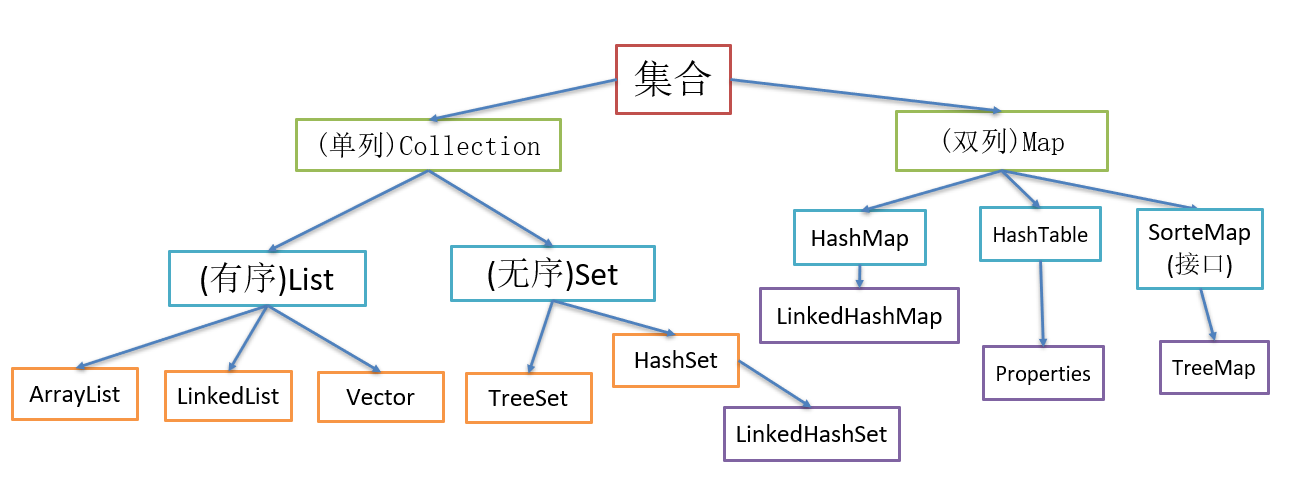
-
Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据键值对:Key—Value
-
在Map中Key与Value都可以存放任何类型的数据。
-
Key是用Set来存放的,不允许重复,允许有null但只能有一个。常用String类作为Map的“键”(key)
-
Value是用Collection存放的,可以是Set也可以是List,所以当Value使用List时允许重复,且可以有多个null值。
-
key与value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定key总能找到唯一的确定的一个value。
-
因为key是用Set存放的,而value是通过key进行查找返回的。所以Map是无序的。
底层结构图:

虚线为实现关系,实线为继承关系。
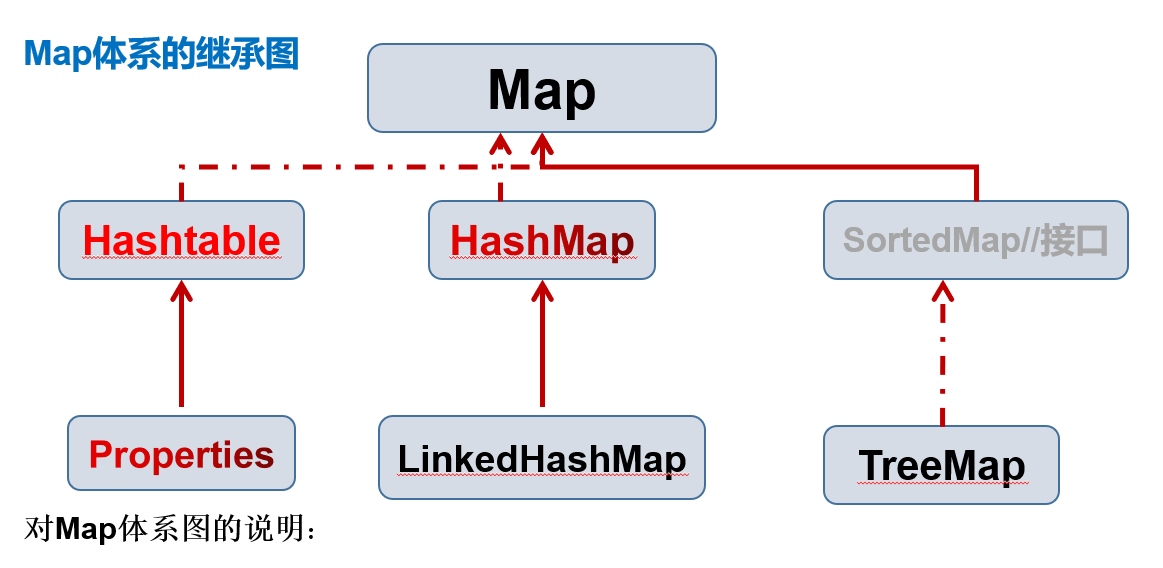
Map接口常用方法
-
put:添加
-
get:根据键获取值
-
size:获取元素个数
-
isEmpty:判断个数是否为0
-
containsKey:查找键是否存在
-
remove:根据键删除映射关系
-
clear:清除
package class_Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassTest01_MapMethods {
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
//put:添加。
/*
1.若要添加的key值集合中没有,则直接添加。
2.若集合中已存在相同的key值,则直接替换掉。
3.key中只能有一个null存在,若存在多个null则根据上面的规则,只会保留最后一个null
4.value中可以有多个null存在。
5.k-v是无序的,取出顺序和添加顺序是不一样的。
*/
map.put("1", "hello01");
map.put("2", "hello02");
map.put("3", "hello03");
map.put("3", "hello05");
map.put("4", "hello02");
map.put(null, "hello02");
map.put("5", null);
//get:根据键获取值
System.out.println(map.get("3"));//返回值:hello05
//size:获取元素个数
System.out.println(map.size());//返回值:6
//isEmpty:判断个数是否为0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); //返回值:false
//containsKey:查找键是否存在
System.out.println(map.containsKey(null)); //返回值:true
//remove:根据键删除映射关系,返回指为键所指的值
System.out.println(map.remove(null)); //返回值:hello02
//clear:清除
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Map接口的遍历方式
需要使用的方法:
-
containsKey():查找键是否存在
-
keySet():获取所有的键,返回一个Set集合
-
entrySet():获取所有关系,返回一个Set集合
-
values():获取所有的值,返回一个Collection集合
两种遍历方式(每种方式又分别有迭代器和增强for两种):
-
遍历键再通过键取出对应的值
-
直接遍历整个键值对k-v
package class_Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class ClassTest02_ForeachMap {
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("1", "hello01");
map.put("2", "hello02");
map.put("3", "hello03");
map.put("3", "hello05");
map.put("4", "hello02");
map.put(null, "hello02");
map.put("5", null);
//方式1:遍历键,再取出值
System.out.println("========方式一:迭代器=======");
Set key = map.keySet(); //取出key,放入Set集合
//迭代器方式:
Iterator iterator = key.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next(); //遍历键,将键赋值给obj
System.out.println(obj + " == " + map.get(obj)); //通过键,访问值,进行遍历
}
iterator = key.iterator();
//增强for循环方式:
System.out.println("========方式一:增强for=======");
for(Object obj:key) {
System.out.println(obj + " -- " + map.get(obj));
}
//方式二:直接遍历键值对
//将键值对放入Set中,此时entrySet编译类型为Set集合,运行类型为HashMap$Node("$"符号代表内部类,后面跟类名是内部类,跟数值是匿名内部类)
Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); //取出键值对k-v,放入Set集合
//迭代器方式:
System.out.println("========方式二:迭代器=======");
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()) {
//这里无法访问HashMap.Node,但Node实现了Map接口中的一个内部接口Entry,可以使用动态绑定机制
// HashMap.Node node = (HashMap.Node)iterator2.next(); //报错:The type HashMap.Node is not visible
/*
理解为什么需要是用Map.Entry来强转从entrySet中取出的键值对:
1.在HashMap中有内部类Node,用于保存键值对,但Node是静态成员内部类,不可以在外部访问,所以不能使用其get方法。
2.由于HashMap继承与Map接口,Node又实现了Map接口中的一个内部接口Entry。
3.即通过Entry接口就可以通过动态绑定的方式访问到Node内部类的方法
*/
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator2.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " :: " + entry.getValue());
}
iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
//增强for循环方式:
System.out.println("========方式二:增强for=======");
for(Object obj:entrySet) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " .. " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
说明:直接遍历键值对所使用的动态绑定机制的思路和"OOP——内部类"最后的思考题相同。
Map接口练习
使用HashMap添加3个员工对象,要求
键:员工id
值:员工对象
并遍历显示工资>18000的员工
(遍历方式最少两种)
员工类:姓名、工资、员工id
package class_Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class ClassWork01 {
@SuppressWarnings({ "unused", "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map hashMap = new HashMap();
Employee employee1 = new Employee("小范", 1001, 22000);
Employee employee2 = new Employee("小黄", 1002, 14000);
Employee employee3 = new Employee("小雨", 1003, 23000);
hashMap.put(employee1.getId(), employee1); //这里第一个参数employee1.getId()自动装箱,因为原本需要是Object类型
hashMap.put(employee2.getId(), employee2); //而取出来是Int类型,自动装箱为Integer。
hashMap.put(employee3.getId(), employee3);
// System.out.println(hashMap);
//遍历方式1:遍历键,再通过键,取出值
Set key = hashMap.keySet();
Iterator iterator = key.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
//将hashMap中的key键取出,放入Set中(实际是HashSet),再通过迭代器遍历取出key,通过hashMap.get方法取出值
Object obj = iterator.next(); //从HashSet中取出key键 , 此时key编译类型是Object,运行类型是Integer(因为键是员工id)
// System.out.println(obj.getClass());
if(isOut(hashMap.get(obj))) {
System.out.println(obj + "--" + hashMap.get(obj));
}
}
iterator = key.iterator();
System.out.println("=========================================");
//遍历方式2:直接遍历键值对
//将键值对放入Set中,此时entrySet编译类型为Set接口,运行类型为HashMap$Node("$"符号代表内部类,后面跟类名是内部类,跟数值是匿名内部类)
Set entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()) {
/*
* 理解为什么需要是用Map.Entry来强转从entrySet中取出的键值对
* 1.在HashMap中有内部类Node,用于保存键值对,但Node是静态成员内部类,不可以在外部访问,所以不能使用其get方法。
* 2.由于HashMap继承与Map接口,Node又实现了Map接口中的一个内部接口Entry。
* 3.即通过Entry接口就可以通过动态绑定的方式访问到Node内部类的方法
*/
Map.Entry node = (Map.Entry)iterator2.next();
if(isOut(node.getValue())) {
System.out.println(node.getKey() + "==" + node.getValue());
}
}
iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
}
public static boolean isOut(Object object) {
if(!(object instanceof Employee)) {
return false;
}
Employee e = (Employee)object;
return e.getSalary() > 18000;
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int id;
private double salary;
public Employee(String name, int id, double salary) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [name=" + name + ", id=" + id + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}
程序输出:
1001--Employee [name=小范, id=1001, salary=22000.0]
1003--Employee [name=小雨, id=1003, salary=23000.0]
=============================================
1001--Employee [name=小范, id=1001, salary=22000.0]
1003--Employee [name=小雨, id=1003, salary=23000.0]