随着线上项目变的日益庞大,每个项目都散落着各种配置文件,如果采用分布式的开发模式,需要的配置文件随着服务增加而不断增多。某一个基础服务信息变更,都会引起一系列的更新和重启,运维苦不堪言也容易出错。
配置中心便是解决此类问题的灵丹妙药。
市面上开源的配置中心有很多,BAT每家都出过,360的QConf、淘宝的diamond、百度的disconf都是解决这类问题。
国外也有很多开源的配置中心Apache Commons Configuration、owner、cfg4j等等。
这里要讲的是Spring Cloud Config,它功能全面强大,可以无缝的和spring体系相结合。
Spring Cloud Config
在我们了解spring cloud config之前,我可以想想一个配置中心提供的核心功能应该有什么
- 提供服务端和客户端支持
- 集中管理各环境的配置文件
- 配置文件修改之后,可以快速的生效
- 可以进行版本管理
- 支持大的并发查询
- 支持各种语言
Spring Cloud Config可以完美的支持以上所有的需求。
Spring Cloud Config项目是一个解决分布式系统的配置管理方案。它包含了Client和Server两个部分,server提供配置文件的存储、以接口的形式将配置文件的内容提供出去,client通过接口获取数据、并依据此数据初始化自己的应用。Spring cloud使用git或svn存放配置文件,默认情况下使用git,我们先以git为例做一套示例。
首先在github上面创建了一个文件夹config-repo用来存放配置文件,为了模拟生产环境,我们创建以下三个配置文件:
// 开发环境 neo-config-dev.properties // 测试环境 neo-config-test.properties // 生产环境 neo-config-pro.properties
每个配置文件中都写一个属性neo.hello,属性值分别是 hello im dev/test/pro 。
下面我们开始配置server端
server 端
1、添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
只需要加入spring-cloud-config-server包引用既可。
2、配置文件
application.yml
server: port: 8001 spring: application: name: spring-cloud-config-server cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://github.com/ityouknow/spring-cloud-starter/ # 配置git仓库的地址 search-paths: config-repo # git仓库地址下的相对地址,可以配置多个,用,分割。 username: # git仓库的账号 password: # git仓库的密码
Spring Cloud Config也提供本地存储配置的方式。
我们只需要设置属性spring.profiles.active=native,Config Server会默认从应用的src/main/resource目录下检索配置文件。
也可以通过 spring.cloud.config.server.native.searchLocations=file:E:/properties/属性来指定配置文件的位置。虽然Spring Cloud Config提供了这样的功能,但是为了支持更好的管理内容和版本控制的功能,还是推荐使用git的方式。
3、启动类
启动类添加 @EnableConfigServer,激活对配置中心的支持
@EnableConfigServer @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args); } }
到此server端相关配置已经完成
4、测试
首先我们先要测试server端是否可以读取到github上面的配置信息,直接访问:http://localhost:8001/neo-config/dev
返回信息如下:
{ "name": "neo-config", "profiles": [ "dev" ], "label": null, "version": null, "state": null, "propertySources": [ { "name": "https://github.com/ityouknow/spring-cloud-starter/config-repo/neo-config-dev.properties", "source": { "neo.hello": "hello im dev" } } ] }
上述的返回的信息包含了配置文件的位置、版本、配置文件的名称以及配置文件中的具体内容,说明server端已经成功获取了git仓库的配置信息。
如果直接查看配置文件中的配置信息可访问:http://localhost:8001/neo-config-dev.properties,返回:neo.hello: hello im dev
修改配置文件 neo-config-dev.properties 中配置信息为:neo.hello=hello im dev update,
再次在浏览器访问http://localhost:8001/neo-config-dev.properties,返回:neo.hello: hello im dev update。
说明server端会自动读取最新提交的内容
仓库中的配置文件会被转换成web接口,访问可以参照以下的规则:
- /{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
- /{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{application}-{profile}.properties
- /{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
以neo-config-dev.properties为例子,它的application是neo-config,profile是dev。
client会根据填写的参数来选择读取对应的配置。
client 端
主要展示如何在业务项目中去获取server端的配置信息
1、添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
引入spring-boot-starter-web包方便web测试
2、配置文件
需要配置两个配置文件,application.properties和bootstrap.properties
application.properties如下:
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-config-client server.port=8002
bootstrap.properties如下:
spring.cloud.config.name=neo-config spring.cloud.config.profile=dev spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8001/ spring.cloud.config.label=master
- spring.application.name:对应{application}部分
- spring.cloud.config.profile:对应{profile}部分
- spring.cloud.config.label:对应git的分支。如果配置中心使用的是本地存储,则该参数无用
- spring.cloud.config.uri:配置中心的具体地址
- spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id:指定配置中心的service-id,便于扩展为高可用配置集群。
特别注意:上面这些与spring-cloud相关的属性必须配置在bootstrap.properties中,config部分内容才能被正确加载。
因为config的相关配置会先于application.properties,而bootstrap.properties的加载也是先于application.properties。
3、启动类
@SpringBootApplication public class ConfigClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientApplication.class, args); } }
4、web测试
使用@Value注解来获取server端参数的值
@RestController class HelloController { @Value("${neo.hello}") private String hello; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String from() { return this.hello; } }
启动项目后访问:http://localhost:8002/hello,返回:hello im dev update说明已经正确的从server端获取到了参数。
到此一个完整的服务端提供配置服务,客户端获取配置参数的例子就完成了。
我们在进行一些小实验,手动修改neo-config-dev.properties中配置信息为:neo.hello=hello im dev update1提交到github,
再次在浏览器访问http://localhost:8002/hello,返回:neo.hello: hello im dev update,
说明获取的信息还是旧的参数,这是为什么呢?
因为springboot项目只有在启动的时候才会获取配置文件的值,修改github信息后,client端并没有在次去获取,所以导致这个问题。
如何去解决这个问题呢?
refresh
Spring Cloud Config分服务端和客户端,服务端负责将git(svn)中存储的配置文件发布成REST接口,客户端可以从服务端REST接口获取配置。但客户端并不能主动感知到配置的变化,从而主动去获取新的配置。客户端如何去主动获取新的配置信息呢,
springcloud已经给我们提供了解决方案,每个客户端通过POST方法触发各自的/refresh。
修改spring-cloud-config-client项目已到达可以refresh的功能。
1、添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
增加了spring-boot-starter-actuator包,spring-boot-starter-actuator是一套监控的功能,可以监控程序在运行时状态,其中就包括/refresh的功能。
2、 开启更新机制
需要给加载变量的类上面加载@RefreshScope,在客户端执行/refresh的时候就会更新此类下面的变量值。
@RestController @RefreshScope // 使用该注解的类,会在接到SpringCloud配置中心配置刷新的时候,自动将新的配置更新到该类对应的字段中。 class HelloController { @Value("${neo.hello}") private String hello; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String from() { return this.hello; } }
3、测试
springboot 1.5.X 以上默认开通了安全认证,所以需要在配置文件application.properties添加以下配置
management.security.enabled=false
OK 这样就改造完了,以post请求的方式来访问 http://localhost:8002/refresh 就会更新修改后的配置文件。
我们再次来测试,首先访问http://localhost:8002/hello,返回:hello im dev,我将库中的值修改为hello im dev update。
在win上面打开cmd执行curl -X POST http://localhost:8002/refresh,返回["neo.hello"]说明已经更新了neo.hello的值。
我们再次访问http://localhost:8002/hello,返回:hello im dev update,客户端已经得到了最新的值。
每次手动刷新客户端也很麻烦,有没有什么办法只要提交代码就自动调用客户端来更新呢,github的webhook是一个好的办法。
4、webhook
WebHook是当某个事件发生时,通过发送http post请求的方式来通知信息接收方。
Webhook来监测你在Github.com上的各种事件,最常见的莫过于push事件。
如果你设置了一个监测push事件的Webhook,那么每当你的这个项目有了任何提交,这个Webhook都会被触发,
这时Github就会发送一个HTTP POST请求到你配置好的地址。
如此一来,你就可以通过这种方式去自动完成一些重复性工作,比如,你可以用Webhook来自动触发一些持续集成(CI)工具的运作,比如Travis CI;又或者是通过 Webhook 去部署你的线上服务器。下图就是github上面的webhook配置。
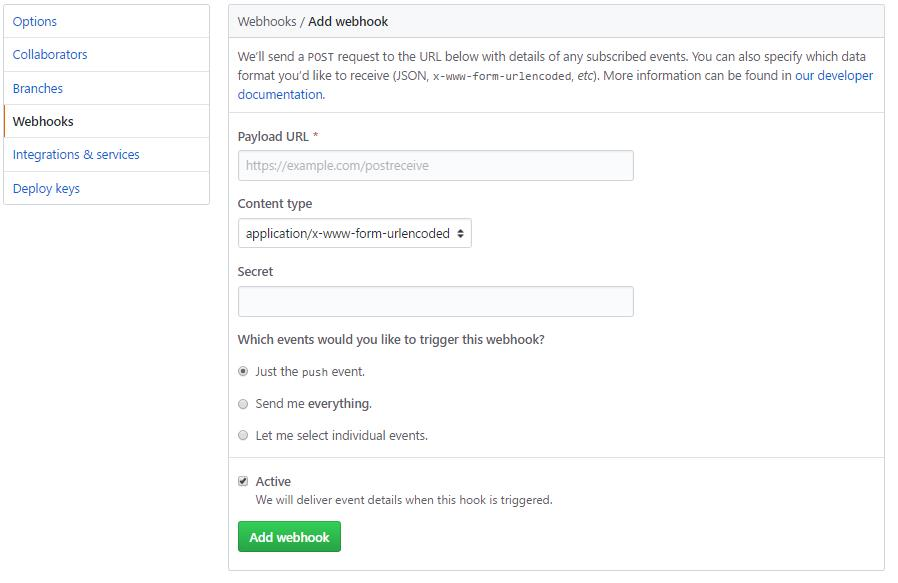
Payload URL:触发后回调的URLContent type:数据格式,两种一般使用jsonSecret:用作给POST的body加密的字符串。采用HMAC算法events:触发的事件列表。
| events事件类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| push | 仓库有push时触发。默认事件 |
| create | 当有分支或标签被创建时触发 |
| delete | 当有分支或标签被删除时触发 |
svn也有类似的hook机制,每次提交后会触发post-commit脚本,我们可以在这里写一些post请求
这样我们就可以利用hook的机制去触发客户端的更新,但是当客户端越来越多的时候hook支持的已经不够优雅,另外每次增加客户端都需要改动hook也是不现实的。其实Spring Cloud给了我们更好解决方案,后面文章来介绍。