一、Spring工厂类的结构
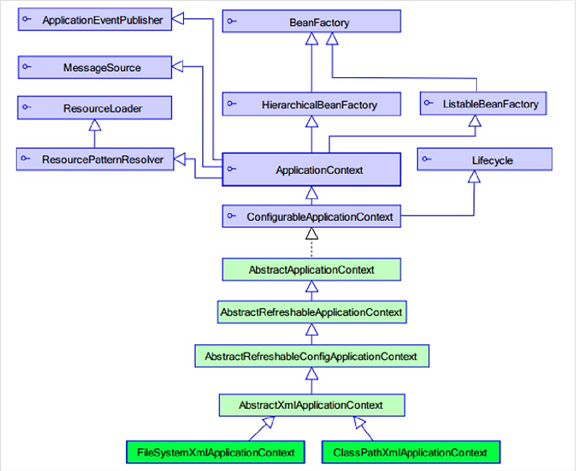
ApplicationContext继承BeanFactory
①、BeanFactory:老版本的工厂类
BeanFactory:调用getBean方法时,才会生成类的实例
②、ApplicationContext:新版本的工厂类
ApplicationContext:加载配置文件时,就会将Spring管理的类都实例化
ApplicationContext有两个实现类
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径(src)下的配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载文件系统(绝对路径如:c\xxapplicationContext.xml)下的配置文件
二、Spring的配置
①、XML的提示配置(无网络情况下)

②、Bean的相关配置
Ⅰ、<bean>标签的id和name的配置
-
-
- id :使用了约束中的唯一约束。里面不能出现特殊字符的。
- name :没有使用约束中的唯一约束(理论上可以出现重复的,但是实际开发不能出现的)。里面可以出现特殊字符。
- Spring和Struts1框架整合的时候 <bean name=”/user” class=””/>
-
Ⅱ、Bean的生命周期的配置(了解)
-
-
- init-method :Bean被初始化的时候执行的方法
- destroy-method :Bean被销毁的时候执行的方法(Bean是单例创建,工厂关闭)
-
Ⅲ、Bean的作用范围的配置(重点)
scope :Bean的作用范围
-
-
- singleton :默认的,Spring会采用单例模式创建对象。
- prototype :多例模式。(Struts2和Spring整合一定会用到)
- request :应用在web项目中,Spring创建对象存入到request范围中。
- session :应用在web项目中,Spring创建对象存入到session范围中。
- globalsession :应用在web项目中,必须在porlet环境下使用。但是如果没有这种环境,相对于session。
-
三、Spring的Bean的实例化方式(Bean已经都交给Spring管理,Spring创建这些类的时候,有几种方式:)
①、无参构造方法的方式(默认)
public class Bean1 { public Bean1() { super(); System.out.println("Bean1的无参的构造方法执行..."); } }
编写配置
<bean id="bean1" class="com.xx.spring.demo1.Bean1"></bean>
②、静态工厂实例化
public class Bean2Factory { public static Bean2 createBean2() { System.out.println("Bean2Factory中方法执行了...."); return new Bean2(); } }
编写配置
<bean id="bean2" class="com.xx.spring.demo1.Bean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2" ></bean>
③、实例工厂(非静态工厂)实例化
public class Bean3Factory { public Bean3 createBean3() { System.out.println("Bean3Factory中方法执行了...."); return new Bean3(); } }
编写配置
<!-- 1、实例化工厂 --> <bean id="bean3Factory" class="com.xx.spring.demo1.Bean3Factory" ></bean> <!-- 2、调用实例化工厂的方法 --> <bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="createBean3" ></bean>
四、Spring的属性注入
①、构造方法的属性注入
编写类
public class Car { private String name; private Long price; /** * @param name * @param price */ public Car(String name, Long price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }
编写配置
<bean id="car" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Car"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="WAMA"/> <constructor-arg name="price" value="1000000"/> </bean>
测试方法
@Test public void demo2() { // 创建Spring的工厂 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Car car = (Car) applicationContext.getBean("car"); System.out.println(car); }
②、Set方法的方式的属性注入
Ⅰ、set方法的属性注入(属性类型:非自定义对象类型)
编写类
public class Car { private String name; private Long price; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setPrice(Long price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }
编写配置
<bean id="car" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Car"> <property name="name" value="WAMA"/> <property name="price" value="1000000"/> </bean>
测试方法使用①测试方法
Ⅱ、set方法的属性注入(属性类型:自定义对象类型)
编写类
public class Employee { private String name; private Car car; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
编写配置
<bean id="car" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Car"> <property name="name" value="WAMA"/> <property name="price" value="1000000"/> </bean> <bean id="employee" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Employee"> <property name="name" value="zhangsan"/> <!-- name:与employee类中的属性名一致( private Car car;) ref:与配置文件中对应对象的bean中的id/name一致 --> <property name="car" ref="car"/> </bean>
测试方法
@Test public void demo2() { // 创建Spring的工厂 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Employee employee = (Employee) applicationContext.getBean("employee"); System.out.println(employee); }
③、P名称空间的属性注入(Spring2.5以后)
Ⅰ、写法:
- 普通属性:p:属性名="值"
- 对象属性:p:属性名-ref="值"
Ⅱ、P名称空间的引入
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
Ⅲ、使用p名称空间
<bean id="car" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Car" p:name="WAMA" p:price="3000000"></bean> <bean id="employee" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Employee" p:name="lisi" p:car-ref="car"></bean>
④、SpEL的属性注入(Spring3.0以后)
SpEL:Spring Expression Language ,Spring的表达式语言
语法:#{SpEL}
<bean id="car" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Car"> <property name="name" value="#{'BWA'}"/> <property name="price" value="#{8000000}"/> </bean> <bean id="employee" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.Employee"> <property name="name" value="#{'wangwu'}"/> <property name="car" value="#{car}"/> </bean>
更多语法链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1XBCKU7rXRO07QBMGjzvhAQ 提取码: 26sc
五、集合类型属性注入
编写类
public class CollectionBean { private String[] arrs; private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private HashMap<String, String> map; public void setArrs(String[] arrs) { this.arrs = arrs; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public void setMap(HashMap<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } @Override public String toString() { return "CollectionBean [arrs=" + Arrays.toString(arrs) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map + "]"; } }
编写配置
<bean id="collectionBean" class="com.xxx.spring.demo2.CollectionBean"> <!-- 数组类型 --> <property name="arrs"> <list> <value>zhangsan</value> <value>lisi</value> <value>wangwu</value> </list> </property> <!-- list --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>zhaoliu</value> <value>tianqi</value> <value>haoba</value> </list> </property> <!-- set --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>jiujiu</value> <value>shishi</value> <value>xixi</value> </set> </property> <!-- map --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="one" value="Vone"/> <entry key="two" value="Vtwo"/> <entry key="three" value="Vthree"/> <entry key="four" value="Vfour"/> </map> </property> </bean>
编写测试方法
@Test public void demo3() { // 创建Spring的工厂 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean collectionBean = (CollectionBean) applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(collectionBean); }
六、Spring分模块开发的配置
①、在加载配置文件的时候加载多个配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml", "applicationContext2.xml", "applicationContext3.xml");
②、在配置文件中引入其他配置文件
<import resource="applicationContext2.xml"/> <import resource="applicationContext3.xml"/> <import resource="applicationContext4.xml"/> <import resource="applicationContext5.xml"/>