这是我Andrew NG的Week2的第一次编程作业,这其中有一些我所学到的东西,以博客的形式记录,随笔。
收获:
- 矩阵运算可以替代循环。
内容包括
- univariate下
- univariate任务下一个demo:
- 数据集绘制为图像
- 损失函数计算
- 梯度下降
- multivariate任务下
- 损失函数代码,梯度下降代码与上述一致(实用矩阵和向量化,从一开始就兼容了多变量的情况)
- normal equation替代梯度下降计算参数
- 提交结果
- 分数
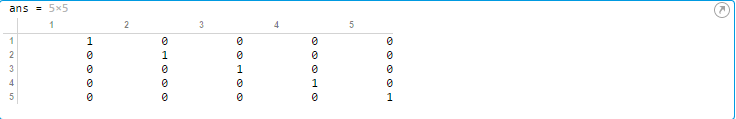
1 function A = warmUpExercise() 2 %WARMUPEXERCISE Example function in octave 3 % A = WARMUPEXERCISE() is an example function that returns the 5x5 identity matrix 4 5 A = []; 6 % ============= YOUR CODE HERE ============== 7 % Instructions: Return the 5x5 identity matrix 8 % In octave, we return values by defining which variables 9 % represent the return values (at the top of the file) 10 % and then set them accordingly. 11 A=eye(5); 12 % =========================================== 13 end
运行效果
1 function plotData(x, y) 2 %PLOTDATA Plots the data points x and y into a new figure 3 % PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points and gives the figure axes labels of 4 % population and profit. 5 6 figure; % open a new figure window 7 8 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== 9 % Instructions: Plot the training data into a figure using the 10 % "figure" and "plot" commands. Set the axes labels using 11 % the "xlabel" and "ylabel" commands. Assume the 12 % population and revenue data have been passed in 13 % as the x and y arguments of this function. 14 % 15 % Hint: You can use the 'rx' option with plot to have the markers 16 % appear as red crosses. Furthermore, you can make the 17 % markers larger by using plot(..., 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10); 18 19 20 plot(x, y, 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10); % Plot the data 21 ylabel('Profit in $10,000s'); % Set the y?axis label 22 xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s'); % Set the x?axis label 23 % ============================================================ 24 25 end
运行效果

1 function J = computeCost(X, y, theta) 2 %COMPUTECOST Compute cost for linear regression 3 % J = COMPUTECOST(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the 4 % parameter for linear regression to fit the data points in X and y 5 6 % Initialize some useful values 7 m = length(y); % number of training examples 8 9 % You need to return the following variables correctly 10 J = 0; 11 12 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== 13 % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta 14 % You should set J to the cost. 15 h_theta = X*theta; 16 sum_vector =ones(1,m); 17 J=sum_vector*((h_theta-y).^2)/(2*m); 18 19 20 21 % ========================================================================= 22 23 end
运行效果
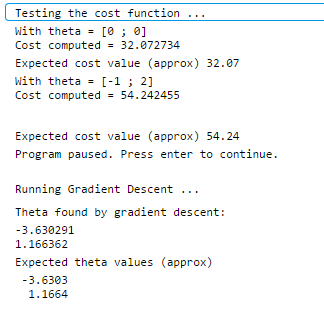
1 function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) 2 %GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta 3 % theta = GRADIENTDESCENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by 4 % taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha 5 6 % Initialize some useful values 7 m = length(y); % number of training examples 8 J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); 9 10 for iter = 1:num_iters 11 12 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== 13 % Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector 14 % theta. 15 % 16 % Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values 17 % of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here. 18 % 19 h_theta = X*theta; 20 errors_vector=h_theta-y; 21 theta_change = (X'*errors_vector)*alpha/(m); 22 theta=theta-theta_change; 23 % ============================================================ 24 25 % Save the cost J in every iteration 26 J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta); 27 28 end 29 30 end
运行效果

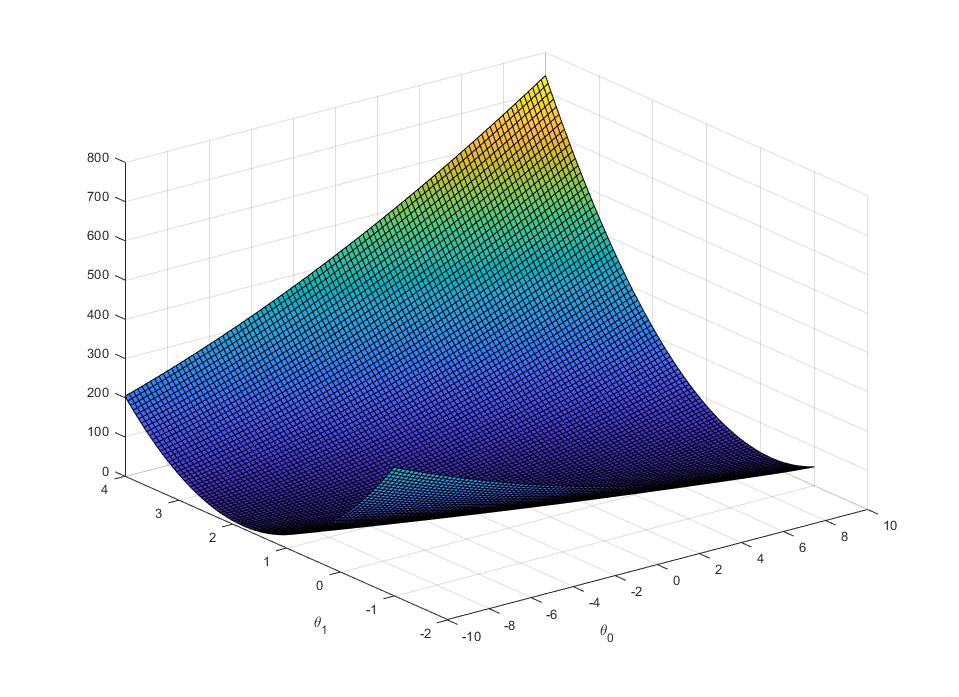
进行数据拟合并预测

损失函数三维立体图像
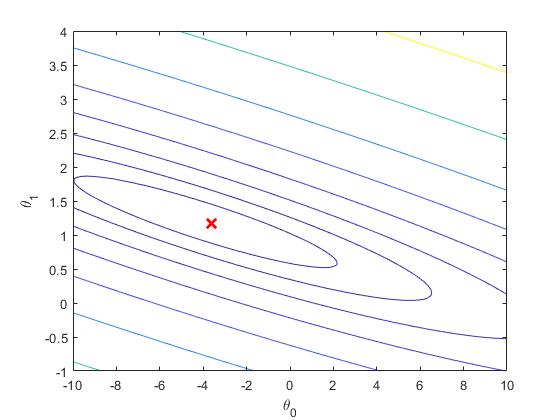
等高线
1 function [theta] = normalEqn(X, y) 2 %NORMALEQN Computes the closed-form solution to linear regression 3 % NORMALEQN(X,y) computes the closed-form solution to linear 4 % regression using the normal equations. 5 6 theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1); 7 8 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== 9 % Instructions: Complete the code to compute the closed form solution 10 % to linear regression and put the result in theta. 11 % 12 13 % ---------------------- Sample Solution ---------------------- 14 15 16 theta=pinv(X'*X)*X'*y; 17 18 % ------------------------------------------------------------- 19 20 21 % ============================================================ 22 23 end
computeCostMulti和gradientDescentMulti与上面univariate一致
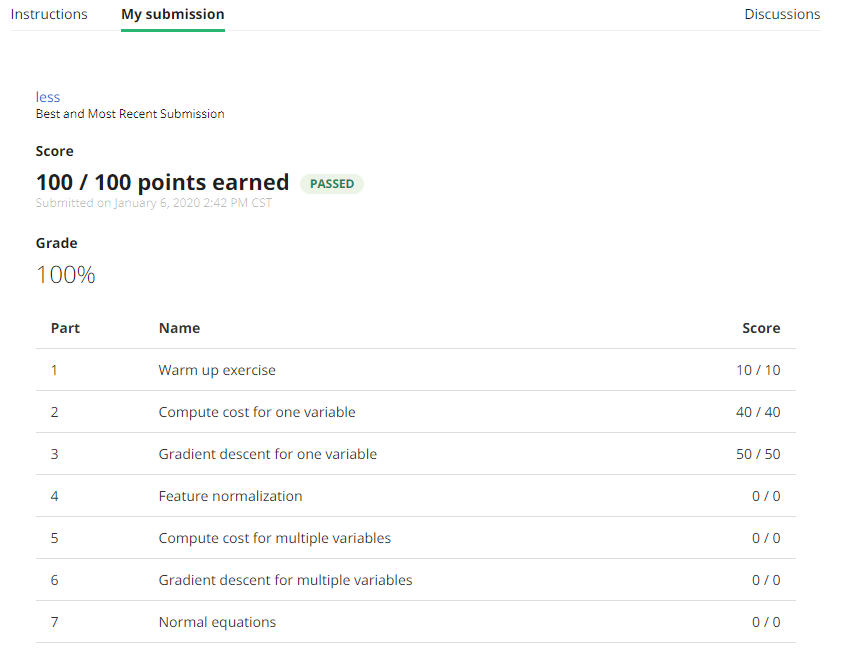
最终结果
1 >> submit 2 == Submitting solutions | Linear Regression with Multiple Variables... 3 Use token from last successful submission (yuhang.tao.email@gmail.com)? (Y/n): Y 4 == 5 == Part Name | Score | Feedback 6 == --------- | ----- | -------- 7 == Warm-up Exercise | 10 / 10 | Nice work! 8 == Computing Cost (for One Variable) | 40 / 40 | Nice work! 9 == Gradient Descent (for One Variable) | 50 / 50 | Nice work! 10 == Feature Normalization | 0 / 0 | Nice work! 11 == Computing Cost (for Multiple Variables) | 0 / 0 | Nice work! 12 == Gradient Descent (for Multiple Variables) | 0 / 0 | Nice work! 13 == Normal Equations | 0 / 0 | Nice work! 14 == -------------------------------- 15 == | 100 / 100 | 16 ==
Coursera上不对选做题加分