本篇从HashMap的put、get、remove方法入手,分析源码流程
(不涉及红黑树的具体算法)
jkd1.8中HashMap的结构为数组、链表、红黑树的形式

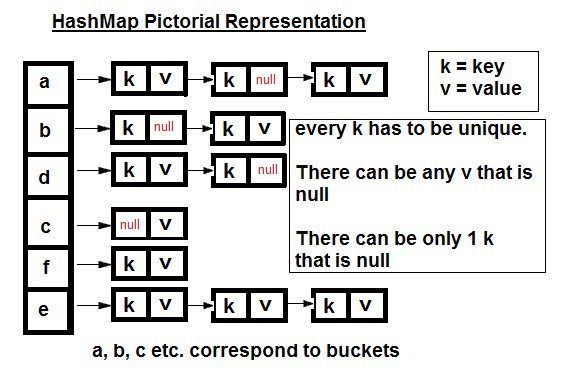
(未转化红黑树时)
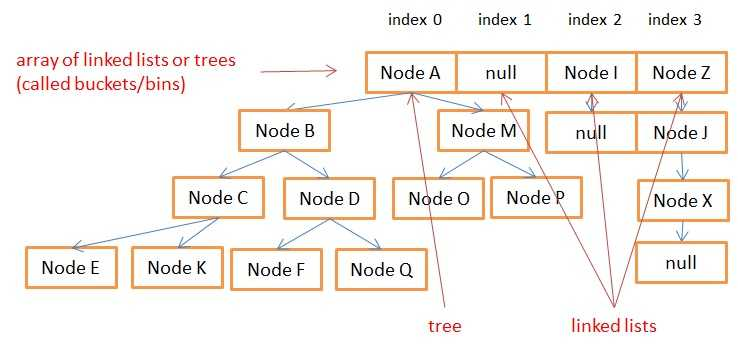
(转化为红黑树时的情况)
一、关于HashMap需要了解的静态常量
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 数组默认初始容量 16
DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR 默认负载因子 0.75
MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY 最小树容量 64
在下面的方法探究中将会提到这些静态常量的用处
二、方法探究
1、put
HashMap中的数组是第一次调用put方法时才创建对象的
下面是从进入put到创建完数组的全过程
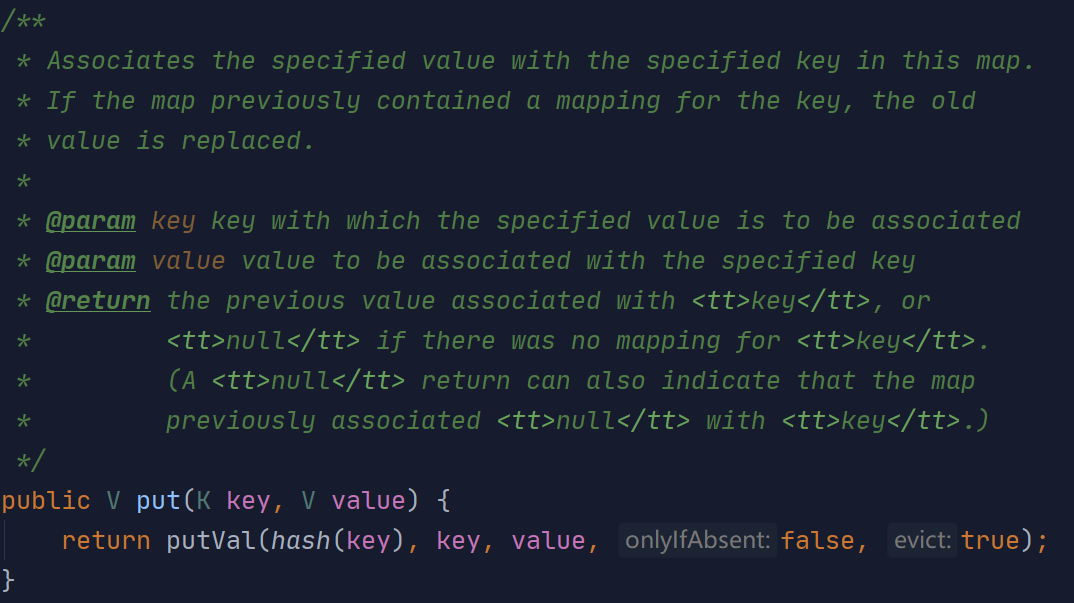
将key、value作为参数传入后,计算key的hash,再传入putVal方法
/** * Implements Map.put and related methods. * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */ final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
putVal()的整个流程如下
1、先判断table是否为null,如果是,调用resize()
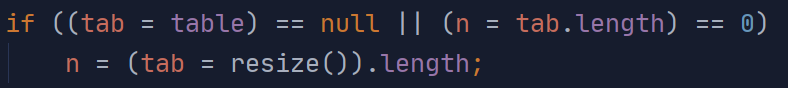

/** * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold. * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move * with a power of two offset in the new table. * * @return the table */ final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
resize():
判断当前table为null后,初始化负载因子DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR
计算当前数组边界DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY
(第一次数组边界为16*0.75=12,当数组超过数组边界时会扩大为两倍。
也就是说数组中的元素达到或大于12时,将第一次扩大数组,大小变为16*2=32)
创建并返回大小为DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY的table对象。
(总的来说resize负责扩大数组容量和初始化数组)
以上就是调用put方法时HashMap对象内数组的创建过程
2、如果进入putVal()判断table不为null
利用hash值与(&)计算出数组下标,并判断是否为空
如果是,创建node对象并存入数组
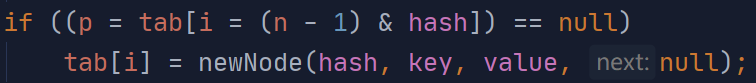
如果不是,从当前下标的链表第一位开始一个个往下对比
①若hash和key值都相同,则break退出循环,之后进行value的替换,并返回oldValue
②若过程中遇到null,则创建node对象
判断是否达到红黑树转换条件:如果当前链表长度达到8,进入treeifyBin方法
判断表长度(如果小于64,则调用resize(),判断要不要增大数组
反之replacementTreeNode,用红黑树代替当前链表
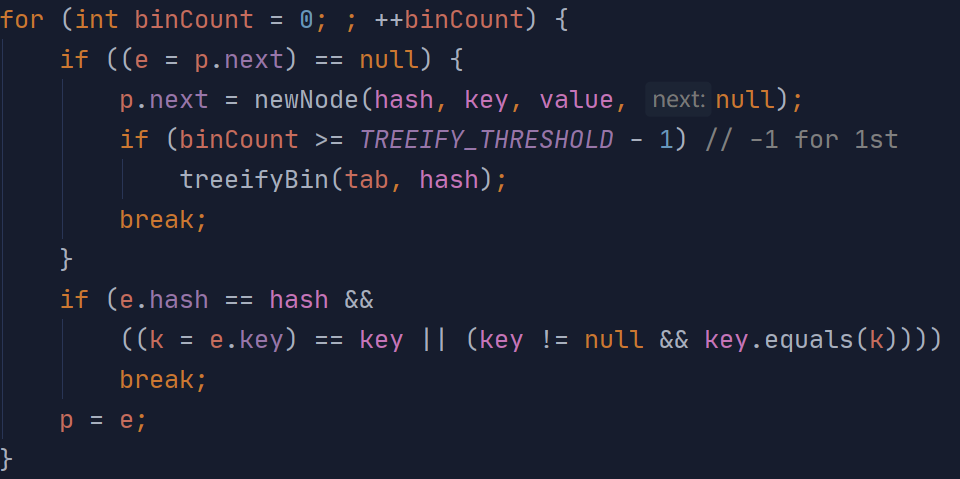
(向下遍历数组当前下标链表的操作)
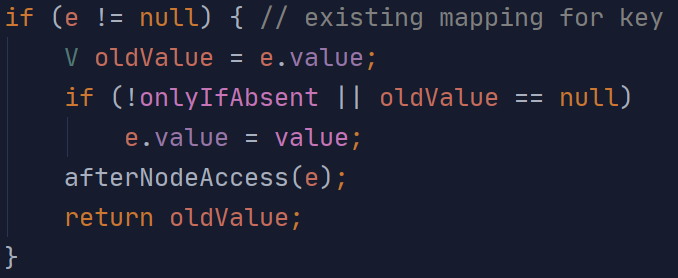
(key相同时value的替换操作)
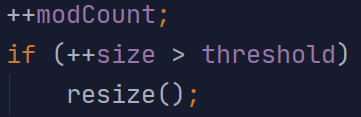
3、增加size(map中元素的数量)和modCount(对map的操作次数)
2、get

* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : * key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise * it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> * indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also * possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. * The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to * distinguish these two cases. * * @see #put(Object, Object) */ public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; }
将key和key的hash传入getNode方法,并获取返回的Node对象的value
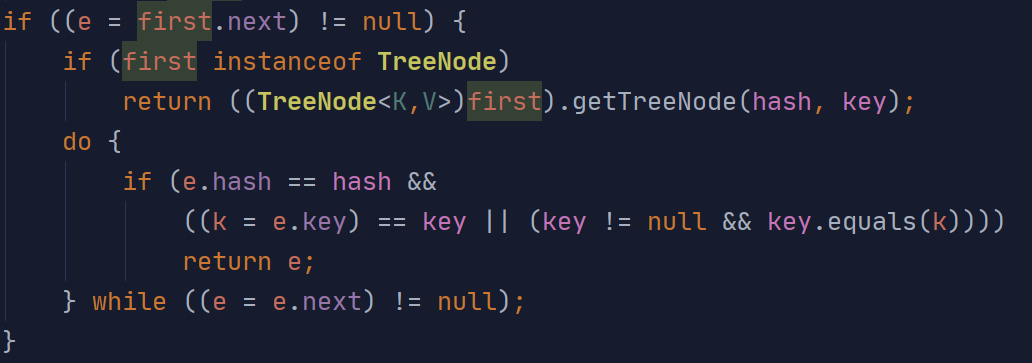
先判断数组不为null,且长度大于0
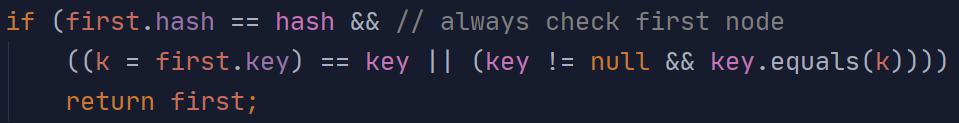
利用hash值先找到node可能在的列的第一个元素(当前传入key可能不存在)
再竖向遍历链表对比hash和key值

(上面的first即为node可能存在的链表的第一个元素)
查找时如果第一个即匹配则直接返回
否则往下遍历直到匹配或node为null
3、removeNode


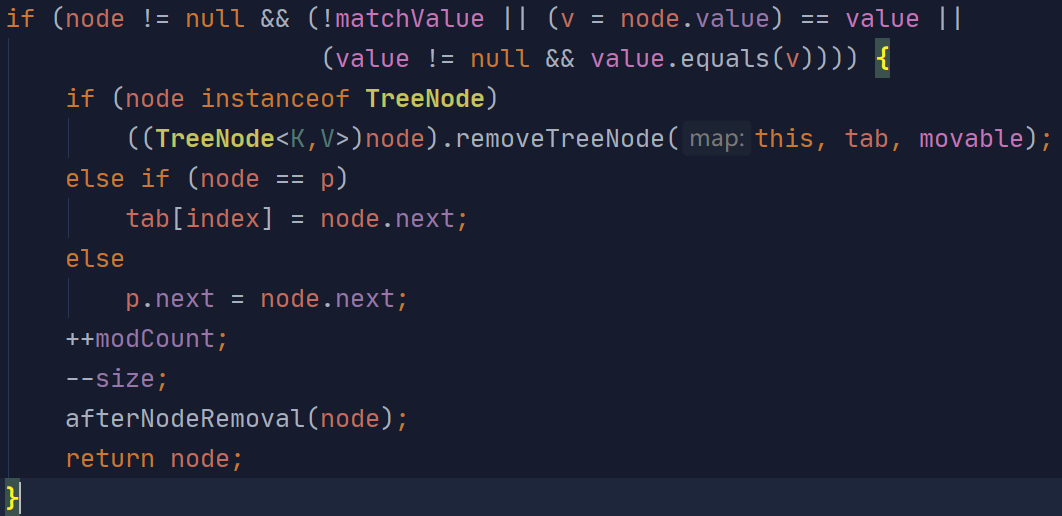
/** * Implements Map.remove and related methods. * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored * @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal * @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing * @return the node, or null if none */ final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) node = p; else if ((e = p.next) != null) { if (p instanceof TreeNode) node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { node = e; break; } p = e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { if (node instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); else if (node == p) tab[index] = node.next; else p.next = node.next; ++modCount; --size; afterNodeRemoval(node); return node; } } return null; }
与getNode的逻辑类似,利用hash值查找可能存在的位置
如果链表第一位就匹配:
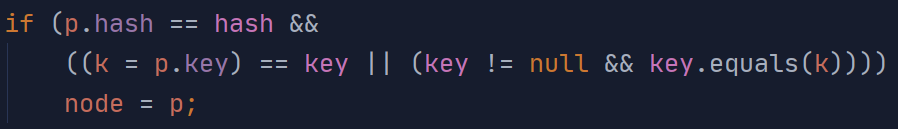
对链表的遍历:
判断node的类型,如果是链表则用node.nest来代替当前位置
最后操作数+1,size-1,返回被remove的node对象