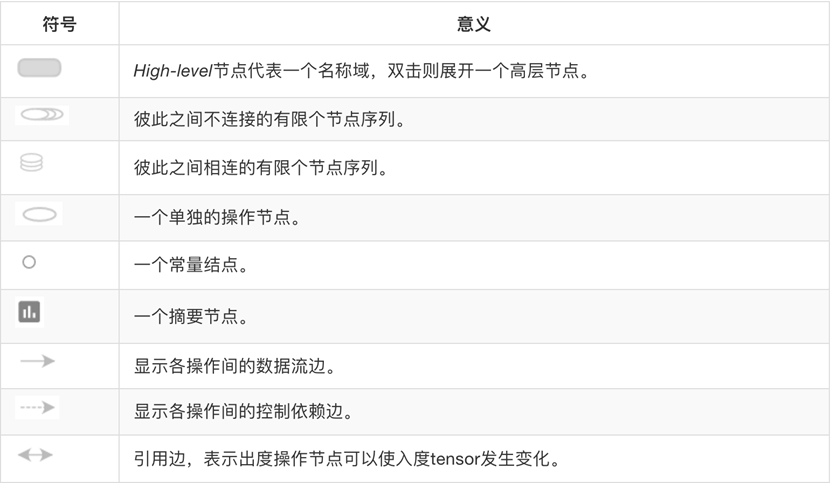
•数据序列化-events文件
TensorBoard 通过读取 TensorFlow 的事件文件来运行
•tf.summary.FileWriter('/tmp/tensorflow/summary/test/',graph=
default_graph)
返回filewriter,写入事件文件到指定目录(最好用绝对路径),以提供给tensorboard使用
•开启
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tensorflow/summary/test/
一般浏览器打开为127.0.0.1:6006 或者 localhost:6006
注:修改程序后,再保存一遍会有新的事件文件,打开默认为最新
import tensorflow as tf import os # 防止警告 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) output = tf.add(input1,input2) with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run([output],feed_dict={input1:10.0,input2:20.0})) summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./tmp/summary/test/', graph=sess.graph)


目的:观察模型的参数、损失值等变量值的变化
1、收集变量
•tf.summary.scalar(name=’’,tensor)收集对于损失函数和准确率等单值变量,name为变量的名字,tensor为值
•tf.summary.histogram(name=‘’,tensor)收集高维度的变量参数
•tf.summary.image(name=‘’,tensor) 收集输入的图片张量能显示图片
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_label, logits=y)) # 梯度下降 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy) # 比较真实标签 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_label, 1)) # tf.cast(xx,tf.float32)改变tensor类型 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) tf.summary.scalar("loss",cross_entropy) tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", accuracy) tf.summary.histogram("W",W)
2、合并变量写入事件文件
•merged= tf.summary.merge_all()
•运行合并:summary= sess.run(merged),每次迭代都需运行
•添加:FileWriter.add_summary(summary,i),i表示第几次的值
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.summary_dir, graph=sess.graph) summary = sess.run(merged) summary_writer.add_summary(summary,i)
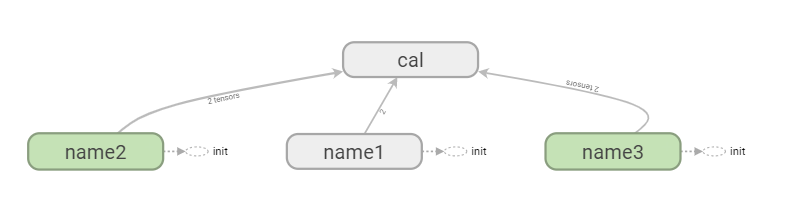
来个复杂一点的:
import tensorflow as tf import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' graph = tf.Graph() with graph.as_default(): with tf.name_scope("name1") as scope: a = tf.Variable([1.0,2.0],name="a") with tf.name_scope("name2") as scope: b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([20]),name="b") c = tf.Variable(tf.ones([20]),name="c") with tf.name_scope("name3") as scope: a1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(21.0), name="a1") b1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(13.0), name="b1") with tf.name_scope("cal") as scope: d = tf.concat([b,c],0) e = tf.add(a,57) c1 = tf.add(a1, b1) with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess: tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # merged = tf.summary.merge_all() summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./tmp/summary/test/', graph=sess.graph) # print(sess.run([d, e, c1]))