分析线程经典案例生产者消费者
1 /** 2 共享数据 3 */ 4 class Resource 5 { 6 private String name; 7 private int count=1; 8 private boolean flag=false; 9 10 public synchronized void set(String name) 11 { 12 if(flag) 13 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 14 this.name=name+count; 15 count++; 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...生产者..." + this.name); 17 flag = true; 18 notify(); 19 } 20 21 public synchronized void out() 22 { 23 if(!flag) 24 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==消费者==" + this.name); 26 flag = false; 27 notify(); 28 } 29 } 30 31 //定义线程任务(生产者线程) 32 class Producer implements Runnable 33 { 34 private Resource r; 35 36 Producer(Resource r) 37 { 38 this.r=r; 39 } 40 public void run() 41 { 42 while(true) 43 { 44 r.set("商品"); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 //定义线程任务(消费者线程) 49 class Consumer implements Runnable 50 { 51 private Resource r; 52 53 Consumer(Resource r) 54 { 55 this.r=r; 56 } 57 58 public void run() 59 { 60 while(true) 61 { 62 r.out(); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 class ProducerConsumerDemo 68 { 69 public static void main(String[] args) 70 { 71 //实例化共享资源 72 Resource r = new Resource(); 73 //实例化线程任务,指定共享资源 74 Producer p=new Producer(r); 75 Consumer c=new Consumer(r); 76 //实例化线程,指定线程任务 77 Thread t0=new Thread(p); 78 Thread t1=new Thread(p); 79 Thread t2=new Thread(c); 80 Thread t3=new Thread(c); 81 //开启线程,执行线程任务中的run方法 82 t0.start(); 83 t1.start(); 84 t2.start(); 85 t3.start(); 86 } 87 }
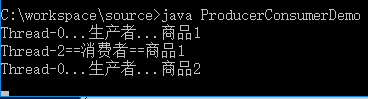
运行结果:

结果分析:

那么怎么再判断flag呢?while
代码如下:
1 class Resource 2 { 3 private String name; 4 private int count=1; 5 private boolean flag=false; 6 7 public synchronized void set(String name) // 有两个线程t0 t1 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 11 this.name=name+count; 12 count++; 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...生产者..." + this.name); 14 flag = true; 15 notify(); 16 } 17 18 public synchronized void out() // 有两个线程t2 t3 19 { 20 while(!flag) 21 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==消费者==" + this.name); 23 flag = false; 24 notify(); 25 } 26 }
结果出现死锁:
结果分析:

通过分析,那能不能每次唤醒只唤醒对方线程(如生产者线程只唤醒消费者线程,消费者线程只唤醒生产者线程),查看Object对象方法中没有,但是有一个notifyAll()方法,实在不行就把所有阻塞线程(相同同步锁的线程)都唤醒。
1 class Resource 2 { 3 private String name; 4 private int count=1; 5 private boolean flag=false; 6 7 public synchronized void set(String name) // 有两个线程t0 t1 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 11 this.name=name+count; 12 count++; 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...生产者..." + this.name); 14 flag = true; 15 notifyAll(); 16 } 17 18 public synchronized void out() // 有两个线程t2 t3 19 { 20 while(!flag) 21 try{this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==消费者==" + this.name); 23 flag = false; 24 notifyAll(); 25 } 26 }
结果:
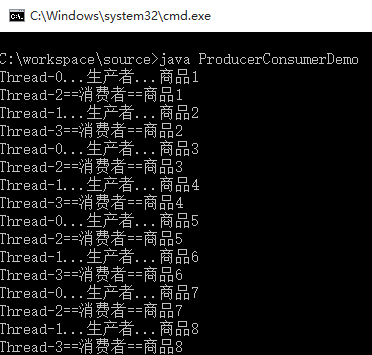
这样就可以了。
总结:
if判断只能判断一次,如果执行等待方法,下次唤醒的线程获取执行权后(唤醒后的线程会从上次等待位置,向下执行)就不能再判断
while判断解决唤醒的线程获取执行权后无法判断
notify:只能唤醒任意一个线程,有可能会唤醒本方线程,while+notify会导致死锁
notifyAll:解决了死锁问题