对图像进行形态学变换。变换对象一般为灰度图或二值图,功能函数放在morphology子模块内。
一 膨胀(dilation)
原理:一般对二值图像进行操作。找到像素值为1的点,将它的邻近像素点都设置成这个值。1值表示白,0值表示黑,因此膨胀操作可以扩大白色值范围,压缩黑色值范围。一般用来扩充边缘或填充小的孔洞。
功能函数:skimage.morphology.dilation(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
from skimage import data
import skimage.morphology as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=data.checkerboard()
dst1=sm.dilation(img,sm.square(5)) #用边长为5的正方形滤波器进行膨胀滤波
dst2=sm.dilation(img,sm.square(15)) #用边长为15的正方形滤波器进行膨胀滤波
plt.figure('morphology',figsize=(8,8))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('origin image')
plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst1,plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst2,plt.cm.gray)
结果如下图所示:

可见滤波器的大小,对操作结果的影响非常大。一般设置为奇数。除了正方形的滤波器外,滤波器的形状还有一些,现列举如下:
morphology.square: 正方形
morphology.disk: 平面圆形
morphology.ball: 球形
morphology.cube: 立方体形
morphology.diamond: 钻石形
morphology.rectangle: 矩形
morphology.star: 星形
morphology.octagon: 八角形
morphology.octahedron: 八面体
注意,如果处理图像为二值图像(只有0和1两个值),则可以调用:
skimage.morphology.binary_dilation(image, selem=None)
用此函数比处理灰度图像要快。
二 腐蚀(erosion)
函数:skimage.morphology.erosion(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
和膨胀相反的操作,将0值扩充到邻近像素。扩大黑色部分,减小白色部分。可用来提取骨干信息,去掉毛刺,去掉孤立的像素。
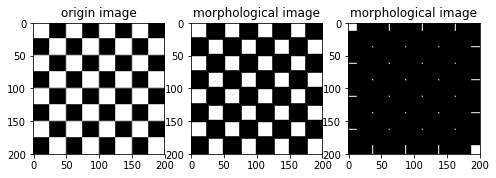
from skimage import data
import skimage.morphology as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=data.checkerboard()
dst1=sm.erosion(img,sm.square(5)) #用边长为5的正方形滤波器进行膨胀滤波
dst2=sm.erosion(img,sm.square(25)) #用边长为25的正方形滤波器进行膨胀滤波
plt.figure('morphology',figsize=(8,8))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('origin image')
plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst1,plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst2,plt.cm.gray)
结果如下图所示:
注意,如果处理图像为二值图像(只有0和1两个值),则可以调用:
skimage.morphology.binary_erosion(image, selem=None)
用此函数比处理灰度图像要快。
三 开运算(opening)
函数:skimage.morphology.openning(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
先腐蚀再膨胀,可以消除小物体或小斑块。
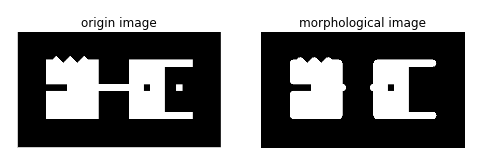
from skimage import io,color
import skimage.morphology as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=color.rgb2gray(io.imread('d:/pic/mor.png'))
dst=sm.opening(img,sm.disk(9)) #用边长为9的圆形滤波器进行膨胀滤波
plt.figure('morphology',figsize=(8,8))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('origin image')
plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
结果如下图所示:
注意,如果处理图像为二值图像(只有0和1两个值),则可以调用:
skimage.morphology.binary_opening(image, selem=None)
用此函数比处理灰度图像要快。
四 闭运算(closing)
函数:skimage.morphology.closing(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
先膨胀再腐蚀,可用来填充孔洞。

注意,如果处理图像为二值图像(只有0和1两个值),则可以调用:
skimage.morphology.binary_closing(image, selem=None)
用此函数比处理灰度图像要快。
五 白帽(white-tophat)
函数:skimage.morphology.white_tophat(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
将原图像减去它的开运算值,返回比结构化元素小的白点
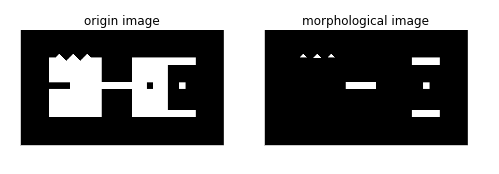
from skimage import io,color
import skimage.morphology as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=color.rgb2gray(io.imread('d:/pic/mor.png'))
dst=sm.white_tophat(img,sm.square(21))
plt.figure('morphology',figsize=(8,8))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('origin image')
plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
结果如下图所示:
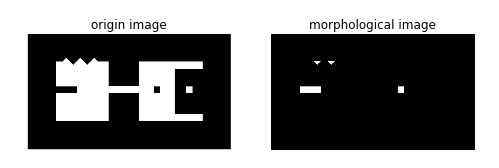
六 黑帽(black-tophat)
函数:skimage.morphology.black_tophat(image, selem=None)
selem表示结构元素,用于设定局部区域的形状和大小。
将原图像减去它的闭运算值,返回比结构化元素小的黑点,且将这些黑点反色。
from skimage import io,color
import skimage.morphology as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=color.rgb2gray(io.imread('d:/pic/mor.png'))
dst=sm.black_tophat(img,sm.square(21))
plt.figure('morphology',figsize=(8,8))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('origin image')
plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.title('morphological image')
plt.imshow(dst,plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
结果如下图所示: