问题牵引:
1.为什么用数组来作为栈的实现,而不是动态分配,指针加减?
2.directionNext和count数组起了什么作用?是如何实现的?
3.为什么需要while(1)?它是如何起作用的?为什么需要贪心?
4.贪心的思想是如何实现的?
5.核心代码过程的实现是怎样的?
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define ROW 8
#define COL 8
#define maxStep 64
typedef struct {
int abscissa;
int ordinate;
int direction;
}MyStack;
int ChessBoard[ROW+1][COL+1]={0};
int HTry1[8]={1, -1, -2, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2};
int HTry2[8]={2, -2, 1, 1, -1, -2, 2, -1};
MyStack PointStack[maxStep];
int top = -1;
int sum = 0;
int flagOperate = 0;
int num = 0;
void printChessBoard() {
printf("棋盘路径是:
");
for(int i = 1;i <= ROW;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j <= COL;j++) {
printf("%5d ", ChessBoard[i][j]);
}
printf("
");
}
printf("
");
}
void push(int abscissa, int ordinate) {
++top;
PointStack[top].abscissa = abscissa;
PointStack[top].ordinate = ordinate;
PointStack[top].direction = -1;
}
void pop() {
PointStack[top].abscissa = 0;
PointStack[top].ordinate = 0;
PointStack[top].direction = -1;
--top;
}
void markChessBoard(int abscissa, int ordinate) {
ChessBoard[abscissa][ordinate] = top+1;
}
int check(int xx,int yy)
{
if(xx > 0 && xx <= ROW && yy > 0 && yy <= COL && ChessBoard[xx][yy] == 0)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
void runChessBoard() {
int xNow, yNow;
while(1) {
if(flagOperate == 1) {
if(top == maxStep - 1) {
printChessBoard();
break;
}
}else if(flagOperate == 2 ) {
if(top == maxStep - 1){
num++;
printf("%d
", num);
printChessBoard();
}
}
if(sum != 0 && num == sum )
break;
xNow = PointStack[top].abscissa;
yNow = PointStack[top].ordinate;
int count[8]={0};
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) {
int xNext = xNow, yNext = yNow;
xNext += HTry1[i];
yNext += HTry2[i];
if(check(xNext,yNext)) {
for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++) {
int xNextNext = xNext, yNextNext = yNext;
xNextNext += HTry1[j];
yNextNext += HTry2[j];
if(check(xNextNext,yNextNext)) {
count[i]++;
}
}
}
}
int directionNext[8] = {0};
int temp = 9;
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) {
temp = 9;
for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++) {
if(count[j]<temp){
directionNext[i] = j;
temp = count[j];
k = j;
}
}
count[k] = 9;
}
int direnow = 0;
for(direnow = PointStack[top].direction + 1 ; direnow < 8 ; direnow++) {
int xRealNext = xNow, yRealNext = yNow;
xRealNext += HTry1[directionNext[direnow]];
yRealNext += HTry2[directionNext[direnow]];
PointStack[top].direction += 1;
if(check(xRealNext,yRealNext)) {
push(xRealNext, yRealNext);
markChessBoard(xRealNext, yRealNext);
break;
}
}
if(PointStack[top].direction >= 7) {
int x, y;
x = PointStack[top].abscissa;
y = PointStack[top].ordinate;
ChessBoard[y][x] = 0;
pop();
}
}
}
void InitStartPoint() {
int x, y;
printf("请输入起始点(x,y)(1~~8):");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("请输入你的选择:
1.找出一个结果
2.找出所有结果(几乎不可能)
3.找多少个解
输入:");
scanf("%d", &flagOperate);
while( x > ROW || x < 1 || y > COL || y < 1 || flagOperate < 1 || flagOperate > 3) {
if((x > ROW||x < 1)&&(y > COL || y < 1 )) {
printf("输入的坐标超出范围,请重新输入(1~8):");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
}else if(flagOperate < 1 || flagOperate > 3) {
printf("输入错误,请重新输入:
");
printf("请输入你的选择:
1.找出一个结果
2.找出所有结果(几乎不可能)
3.找多少个解
输入:");
scanf("%d", &flagOperate);
}
}
if(flagOperate == 3){
printf("请输入所找的解的数量:( > 0)");
scanf("%d",&sum);
flagOperate = 2;
}
push(x, y);
markChessBoard(x, y);
}
int main(void) {
InitStartPoint();
clock_t start,finish;
double duration;
start = clock();
runChessBoard();
finish = clock();
duration = (double) (finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("运行用时: %f second
", duration);
}
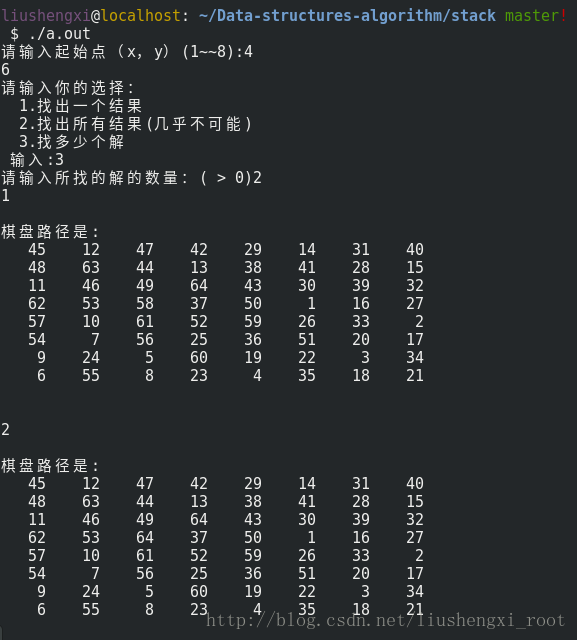
运行截图:
小枝小解:
1.为什么用数组来作为栈的实现,而不是动态分配,指针加减?因为数组含有自然下标,第几步可以直接等于 top+1 ;用指针的话 ,还必须用 top-base 来计算一下,带来了一定的麻烦。
2.directionNext和count数组起了什么作用?是如何实现的?先不着急,让我们来看几段小示例,你就会知道了。
(1).(count数组)我们将文中的代码进行下面的改动:
xNow = PointStack[top].abscissa;
yNow = PointStack[top].ordinate;
int count[8]={0};
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) {
int xNext = xNow, yNext = yNow;
xNext += HTry1[i];
yNext += HTry2[i];
printf("计算出来的下一步的坐标是:");
printf("%5d%5d
",xNext,yNext);
if(check(xNext,yNext)) {
for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++) {
int xNextNext = xNext, yNextNext = yNext;
xNextNext += HTry1[j];
yNextNext += HTry2[j];
if(check(xNextNext,yNextNext)) {
count[i]++;
}
}
}
}
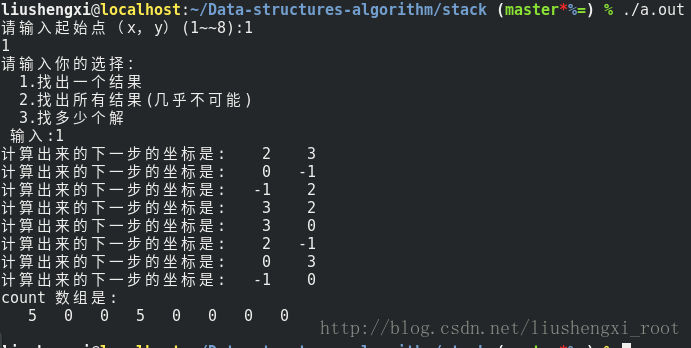
printf("count 数组是:
");
for(int j = 0 ;j< 8;j++)
printf("%4d",count[j]);
printf("
");
exit(1);
运行结果:
分析:
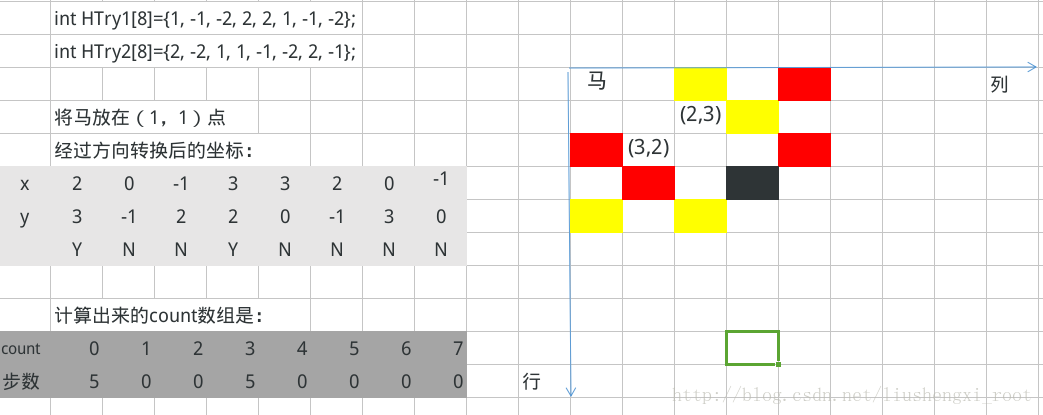
图中黄色表示(3,2)这一点能走的地方,红色表示(2,3)这一点能走的地方,黑色代表重合。可见都是5个地方。那么count数组中其实就是存储了一个方向上的下一步可走的步数
(2).(directionNext数组) 示例代码:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int count[8]={3,2,5,1,4,7,6,9};
int i ;
int directionNext[8] = {0};
int temp = 9;
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) {
temp = 9;
for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++) {
if(count[j]<temp){
directionNext[i] = j;
temp = count[j];
k = j;
}
}
count[k] = 9;
}
for(i= 0;i< 8;i++)
{
printf("count下标:%d : %d
",i,count[i]);
}
for(i= 0;i< 8;i++)
{
printf("directionNext下标:%d : %d
",i,directionNext[i]);
}
}
运行结果:
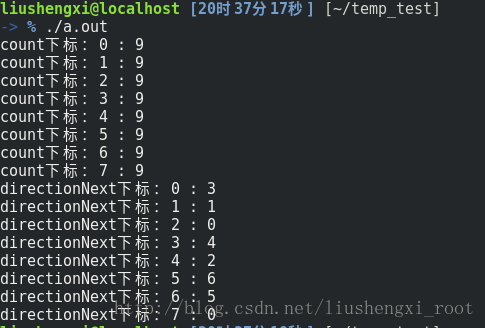
分析:由结果可以看到,directionNext 中是存储了count数组中从小到大排列之后的下标
3.为什么需要while(1)?它是如何起作用的?为什么需要贪心?因为如果要求所有解的话,就需要用到它。如果已经找到一个方法,就进行下一步,判断无路可走, 又出栈,进行下一个方向的寻找,即可满足找多少条路的要求。
4.贪心的思想是如何实现的?哪一个点的下一步少,就选哪一个先走,就能达到优化的需求
PS: 其实这个程序的效率还不是我想要的,因为这个程序去计算10万条路径的话,还是需要一定的时间的(30多秒吧好像是),而我想要的是在一秒中之内解决。在网上搜到一篇文章,贴出链接:文章但是无奈能力有限,没有改造出来,如果有人愿意搞搞,欢迎联系我(QQ:1589570280)



