1.语法
- 缩进来表示语句块
- 注释:单行用# 多行用""" 注释内容 “”“ ,就是前后三个双引号。
2.变量
- 变量不需要声明,直接可以赋值。
- 数字主要有 int 和float两种,可以通过 print( type(变量名) ) 查看变量类型。
- 强制转化用 int() float() str()
- 字符串:用双引号或单引号引起来
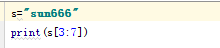

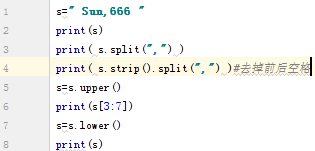
一些函数:len() upper() lower() strip() split()
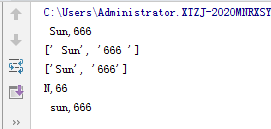
3.部分 运算符
/ Division
// Floor division
and 相当于C的 &&
or 相当于C的 ||
not 相当于C的!
还有特殊的属于运算符 in 和 not in
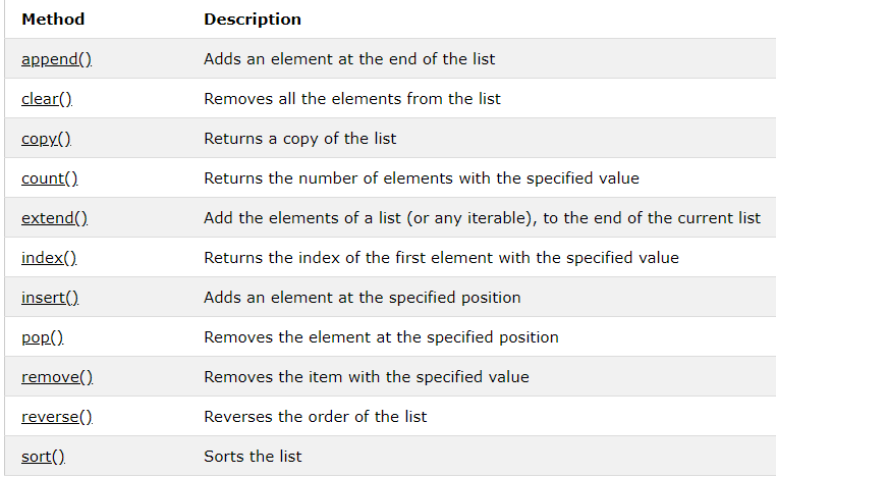
4.测试LIST
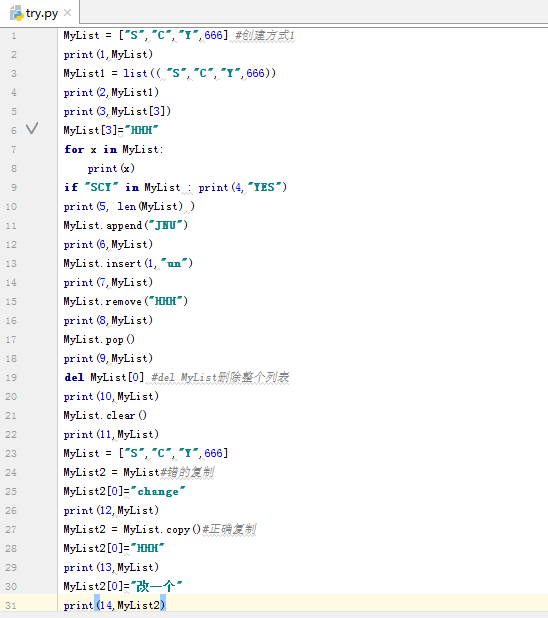
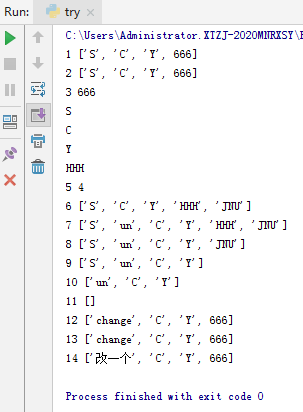
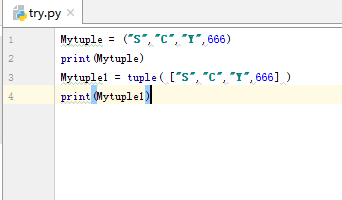
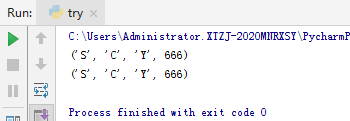
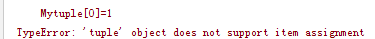
5.测试 元组tuple
元组里的数据不能改变
6.测试 集合SET(简单用一下)
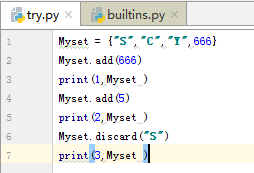
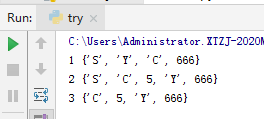
这个类还有很多功能,先不学了,按ctrl+set进入这个说明
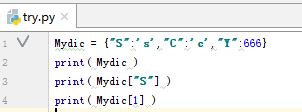
7.字典Dictionary 简单测试

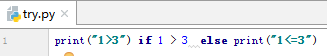
8.分支结构

9.循环
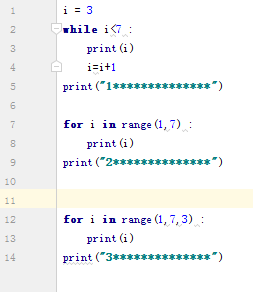

10.zip函数

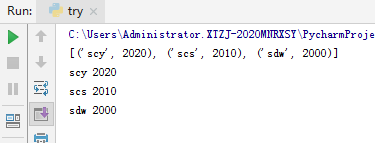
11.enumerate枚举函数
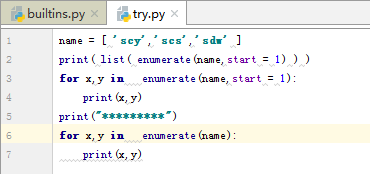
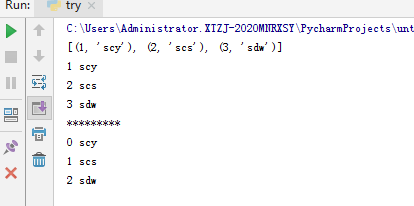

12.效率比较(列表解析式不仅方便,效率也更高)

13.FUNCTION
14.案例
实现单词个数的统计
import string def main(): file = r"C:UsersAdministrator.XTZJ-2020MNRXSYDesktopSCY新建文本文档.txt" with open(file,'r') as text: words = [ raw_word.strip(string.punctuation).lower() for raw_word in text.read().split() ] print(words) words_index = set(words) count_dict = { index:words.count(index) for index in words_index } for word in sorted(count_dict,key= lambda x:count_dict[x],reverse = True): print( "{}--{} times".format(word,count_dict[word]) ) if __name__ == "__main__": main()



15.作业
