HashSet
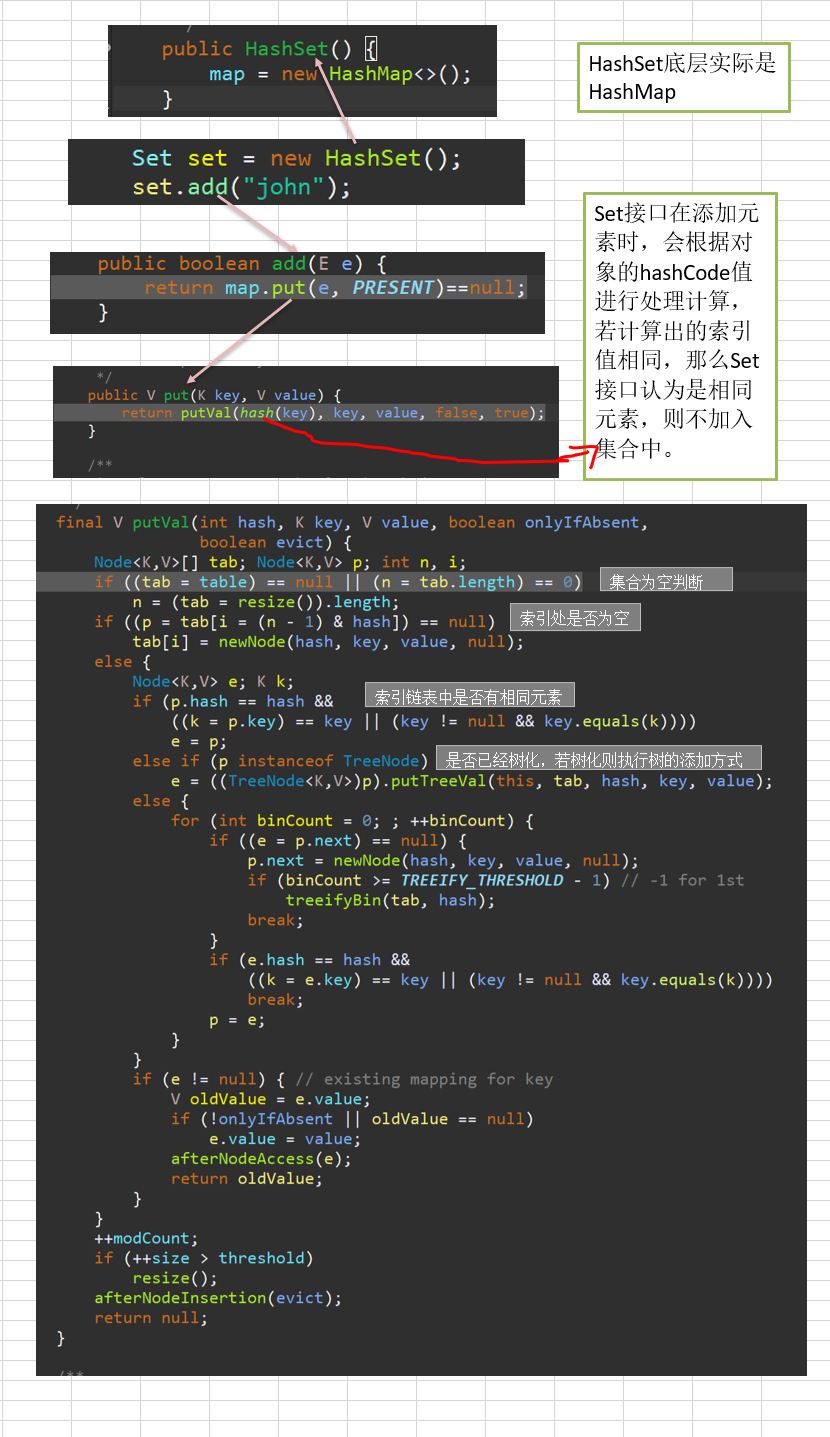
HashSet实现了Set接口(不可以重复元素),HashSet实际上底层是HashMap(看后面源码以及HashMap)。
HashSet不保证元素是有序的,顺序取决于hash之后,再进行去索引的结果。
HashSet底层机制(hashCode + equals)
-
HashSet底层是HashMap
-
添加一个元素时,先得到此元素的hashCode值,对HashCode值进行计算得到索引值。
-
找到存储数据表table,查看此索引值位置上是否已经存放有元素。
-
若没有则直接加入,若有则需要调用equals方法进行比较,如果相同则放弃添加(Set接口不允许重复就是这样判断的)。
-
若在同一个索引位上有多个元素,它们是以链表的形式存放的,当达到一定数量时,链表会自动树化,变为红黑树。

简单案例
package class_HashSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class ClassTest01{
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add("Hello01");
hashSet.add("Hello02");
hashSet.add("Hello03");
hashSet.add("Hello04");
for(int i = 0;i<8;i++) { //将会有8个Dog对象,放在同一个索引处,形成链表
hashSet.add(new Dog());
}
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}
class Dog{
@Override
public int hashCode() {
//让Dog的所有实例对象的hashCode都为1
return 1;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//让Dog的所有实例对象在比较时都返回false,即都不相同。
return false;
}
//当hashCode固定为1,equals为false时,会一直加入到HashSet数据表中的一个索引位上
}
实际应用案例
定义一个Employee类,该类包含:private成员属性name(String),age(int),birthday(MyDate),
其中 birthday 为 MyDate类(属性包括:year(int), month(int),day(int))的对象, 要求:
创建3个Employee 放入 HashSet中,当 name和birthday一样时,认为是同一个员工, 就不能添加到HashSet集合中
提示: 根据前面HashSet 的添加机制,想办法 重写 Employe和MyDate的hashCode 和 equals方法
比如 “张三”, 2000-11-11
package class_HashSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class ClassWork01 {
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee("小范", 20, new MyDate(2000, 3, 26));
Employee employee2 = new Employee("小黄", 18, new MyDate(1999, 11, 25));
Employee employee3 = new Employee("小范", 20, new MyDate(2000, 3, 26));
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(employee);
set.add(employee2);
set.add(employee3);
for(Object obj : set) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee(String name, int age, MyDate birthday) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((birthday == null) ? 0 : birthday.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (birthday == null) {
if (other.birthday != null)
return false;
} else if (!birthday.equals(other.birthday))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + "]";
}
}
class MyDate{
private int year;
private int mouth;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int mouth, int day) {
super();
this.year = year;
this.mouth = mouth;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMouth() {
return mouth;
}
public void setMouth(int mouth) {
this.mouth = mouth;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + day;
result = prime * result + mouth;
result = prime * result + year;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
MyDate other = (MyDate) obj;
if (day != other.day)
return false;
if (mouth != other.mouth)
return false;
if (year != other.year)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return year + "-" + mouth + "-" + day;
}
}
程序输出:
Employee [name=小范, age=20, birthday=2000-3-26]
Employee [name=小黄, age=18, birthday=1999-11-25]
HashSet源码追踪
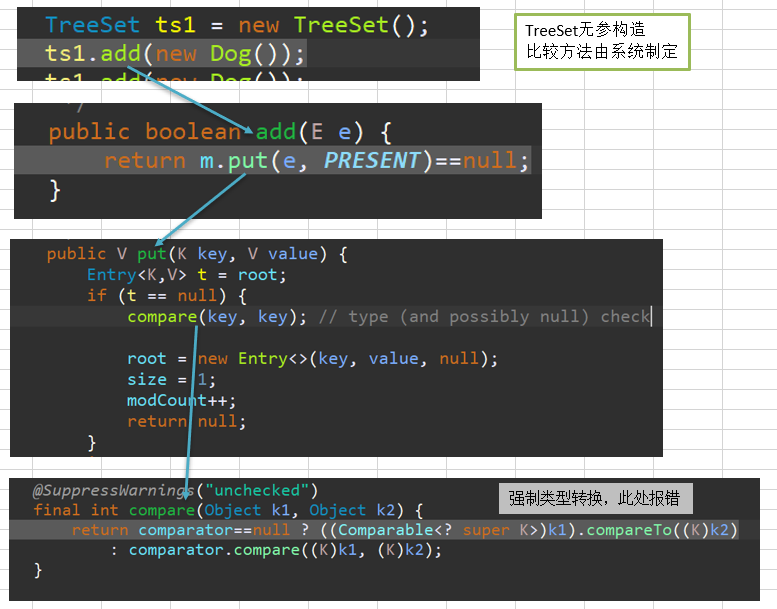
TreeSet
TreeSet实现了Set接口,所以有Set接口的所有特性。
TreeSet与HashSet不同的是,TreeSet有序的。
TreeSet可以自定义一个Comparator,定义一个排序规则。
package class_TreeSet_LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class ClassTest01_TreeSet {
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String)o1).length() - ((String)o2).length();
}
}) ;
//假设ts集合中放的都是字符串,让ts集合中的元素按照长度从小到大排列输出。
ts.add("Hello");
ts.add("小范");
ts.add("aaaaa");
ts.add("xiaofan");
System.out.println(ts);
TreeSet ts1 = new TreeSet();
ts1.add(new Dog());
ts1.add(new Dog());
ts1.add(new Dog());
}
}
class Dog{
}
程序输出:
[小范, Hello, xiaofan]
程序说明:
可以从结果上面看到,"aaaaa"并没有加入到ts集合中。其原因是,由于我们自定义了比较机制,当compare方法返回值为0时,TreeSet集合里的比较机制就认为两个元素是相同的。(所以这里只要长度相同,就是同一个对象)

而下面的ts1集合中,存入的是Dog对象,但Dog对象本身并没有实现Comparable接口。在底层实现TreeSet的去重机制时,需要将即将添加的对象进行强制类型转换为Comparable类型,再使用其compareTo方法进行比较。所以因为Dog类没有实现Comparable接口,这里会报类型转换异常。