1、数据结构
ThreadLocal对象可以提供线程局部变量,每个线程Thread拥有一份自己的副本变量,多个线程互不干扰。
数据结构如下:
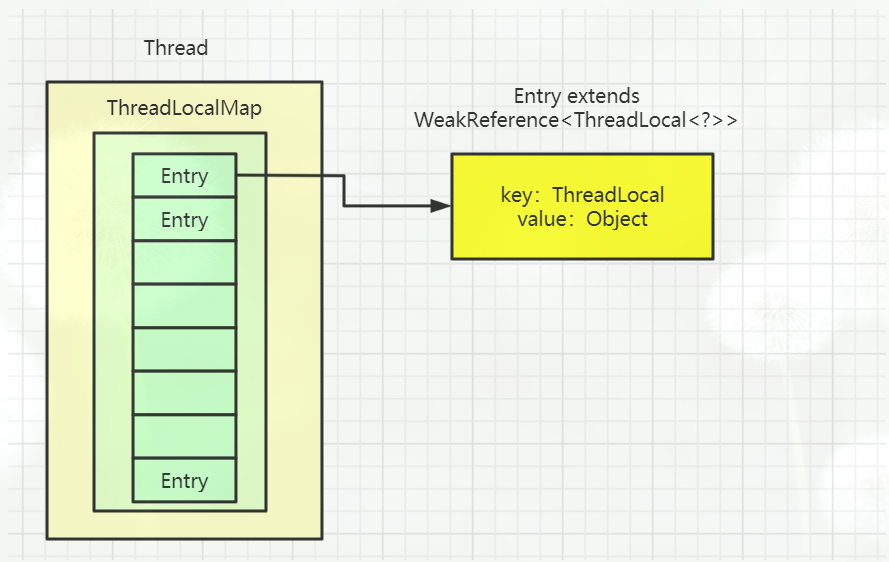
- Thread中存在threadLocals变量,类型是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
- ThreadLocalMap中存在Entry,弱引用
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } } /** * The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two. */ private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** * The table, resized as necessary. * table.length MUST always be a power of two. */ private Entry[] table;
2、set()方法
1 public void set(T value) { 2 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 3 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); 4 if (map != null) 5 map.set(this, value); 6 else 7 createMap(t, value); 8 }
重点看下 map.set(this, value);
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); //获取下标 // 如果tab[i]不为空,那么获取它的下一个 for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); //如果key相同,覆盖 if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } //如果k == null ,说明Entry是过期数据,进行replaceStaleEntry if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size;
//看情况是否扩容 if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
- threadLocalHashCode中涉及一个HASH_INCREMENT,它的黄金分割数。hash增量为这个数字,带来的好处就是hash分布非常的均匀
/** * The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns * implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread * multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables. */ private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
- replaceStaleEntry操作
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value, int staleSlot) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; Entry e; // Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run. // We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual // incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing // up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs). int slotToExpunge = staleSlot; //staleSlot向前查找,当Entry == null则停止,如果找到过期数据,更新soltToExpunge = i for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = prevIndex(i, len)) if (e.get() == null) slotToExpunge = i; // Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever // occurs first // staleSlot向后查找,当Entry == null停止 for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); // If we find key, then we need to swap it // with the stale entry to maintain hash table order. // The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot // encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry // to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run. //替换逻辑 if (k == key) { e.value = value; tab[i] = tab[staleSlot]; tab[staleSlot] = e; // Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists //如果之前slotToExpunge没有改变即没有找到过期数据 if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot) slotToExpunge = i; cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); return; } // If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the // first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the // first still present in the run. if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot) slotToExpunge = i; } // If key not found, put new entry in stale slot 如果没有找到key相同的,那么在staleSlot位置添加元素 tab[staleSlot].value = null; tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value); // If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them 不相同证明存在过期数据,进行清理 if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot) cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); }
如果执行完启发式清理工作后,未清理到任何数据,且当前散列数组中Entry的数量已经达到了列表的扩容阈值(len*2/3),就开始执行rehash()
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash();
首先是会进行探测式清理工作,清理完成之后,table中可能有一些key为null的Entry数据被清理掉,所以此时通过判断size >= threshold - threshold / 4 也就是size >= threshold* 3/4 来决定是否扩容
private void rehash() { expungeStaleEntries(); // Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) resize(); }
扩容,两倍
/** * Double the capacity of the table. */ private void resize() { Entry[] oldTab = table; int oldLen = oldTab.length; int newLen = oldLen * 2; Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen]; int count = 0; for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) { Entry e = oldTab[j]; if (e != null) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == null) { e.value = null; // Help the GC } else { int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); while (newTab[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, newLen); newTab[h] = e; count++; } } } setThreshold(newLen); size = count; table = newTab; }
3、get()方法
public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); }
setInitialValue(),简单明了
private T setInitialValue() { T value = initialValue(); Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); return value; }
4、ThreadLocal内存泄漏问题
现象:比如在使用线程池的情况下,线程一直存活,Entry的key是弱引用会在GC的时候被回收,而value由于存在线程的强引用,不会被回收。虽然ThreadLocal在get()、set()、remove()中都有堆key == null数据的处理。但是极端情况下还是会出现内存泄漏。
解决方法:每次使用完ThreadLocal,都调用它的remove()方法,清除数据。
5、InheritableThreadLocal
如果线程A创建了B线程,那么B线程就是A线程的子线程。
InheritableThreadLocal可以让子线程获取父线程设置的变量。
public class Test01 { private static ThreadLocal threadLocal1 = new InheritableThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("begin"); threadLocal1.set("jack"); System.out.println("1====" + threadLocal1.get()); //jack Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("2====" + threadLocal1.get()); // jack threadLocal1.set("rose"); System.out.println("3====" + threadLocal1.get()); //rose }); thread.start(); thread.join(); System.out.println("4====" + threadLocal1.get()); //jack }
源码分析
public Thread(Runnable target) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); }
走
/** * Initializes a Thread with the current AccessControlContext. * @see #init(ThreadGroup,Runnable,String,long,AccessControlContext,boolean) */ private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true); }
走
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc, boolean inheritThreadLocals) { if (name == null) { throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); } this.name = name; Thread parent = currentThread(); SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); if (g == null) { /* Determine if it's an applet or not */ /* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager what to do. */ if (security != null) { g = security.getThreadGroup(); } /* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter use the parent thread group. */ if (g == null) { g = parent.getThreadGroup(); } } /* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is explicitly passed in. */ g.checkAccess(); /* * Do we have the required permissions? */ if (security != null) { if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION); } } g.addUnstarted(); this.group = g; this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); this.priority = parent.getPriority(); if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); else this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; this.inheritedAccessControlContext = acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); this.target = target; setPriority(priority); if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */ this.stackSize = stackSize; /* Set thread ID */ tid = nextThreadID(); }
走
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap); }
走
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table; int len = parentTable.length; setThreshold(len); table = new Entry[len]; //复制了parent中的值 for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { Entry e = parentTable[j]; if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get(); if (key != null) { Object value = key.childValue(e.value); Entry c = new Entry(key, value); int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); while (table[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); table[h] = c; size++; } } } }