题目:
In Complexity theory, some functions are nearly O(1)O(1), but it is greater then O(1)O(1). For example, the complexity of a typical disjoint set is O(nα(n))O(nα(n)). Here α(n)α(n) is Inverse Ackermann Function, which growth speed is very slow. So in practical application, we often assume α(n) le 4α(n)≤4.
However O(α(n))O(α(n)) is greater than O(1)O(1), that means if nn is large enough, α(n)α(n) can greater than any constant value.
Now your task is let another slowly function log*log∗ xx reach a constant value bb. Here log*log∗ is iterated logarithm function, it means “the number of times the logarithm function iteratively applied on xx before the result is less than logarithm base aa”.
Formally, consider a iterated logarithm function log_{a}^*loga∗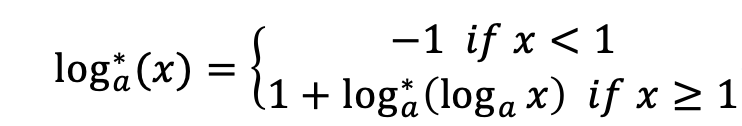
Find the minimum positive integer argument xx, let log_{a}^* (x) ge bloga∗(x)≥b. The answer may be very large, so just print the result xx after mod mm.
Input
The first line of the input is a single integer T(Tle 300)T(T≤300) indicating the number of test cases.
Each of the following lines contains 33 integers aa, bb and mm.
1 le a le 10000001≤a≤1000000
0 le b le 10000000≤b≤1000000
1 le m le 10000001≤m≤1000000
Note that if a==1, we consider the minimum number x is 1.
Output
For each test case, output xx mod mm in a single line.
Hint
In the 4-th4−th query, a=3a=3 and b=2b=2. Then log_{3}^* (27) = 1+ log_{3}^* (3) = 2 + log_{3}^* (1)=3+(-1)=2 ge blog3∗(27)=1+log3∗(3)=2+log3∗(1)=3+(−1)=2≥b, so the output is 2727 mod 16 = 1116=11.
样例输入
5 2 0 3 3 1 2 3 1 100 3 2 16 5 3 233
样例输出
1 1 3 11 223
解题报告:严重怀疑这场比赛的出题方,读题实在是太困难了,看了半个小时才理解了要求解什么东西,一看就是一个广义欧拉降幂,然后就直接去写的之前的模板,求解无穷个2的幂次,
但是修修改改的过了样例,但是忘记了广义欧拉降幂的实现,疯狂wa,在比赛结束后找了好久才发现是没有去使用广义欧拉降幂的性质,忘记在该加欧拉(m)的地方进行加了,隔壁队的
数论手,给了一个能够实现这个功能的快速幂,稍微一修改就A了。这个需要掌握了,当时时间太紧,头脑已经混了。
ac代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<map> 7 #include<vector> 8 using namespace std; 9 typedef long long ll; 10 11 const int maxn=1e7+10; 12 vector<int> prime; 13 int phi[maxn]; 14 15 void db_Onion() 16 { 17 phi[1]=1; 18 for(int i=2;i<maxn;i++) 19 { 20 if(phi[i]==0) 21 { 22 prime.push_back(i); 23 phi[i]=i-1; 24 } 25 for(int j=0;j<prime.size()&&prime[j]*i<maxn;j++) 26 { 27 if(i%prime[j]==0) 28 { 29 phi[i*prime[j]]=phi[i]*prime[j]; 30 break; 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 phi[i*prime[j]]=phi[i]*(prime[j]-1); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 ll a,b,m; 40 ll cal(ll x,ll m) 41 { 42 if(x<m) 43 return x; 44 else 45 return x%m+m; 46 } 47 48 ll ans; 49 50 ll ksm(ll r,ll n,ll m) 51 { 52 ll d=r,ans=1; 53 bool f=0; 54 if(r==0&&n==0)return 1; 55 while(n){ 56 if(n&1){ 57 ans=ans*d; 58 if(ans>=m){ 59 ans%=m;f=1; 60 } 61 } 62 d=d*d; 63 if(n>1&&d>=m){ 64 d%=m;f=1; 65 } 66 n>>=1; 67 } 68 if(f)ans+=m; 69 return ans; 70 } 71 ll slove(ll p,int tot) 72 { 73 if(tot==b+1) 74 return 1; 75 if(p==1) 76 return 1; 77 78 ll tmp=slove(phi[p],tot+1); 79 return ksm(a,tmp,p); 80 } 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 db_Onion(); 85 int t; 86 scanf("%d",&t); 87 while(t--) 88 { 89 scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&m); 90 if(b==0||a==1) 91 { 92 printf("%lld ",1%m); 93 continue; 94 } 95 ans=0; 96 printf("%lld ",slove(m,1)%m); 97 } 98 }