
}
private void cry() {
}
public AA() {
}
public AA(String name) {
}
}
class BB extends AA{
public void m1() {
//访问父类的属性 , 不能访问父类的private属性 [案例] super.属性名
//如果子类,和父类不在同一个包 ,默认的属性是否可以访问? 答不能
System.out.println(super.n1 + " " + super.n2 + " " + super.n3 /*+ super.n4*/);
}
//访问父类的方法,不能访问父类的private方法 super.方法名(参数列表);
//如果子类,和父类不在同一个包 ,默认的方法是否可以访问? 答不能
public void m2() {
super.eat();
super.run();
super.sleep();
//super.cry();
}
//访问父类的构造器(这点前面用过): super(参数列表);只能放在构造器的第一句,而且只能出现一句
//也只能访问 非私有的构造器,如果子类和父类不在同一个包,默认的构造器,也不能使用
public BB() {
// super();
super("hello");
}
}
特别注意:如果子类,和父类不在同一个包 ,默认的属性不可以访问。在上面的案例中可以可以通过super访问AA类中的属性与方法,是因为AA与BB在同一个包下!
super与this
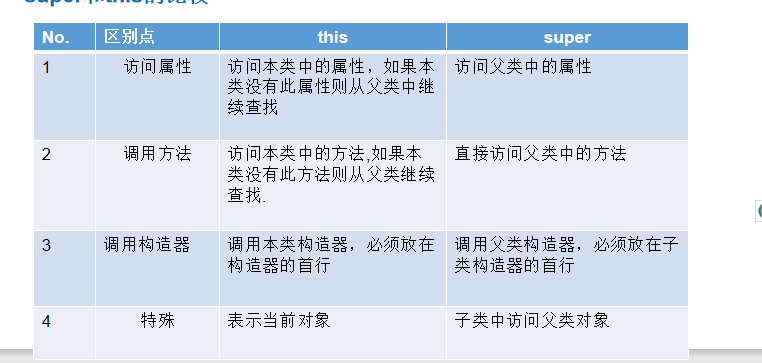
对于继承的总结:
继承的本质是建立一种查找关系,就像this关键字中的访问属性和调用方法时一样。
继承应用案例1
为了代码方便阅读这里将各个类写在了一起,但在实际开发中应该保证一个类一个文件,所有类在同一个包下。
/**
*
* 编写Computer类,包含CPU、内存、硬盘等属性,getDetails方法用于返回Computer的详细信息
* 编写PC子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【品牌brand】 编写NotePad子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【演示color】
* 编写Test类,在main方法中创建PC和NotePad对象,分别给对象中特有的属性赋值,
* 以及从Computer类继承的属性赋值,并使用方法并打印输出信息
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PC pc = new PC("intel_i9", "16GB", "1TB", "PCbrand");
NotePad notePad = new NotePad("cpu", "8GB", "128GB", "NotePadcolor");
System.out.println(pc.getDetails());
System.out.println(notePad.getDetails());
}
}
//编写Computer类,包含CPU、内存、硬盘等属性,getDetails方法用于返回Computer的详细信息
class Computer {
//private + set & get 方法,体现封装
private String CPU;
private String memory;
private String disk;
public String getCPU() {
return CPU;
}
public void setCPU(String cPU) {
CPU = cPU;
}
public String getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public void setMemory(String memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public String getDisk() {
return disk;
}
public void setDisk(String disk) {
this.disk = disk;
}
public String getDetails() {
return "Computer [CPU=" + CPU + ", memory=" + memory + ", disk=" + disk + "]";
}
public Computer(String cPU, String memory, String disk) {
super();
CPU = cPU;
this.memory = memory;
this.disk = disk;
}
public Computer() {
super();
}
}
//编写PC子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【品牌brand】
class PC extends Computer {
private String brand; //private + set & get 方法,体现封装
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
@Override
public String getDetails() {
return super.getDetails() + "
PC [brand=" + brand + "]";
}
public PC(String cPU, String memory, String disk, String brand) {
super(cPU, memory, disk);
this.brand = brand;
}
}
//编写NotePad子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【演示color】
class NotePad extends Computer {
private String color; //private + set & get 方法,体现封装
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String getDetails() {
return super.getDetails() + "
NotePad [color=" + color + "]";
}
public NotePad(String cPU, String memory, String disk, String color) {
super(cPU, memory, disk);
this.color = color;
}
}
继承应用案例2
为了代码方便阅读这里将各个类写在了一起,但在实际开发中应该保证一个类一个文件,所有类在同一个包下。
/**
* 定义一个ManKind类: 成员变量int sex和int salary; 要求加上两个参数有参构造
* 方法void manOrWomen():根据sex的值显示“man”(sex==1)或者“women”(sex==0);
* 方法void employeed():根据salary的值显示“no job”(salary==0)或者“ job”(salary!=0)。
* 定义类Kids继承ManKind,并包括成员变量int yearsOld; 方法printAge()打印yearsOld的值。
* 在Kids类的main方法中实例化Kids的对象someKid,用该对象访问其父类的成员变量及方法。
*/
public class HomeWork {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Kids kids = new Kids(2,-100,18);
kids.manOrWomen();
kids.employeed();
kids.printAge();
}
}
class ManKind {
private int sex;
private int salary;
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
// 方法void manOrWomen():根据sex的值显示“man”(sex==1)或者“women”(sex==0);
public void manOrWomen() {
if (sex == 1) {
System.out.println("man");
} else{
System.out.println("women");
}
}
// 方法void employeed():根据salary的值显示“no job”(salary==0)或者“ job”(salary!=0)。
public void employeed() {
if (salary == 0) {
System.out.println("no job!");
} else {
System.out.println("job!");
}
}
public ManKind(int sex, int salary) {
super();
if(sex != 0 && sex !=1) {
System.out.println("性别输入内容错误,0表示女,1表示男!");
this.sex = 0;
}else {
this.sex = sex;
}
if (salary < 0) {
System.out.println("输入工资错误,默认值1000");
this.salary = 1000;
} else {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
public ManKind() {
super();
}
}
//定义类Kids继承ManKind,并包括成员变量int yearsOld; 方法printAge()打印yearsOld的值。
class Kids extends ManKind{
private int yearsOld;
public int getYearsOld() {
return yearsOld;
}
public void setYearsOld(int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public void printAge() {
System.out.println("年龄:"+yearsOld);
}
public Kids(int sex, int salary, int yearsOld) {
super(sex, salary);
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在另外一个非public类中 也有一个main时,点击Run As 会询问执行哪一个main
Kids kids = new Kids(1,2000,18);
kids.setSex(0);
kids.manOrWomen();
kids.employeed();
kids.printAge();
}
}