起泡排序(bubble sort)
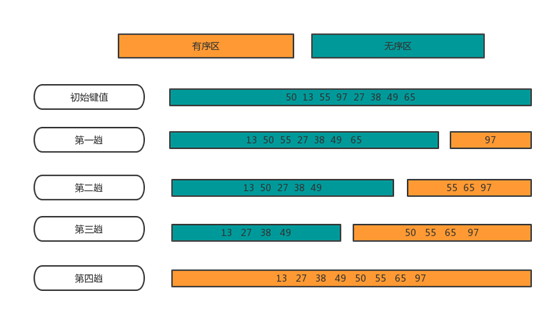
起泡排序是交换排序中最简单的排序方法,其基本思想是:两两比较相邻记录的关键码,如果反序则交换,直到没有反序的记录为止。
-
将整个待排序记录分为无序区和有序区,初始时有序区为空。
-
对无序区从前到后依次将相邻记录的关键码进行比较,若反序则交换,从而使得关键码小的记录向前移,关键码大的记录向后移。
-
重复执行2,直到无序区中没有记录。
在编写实现算法时,有些小技巧可以利用。我们可以设置一个变量bound用来记录无序区和有序区的分界,用另一个变量exchange记录每次记录交换的位置。在一趟排序后,exchange记录了最后一次变换的位置,此时exchange即无序区与有序区的分界,传递给bound。如果exchange等于第一个记录的序号(即没有发生交换),则结束排序。
代码示例

1 int BubbleSort(int a[], int ArrayStart, int ArrayEnd) 2 { 3 //bound为无序区和有序区的分界 4 int exchange = ArrayEnd, bound = ArrayStart; 5 while(exchange != ArrayStart) 6 { 7 bound = exchange; 8 exchange = ArrayStart; 9 for(int i = ArrayStart; i < bound; i++) 10 { 11 if(a[i] > a[i+1]) 12 { 13 int temp = a[i]; 14 a[i] = a[i+1]; 15 a[i+1] = temp; 16 exchange = i+1; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 return 1; 21 }
快速排序(quick sort)
快速排序(又称分区交换排序)是对起泡排序的一种改进,改进的着眼点是:在起泡排序中,记录的比较和移动是在相邻位置进行的,记录每次交换只能后移一个位置,因而总的比较次数和移动次数较多。在快速排序中,记录的比较和移动是从两端向中间进行的,关键码较大的记录一次就能从前面移动到后面,关键码较小的记录一次就能从后面移动到前面,记录移动的距离较远,从而减少了总的比较次数和移动次数。
基本思想:选取一个轴值,将待排序记录划分成独立的两部分,左侧记录的关键码均小于或等于轴值,右侧记录的关键码均大于或等于轴值,然后分别对这两部分重复上述过程,直到整个序列有序。
代码示例

1 int QuickSort(int a[], int ArrayStart, int ArrayEnd) 2 { 3 int QuickSortPartition(int*, int, int); 4 int pivot = 0; 5 if(ArrayStart < ArrayEnd) 6 { 7 pivot = QuickSortPartition(a, ArrayStart, ArrayEnd); 8 QuickSort(a, ArrayStart, pivot-1); 9 QuickSort(a, pivot+1, ArrayEnd); 10 } 11 return 1; 12 } 13 14 int QuickSortPartition(int a[], int ArrayStart, int ArrayEnd) 15 { 16 int i = ArrayStart, j = ArrayEnd; 17 while(i < j) 18 { 19 while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) 20 { 21 j--; 22 } 23 if(i < j) 24 { 25 int temp = a[i]; 26 a[i] = a[j]; 27 a[j] = temp; 28 i++; 29 } 30 while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) 31 { 32 i++; 33 } 34 if(i < j) 35 { 36 int temp = a[i]; 37 a[i] = a[j]; 38 a[j] = temp; 39 j--; 40 } 41 } 42 return i; 43 }
