spark -- Spark RDD Transformation和Action
目录
- Transformation算子
- 基本的初始化
- 一、map、flatMap、mapParations、mapPartitionsWithIndex
- 1.1map
- 1.2flatMap
- 1.3mapPartitions
- 1.4mapPartitionsWithIndex
- 二、reduce、reduceByKey
- 2.1reduce
- 2.2reduceByKey
- 三、union,join和groupByKey
- 3.1union
- 3.2groupByKey
- 3.3join
- 四、sample、cartesian
- 4.1sample
- 4.2cartesian
- 五、filter、distinct、intersection
- 5.1filter
- 5.2distinct
- 5.3intersection
- 六、coalesce、repartition、repartitionAndSortWithinPartitions
- 6.1coalesce
- 6.2 replication
- 6.3repartitionAndSortWithinPartitions
- 七、cogroup、sortBykey、aggregateByKey
- 7.1cogroup
- 7.2sortBykey
- 7.3aggregateByKey
Transformation算子
基本的初始化
val config = new SparkConf().setAppName("MapPartitionsAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(config) // 获取spark 上下文
一、map、flatMap、mapParations、mapPartitionsWithIndex
1.1 map
def map: Unit ={ val list = List("spark","hadoop","sqoop","hive","storm") val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list) //parallelize第二个参数可以指定RDD分区个数
/**
* 对于map算子,源JavaRDD的每个元素都会进行计算,由于是依次进行传参,所以他是有序的,新RDD的元素顺序与源RDD是相同的。而由有序又引出接下来的flatMap
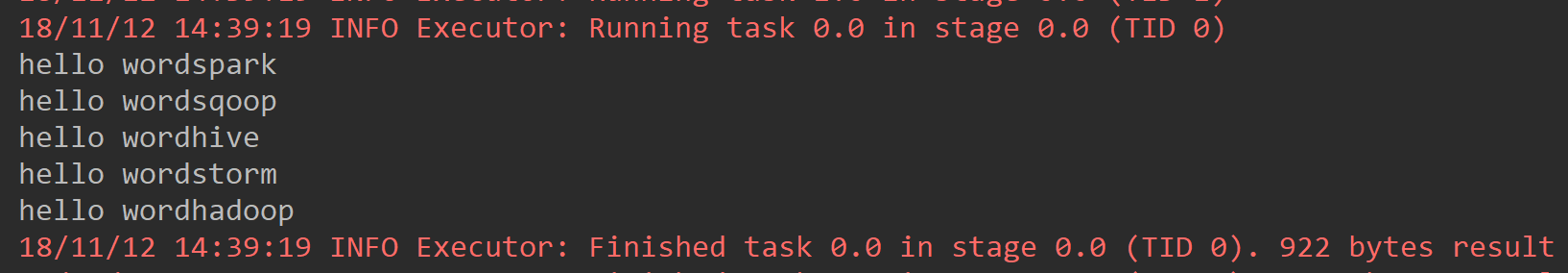
*/ val listMapRDD = listRDD.map(name =>{ "hello word" + name }) listMapRDD.foreach(println(_)) }
1.2 flatMap
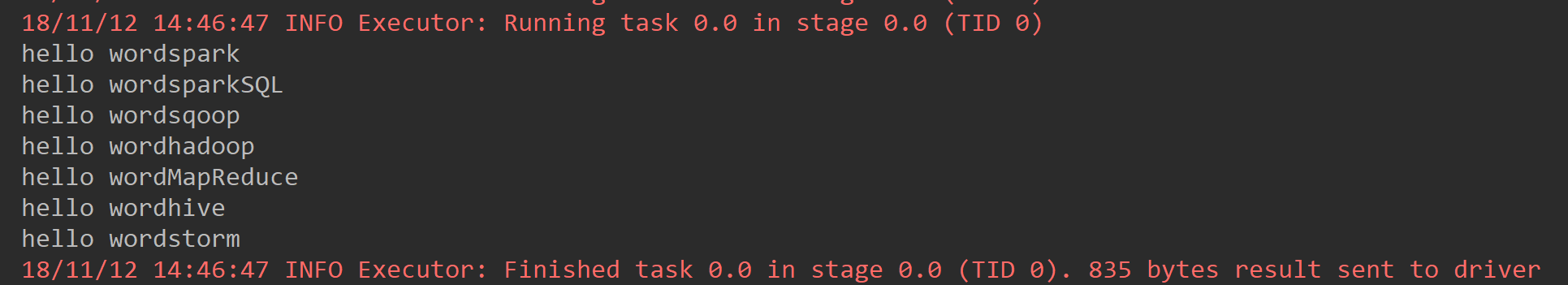
def flatMap: Unit ={ val list = List("spark sparkSQL","hadoop MapReduce","sqoop","hive","storm") val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list) val flatMapRDD = listRDD.flatMap(name => { name.split(" ").map(name =>"hello word"+name) }) flatMapRDD.foreach(println(_)) }
1.3 mapPartitions
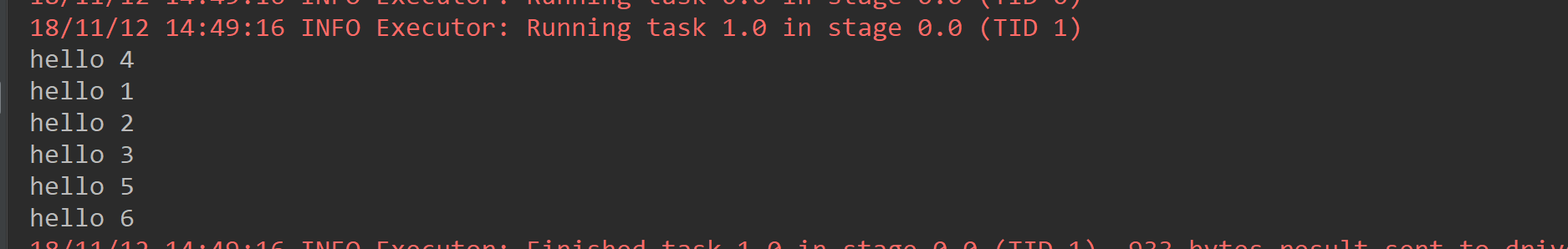
def mapPartitions: Unit ={ val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list,2) /** * map和flatMap都是依次进行参数传递的, * 但有时候需要RDD中的两个元素进行相应操作时(例如:算存款所得时,下一个月所得的利息是要原本金加上上一个月所得的本金56的), * 这两个算子便无法达到目的了,这是便需要mapPartitions算子,他传参的方式是将整个RDD传入, * 然后将一个迭代器传出生成一个新的RDD,由于整个RDD都传入了,所以便能完成前面说的业务。 */ listRDD.mapPartitions(iterator => { val newList: ListBuffer[String] = ListBuffer() while (iterator.hasNext){ newList.append("hello " + iterator.next()) } newList.toIterator }).foreach(name => println(name)) }
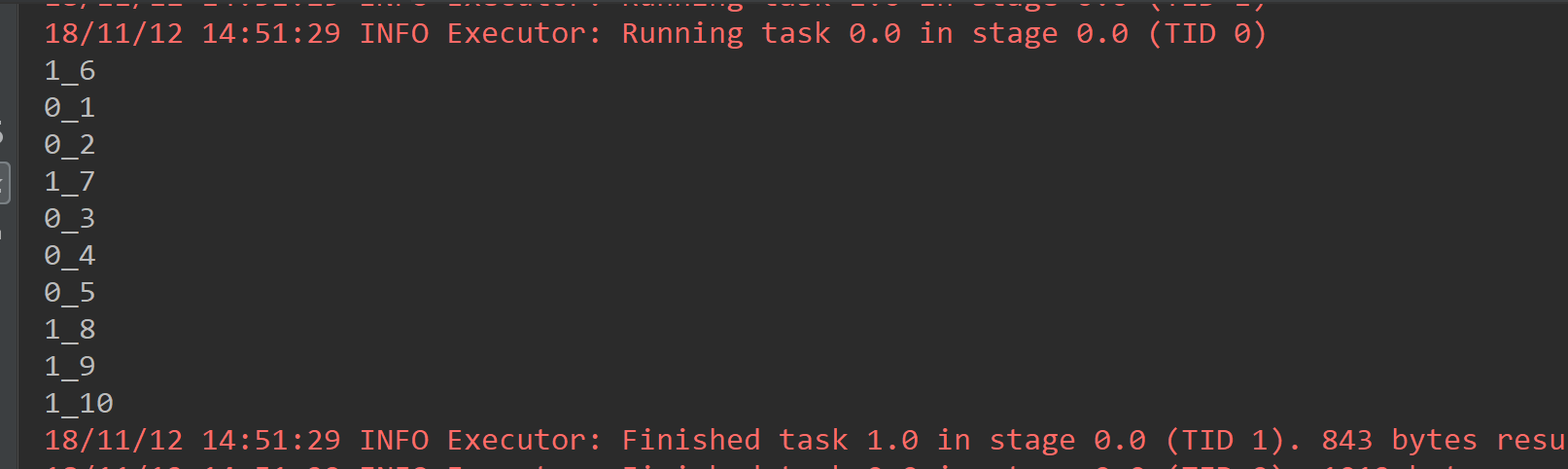
1.4 mapPartitionsWithIndex
每次获取和处理的就是一个分区的数据,并且知道处理的分区的分区号
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("MapPartitionsWithIndexAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) /** * mapPartitionsWithIndex * 每次获取和处理的就是一个分区的数据,并且知道处理的分区的分区号index */ val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list).mapPartitionsWithIndex((index,iterator) => { val listBuffer:ListBuffer[String] = new ListBuffer while (iterator.hasNext){ listBuffer.append(index+"_"+iterator.next()) } listBuffer.iterator },true).foreach(println(_)) }
二、reduce、reduceByKey
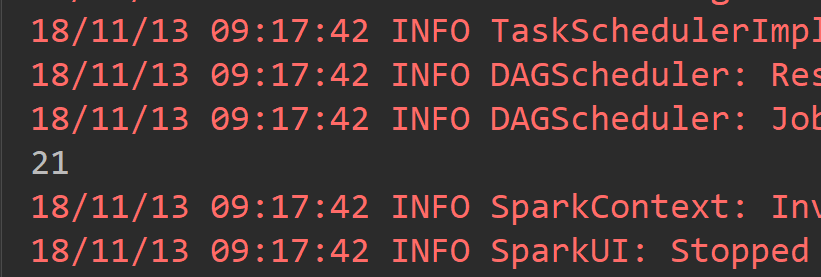
2.1reduce
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ReduceAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list = Array(1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3) val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list) /** * reduce其实是将RDD中的所有元素进行合并, * 当运行call方法时,会传入两个参数, * 在call方法中将两个参数合并后返回,而这个返回值回合一个新的RDD中的元素再次传入call方法中,继续合并,直到合并到只剩下一个元素时。 */ val resule = listRDD.reduce((x,y) => x+y ) println(resule) }
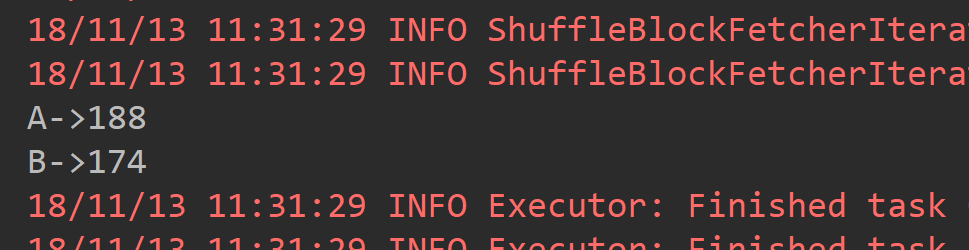
2.2 reduceByKey
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ReduceByKeyAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list = List(("A", 99), ("B", 97), ("A", 89), ("B", 77)) val mapRDD = sc.parallelize(list) /** * reduceByKey仅将RDD中所有K,V对中K值相同的V进行合并。 */ val resultRDD = mapRDD.reduceByKey((_+_)) resultRDD.foreach(tuple => println(tuple._1 + "->"+tuple._2)) }
三、union,join和groupByKey
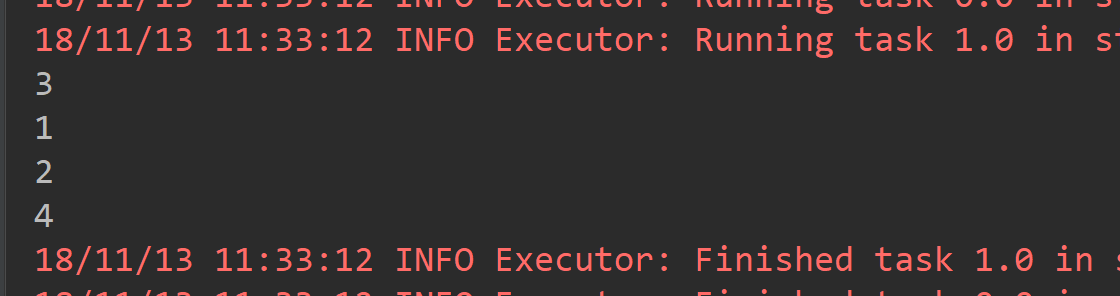
3.1union
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ReduceByKeyAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list1 = List(1,2,3,4) val list2 = List(2,2,3,4) val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(list1) val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(list2) /** * union 操作只是将两个RDD连接起来,相当于List的 ADDALL操作,local[2] 导致有两个分区 */ rdd1.union(rdd2).foreach(println(_)) }
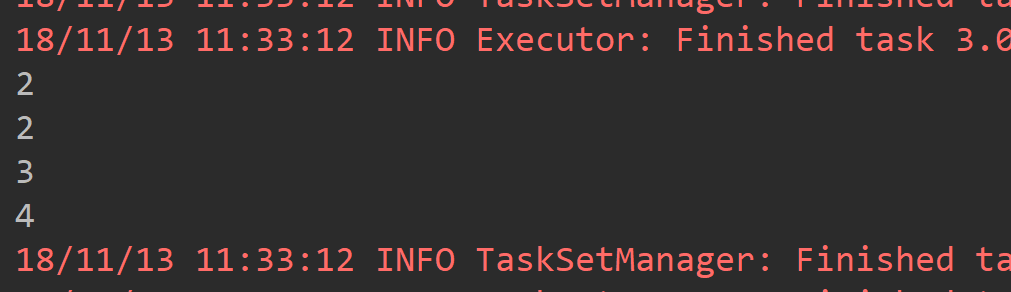
3.2groupByKey
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ReduceByKeyAPP").setMaster("local[2]") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list = List(("hadoop", "MapReduce"), ("hadoop", "hive"), ("Spark", "SparkSQL"), ("Spark", "SpartStreaming")) val listRDD = sc.parallelize(list) /** * groupByKey是将PairRDD中拥有相同key值得元素归为一组 */ val groupByKeyRDD = listRDD.groupByKey() groupByKeyRDD.foreach(touple => { val key = touple._1 val valuesiter = touple._2.iterator var people = "" while(valuesiter.hasNext){ people = people + valuesiter.next + " " } println(key + " -> " + people) }) }
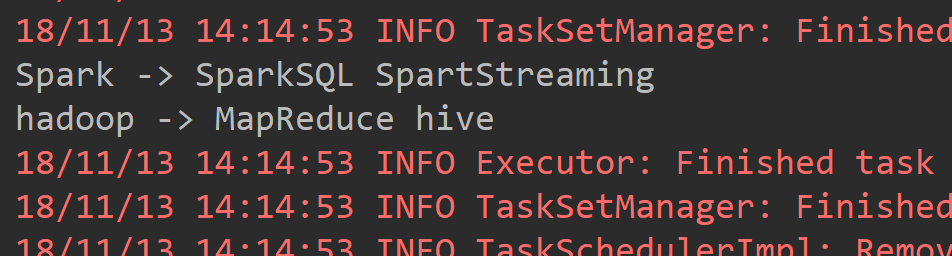
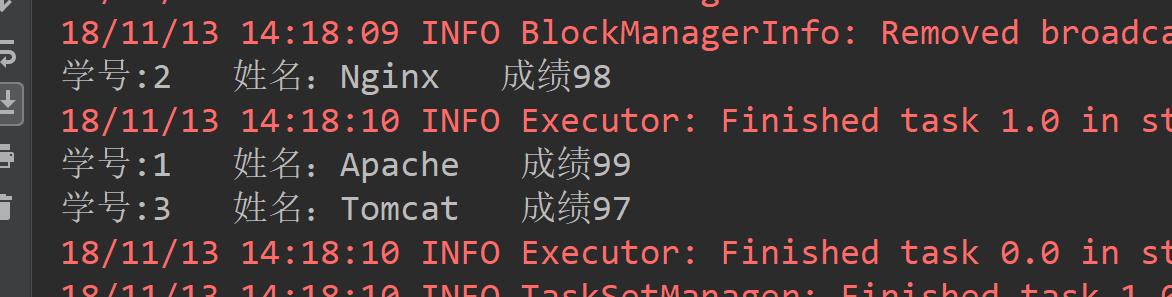
3.3join
def join(): Unit ={ val list1 = List((1, "Apache"), (2, "Nginx"), (3, "Tomcat")) val list2 = List((1, 99), (2, 98), (3, 97)) val list1RDD = sc.parallelize(list1) val list2RDD = sc.parallelize(list2) /** * join是将两个PairRDD合并,并将有相同key的元素分为一组,可以理解为groupByKey和Union的结合 */ val joinRDD = list1RDD.join(list2RDD) joinRDD.foreach(t => { println("学号:"+ t._1 +" 姓名:"+t._2._1 + " 成绩" + t._2._2) }) }