 When a thin rod of length L is heated n degrees, it expands to a new length L'=(1+n*C)*L, where C is the coefficient of heat expansion.
When a thin rod of length L is heated n degrees, it expands to a new length L'=(1+n*C)*L, where C is the coefficient of heat expansion. When a thin rod is mounted on two solid walls and then heated, it expands and takes the shape of a circular segment, the original rod being the chord of the segment.
Your task is to compute the distance by which the center of the rod is displaced.
Input
The input contains multiple lines. Each line of input contains three non-negative numbers: the initial lenth of the rod in millimeters, the temperature change in degrees and the coefficient of heat expansion of the material. Input data guarantee that no rod expands by more than one half of its original length. The last line of input contains three negative numbers and it should not be processed.
Output
For each line of input, output one line with the displacement of the center of the rod in millimeters with 3 digits of precision.
大致题意:一根两端固定在两面墙上的杆 受热弯曲后变弯曲.求前后两个状态的杆的中点位置的距离
(1) 角度→弧度公式 θr = 1/2*s
(2) 三角函数公式 sinθ= 1/2*L/r
(3) 勾股定理 r^2 – ( r – h)^2 = (1/2*L)^2
把四条关系式化简可以得到
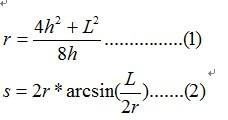
逆向思维解二元方程组:
要求(1)式的h,唯有先求r
但是由于(2)式是三角函数式,直接求r比较困难
因此要用顺向思维解方程组:
在h的值的范围内枚举h的值,计算出对应的r,判断这个r得到的(2)式的右边 与 左边的值S的大小关系 ( S= (1+n*C)*L )
很显然的二分查找了。。。。。
那么问题只剩下 h 的范围是多少了
下界自然是0 (不弯曲)
关键确定上界
题中提及到
Input data guarantee that no rod expands by more than one half of its original length.
意即输入的数据要保证没有一条杆能够延伸超过其初始长度的一半
就是说 S max = 3/2 L
理论上把上式代入(1)(2)方程组就能求到h的最小上界,但是实际操作很困难
因此这里可以做一个范围扩展,把h的上界扩展到 1/2L ,不难证明这个值必定大于h的最小上界,那么h的范围就为 0<=h<1/2L
这样每次利用下界low和上界high就能得到中间值mid,寻找最优的mid使得(2)式左右两边差值在精度范围之内,那么这个mid就是h
精度问题是必须注意的
由于数据都是double,当low无限接近high时, 若二分查找的条件为while(low<high),会很容易陷入死循环,或者在得到要求的精度前就输出了不理想的“最优mid”.
代码:
#include<iostream> #include<math.h> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; const double esp= 1e-5; //最低精度设置 int main() { double L,n,c,s; double r; while(cin>>L>>n>>c && L >=0 && n >= 0 && c >= 0) { double h = 0; double low=0.0; double high=0.5*L;//扩展上界 double mid = 0; s =(1+n*c)*L; while(high-low>esp)
//由于都是double,不能用low<high,否则会陷入死循环,必须限制low与high的精度差
{ mid=(low+high)/2; r=(4 * mid * mid+L * L) / (8 * mid); if( 2 * r * asin( L / (2*r )) < s ) low=mid; else high=mid; } h=mid; cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<<h<<endl; } return 0; }