下面从一个问题引入:
// ConsoleApplication5.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include<random> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<thread> #include<algorithm> #include<future> using namespace std; int x = 0; void mythread_one() { for (int i = 1; i < 1000000; i++) { x++; } } void mythread_two() { for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { x++; } } int main() { thread th_one(mythread_one); thread th_two(mythread_two); th_one.join(); th_two.join(); cout << "x的值为:" << x << endl; return 0; }
执行结果:
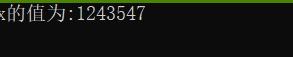
这段程序设置了两个线程,然后对全局变量进行加加操作,但是执行的结果却不是我们真正想要的。
解决办法可以对访问的数据加锁:
// ConsoleApplication5.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include<random> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<thread> #include<algorithm> #include<future> using namespace std; int x = 0; mutex g; void mythread_one() { for (int i = 1; i < 10000000; i++) { g.lock(); x++; g.unlock(); } } void mythread_two() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { g.lock(); x++; g.unlock(); } } int main() { thread th_one(mythread_one); thread th_two(mythread_two); th_one.join(); th_two.join(); cout << "x的值为:" << x << endl; return 0; }
这样的确可以解决问题,但是为了提升效率,C++11引入了原子操作atomic<>,它能够保证在读取数据的时候不会被打断,和加锁机制相比,他的效率更高.
代码演示:
// ConsoleApplication5.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include<random> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<thread> #include<algorithm> #include<future> using namespace std; int x = 0; atomic<int> g = 0; void mythread_one() { for (int i = 1; i < 10000000; i++) { g++; } } void mythread_two() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { g++; } } int main() { thread th_one(mythread_one); thread th_two(mythread_two); th_one.join(); th_two.join(); cout << "x的值为:" << x << endl; return 0; }
接下来再看另一个原子操作atomic<bool> ,他用于终止线程的执行:
// ConsoleApplication5.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include<random> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<thread> #include<algorithm> #include<future> using namespace std; int x = 0; atomic<bool> g_ifend=false; void mythread() { cout << "子线程1开始执行了" << endl; while (g_ifend == false) { cout << "任务执行中..." << endl; this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(2)); } cout << "子线程任务执行结束" << endl; } int main() { cout << "主线程开始执行了" << endl; thread th(mythread); this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(5)); g_ifend = true;//让主线程等待5秒,过了5秒,让子线程结束任务 th.join(); cout << "主线程执行任务结束了" << endl; return 0; }