双摆是物理中的一个概念,先给下单摆与双摆的定义:
单摆:由一根不可伸长、质量不计的绳子,上端固定,下端系一个质点的装置。
双摆:是一个摆的支点装在另一摆的下部所形成的组合物体。双摆有两个摆角,所以有两个自由度。双摆是多自由度振动系统的最简单的力学模型之一,它也是一种混沌实例。
这里对双摆的实现程序与上一篇文章中三体的实现很相似,要实现它的程序需要一定的数学基础。
下面两个GIF动画图像为双摆的录屏:
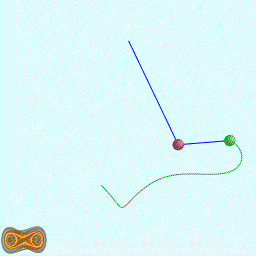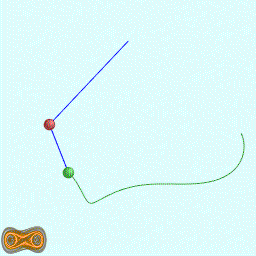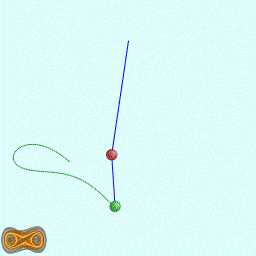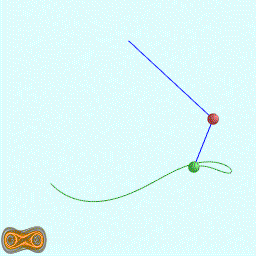
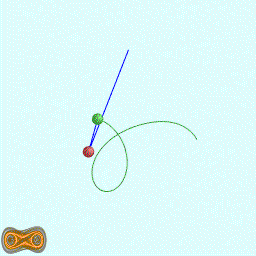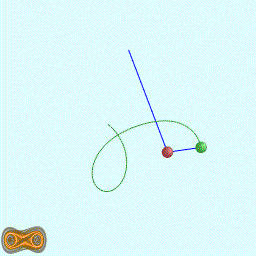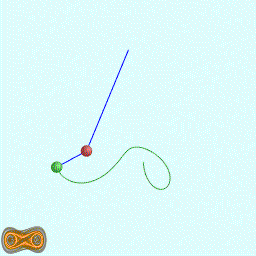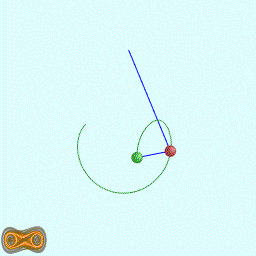
先写了一个双摆的抽象基类:
1 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 inline float rand2(float a, float b) 4 { 5 const float r = (float)(::rand() / ((float)RAND_MAX + 1)); 6 return r*(b-a) + a; 7 } 8 9 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10 11 class IDoublePendulum 12 { 13 public: 14 15 IDoublePendulum() 16 { 17 m_fGravity = 9.8f; 18 19 m_m1 = 1.0f; 20 m_m2 = 2.0f; 21 22 m_l1 = 1.0f; 23 m_l2 = 2.0f; 24 } 25 26 virtual ~IDoublePendulum() {} 27 28 // 重置 29 virtual void Reset() 30 { 31 m_m1 = rand2(1.0f, 5.0f); 32 m_m2 = rand2(1.0f, 5.0f); 33 34 m_l1 = rand2(1.0f, 5.0f); 35 m_l2 = rand2(1.0f, 5.0f); 36 } 37 38 // 按时更新 39 virtual void Update(float deltaTime) = NULL; 40 41 // 重力系数 42 virtual void SetGravity(float g) 43 { 44 m_fGravity = g; 45 } 46 47 // 质量 48 virtual void SetMass1(float m) 49 { 50 m_m1 = m; 51 } 52 53 virtual void SetMass2(float m) 54 { 55 m_m2 = m; 56 } 57 58 // 长度 59 virtual void SetLength1(float l) 60 { 61 m_l1 = l; 62 UpdatePosition(); 63 } 64 65 virtual void SetLength2(float l) 66 { 67 m_l2 = l; 68 UpdatePosition(); 69 } 70 71 float GetGravity() const 72 { 73 return m_fGravity; 74 } 75 76 float GetMass1() const 77 { 78 return m_m1; 79 } 80 81 float GetMass2() const 82 { 83 return m_m2; 84 } 85 86 float GetLength1() const 87 { 88 return m_l1; 89 } 90 91 float GetLength2() const 92 { 93 return m_l2; 94 } 95 96 const Vec3& GetPosition1() const 97 { 98 return m_pos1; 99 } 100 101 const Vec3& GetPosition2() const 102 { 103 return m_pos2; 104 } 105 106 protected: 107 // 更新两球位置 108 virtual void UpdatePosition() = NULL; 109 110 protected: 111 float m_fGravity; // 重力系数 112 113 float m_m1, m_m2; // 两球质量 114 float m_l1, m_l2; // 两球距离 115 116 Vec3 m_pos1, m_pos2;// 两球位置 117 };
从IDoublePendulum中可以看到双摆的几个输入数据是:重力系数,两摆的距离和两球质量。而计算的数据是:每一个时刻两个球的位置。
下一步是对该基类进行继承实现。
.h
1 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 #ifndef _DoublePendulum01_H_ 4 #define _DoublePendulum01_H_ 5 6 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 8 #include "IDoublePendulum.h" 9 10 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11 12 class DoublePendulum01 : public IDoublePendulum 13 { 14 public: 15 DoublePendulum01() 16 { 17 m_a1 = 1.0f; 18 m_a2 = 2.0f; 19 20 m_v1 = 0.0f; 21 m_v2 = 0.0f; 22 23 m_w1 = m_a1; 24 m_w2 = m_a2; 25 } 26 27 // 重置 28 void Reset(); 29 30 // 按时更新 31 void Update(float deltaTime); 32 33 protected: 34 void UpdatePosition() 35 { 36 m_pos1.x = m_l1*sinf(m_w1); 37 m_pos1.y = -m_l1*cosf(m_w1); 38 m_pos1.z = 0.0f; 39 40 m_pos2.x = m_pos1.x + m_l2*sinf(m_w2); 41 m_pos2.y = m_pos1.y - m_l2*cosf(m_w2); 42 m_pos2.z = 0.0f; 43 } 44 45 private: 46 float m_a1, m_a2; // 两球初始角度 47 float m_w1, m_w2; // 两球当前角度 48 float m_v1, m_v2; // 两球的角加速度 49 }; 50 51 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 52 53 #endif
CPP
1 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 #include "DoublePendulum01.h" 4 5 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6 7 /* 8 求解线型方程组 9 a*x + b*y + c = 0 10 d*x + e*y + f = 0 11 */ 12 inline bool SolveLinalg(float a, float b, float c, float d, float e, float f, float& x, float& y) 13 { 14 float t = b*d - a*e; 15 if (fabs(t) < FLT_EPSILON) 16 { 17 x = 0.0f; 18 y = 0.0f; 19 20 return false; 21 } 22 23 x = (c*e - b*f)/t; 24 y = (a*f - c*d)/t; 25 26 return true; 27 } 28 29 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 30 31 void DoublePendulum01::Reset() 32 { 33 IDoublePendulum::Reset(); 34 35 m_a1 = rand2(-2.0f, 2.0f); 36 m_a2 = rand2(-2.0f, 2.0f); 37 38 m_v1 = 0.0f; 39 m_v2 = 0.0f; 40 41 m_w1 = m_a1; 42 m_w2 = m_a2; 43 44 UpdatePosition(); 45 } 46 47 void DoublePendulum01::Update(float deltaTime) 48 { 49 float a = m_l1*m_l1*(m_m1+m_m2); 50 float b = m_l1*m_m2*m_l2*cos(m_w1-m_w2); 51 float c = m_l1*(m_m2*m_l2*sin(m_w1-m_w2)*m_v2*m_v2 + (m_m1+m_m2)*m_fGravity*sin(m_w1)); 52 53 float d = m_m2*m_l2*m_l1*cos(m_w1-m_w2); 54 float e = m_m2*m_l2*m_l2; 55 float f = m_m2*m_l2*(-m_l1*sin(m_w1-m_w2)*m_v1*m_v1 + m_fGravity*sin(m_w2)); 56 57 // 角加速度 58 float dv1; 59 float dv2; 60 SolveLinalg(a, b, c, d, e, f, dv1, dv2); 61 62 // 角速度 63 m_v1 += dv1*deltaTime; 64 m_v2 += dv2*deltaTime; 65 66 // 角度 67 m_w1 += m_v1*deltaTime; 68 m_w2 += m_v2*deltaTime; 69 70 UpdatePosition(); 71 }
这里使用的是角度变化实现双摆,参考的资料是:
http://sebug.net/paper/books/scipydoc/double_pendulum.html
它的理论有些难,我看得也似懂非懂的。好在公式就在那里,只要会用,不求会懂,程序就能实现。
这个程序是在2D的,双摆可以出现在三维空间中.我也试着写了下,使用力学来进行模拟,效果不太精确:
.h

1 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 #ifndef _DoublePendulum02_H_ 4 #define _DoublePendulum02_H_ 5 6 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 8 #include "IDoublePendulum.h" 9 10 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11 12 class DoublePendulum02 : public IDoublePendulum 13 { 14 public: 15 DoublePendulum02() 16 { 17 m_velocity1 = Vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 18 m_velocity2 = Vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 19 } 20 21 // 重置 22 void Reset(); 23 24 // 按时更新 25 void Update(float deltaTime); 26 27 protected: 28 void UpdatePosition() 29 { 30 Vec3 v = m_pos2 - m_pos1; 31 v.Normalize(); 32 33 m_pos1.Normalize(); 34 m_pos1 *= m_l1; 35 36 m_pos2 = m_pos1 + v*m_l2; 37 } 38 39 private: 40 Vec3 m_velocity1, m_velocity2; // 两球当前速度 41 }; 42 43 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 44 45 #endif
.cpp

1 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 #include "DoublePendulum02.h" 4 5 // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6 7 void DoublePendulum02::Reset() 8 { 9 IDoublePendulum::Reset(); 10 11 m_pos1.x = rand2(-1.0f, 1.0f); 12 m_pos1.y = rand2(-1.0f, 0.0f); 13 m_pos1.z = rand2(-1.0f, 1.0f); 14 m_pos2.x = rand2(-1.0f, 1.0f); 15 m_pos2.y = rand2(-0.5f, 0.5f); 16 m_pos2.z = rand2(-1.0f, 1.0f); 17 m_pos2 += m_pos1; 18 19 m_velocity1 = Vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 20 m_velocity2 = Vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 21 22 UpdatePosition(); 23 } 24 25 void DoublePendulum02::Update(float t) 26 { 27 float dot; 28 29 Vec3 line2 = m_pos2 - m_pos1; 30 line2.Normalize(); 31 32 float xzsq = line2.x*line2.x + line2.z*line2.z; 33 float xz = sqrtf(xzsq); 34 35 // 下面的物体当前的加速度 36 Vec3 dir2(-line2.x, xzsq/line2.y,-line2.z); 37 if (line2.y > 0.0f) 38 { 39 dir2 = -dir2; 40 } 41 float d = dir2.Magnitude(); 42 if (d > 0.00001f) 43 { 44 dir2 /= d; 45 } 46 else 47 { 48 dir2 = m_velocity2; 49 dir2.Normalize(); 50 } 51 Vec3 acc2 = dir2*(m_fGravity*xz/m_l2); 52 53 dot = dir2|m_velocity2; 54 m_velocity2 = dir2*m_velocity2.Magnitude(); 55 if (dot < 0.0f) 56 { 57 m_velocity2 = -m_velocity2; 58 } 59 m_pos2 += m_velocity2*t + acc2*(0.5f*t*t); 60 m_velocity2 += acc2*t; 61 62 // 上面的物体受到下面绳子的拉力 63 Vec3 force = line2*(-m_m2*m_fGravity*line2.y/m_l2); 64 // 加上重力 65 force.y -= m_m1*m_fGravity; 66 67 // 上面的物体 68 Vec3 line1 = m_pos1; 69 line1.Normalize(); 70 xzsq = line1.x*line1.x + line1.z*line1.z; 71 xz = sqrtf(xzsq); 72 Vec3 dir1(-line1.x, xzsq/line1.y,-line1.z); 73 if (line1.y > 0.0f) 74 { 75 dir1 = -dir1; 76 } 77 d = dir1.Magnitude(); 78 if (d > 0.00001f) 79 { 80 dir1 /= d; 81 } 82 else 83 { 84 dir1 = m_velocity1; 85 dir1.Normalize(); 86 } 87 88 dot = dir1|force; 89 Vec3 acc1 = dir1*(dot/m_m1); 90 91 dot = dir1|m_velocity1; 92 m_velocity1 = dir1*m_velocity1.Magnitude(); 93 if (dot < 0.0f) 94 { 95 m_velocity1 = -m_velocity1; 96 } 97 m_pos1 += m_velocity1*t + acc1*(0.5f*t*t); 98 m_velocity1 += acc1*t; 99 100 UpdatePosition(); 101 102 }
软件截图:
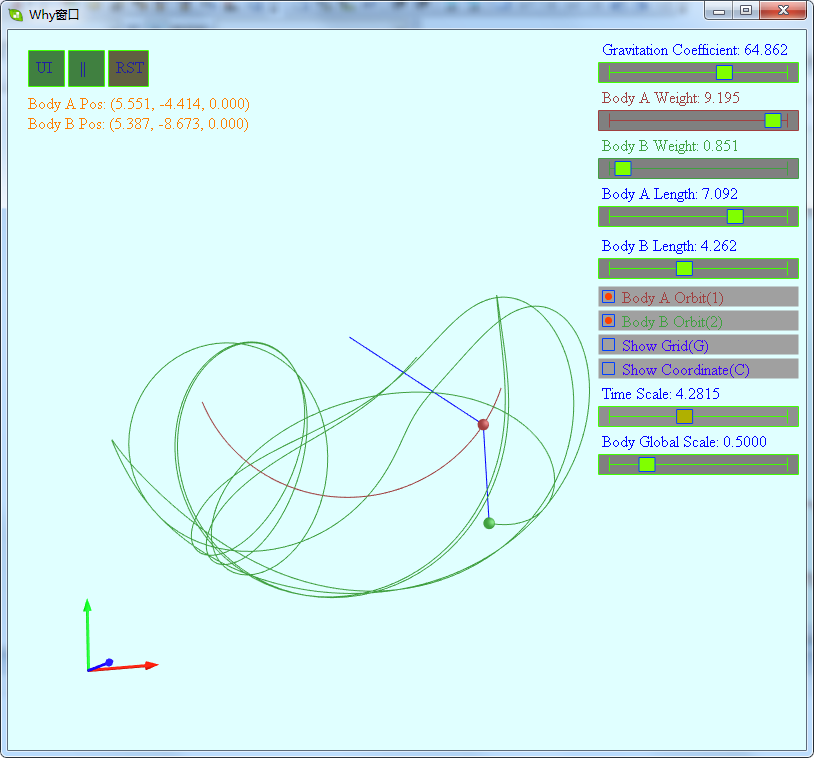
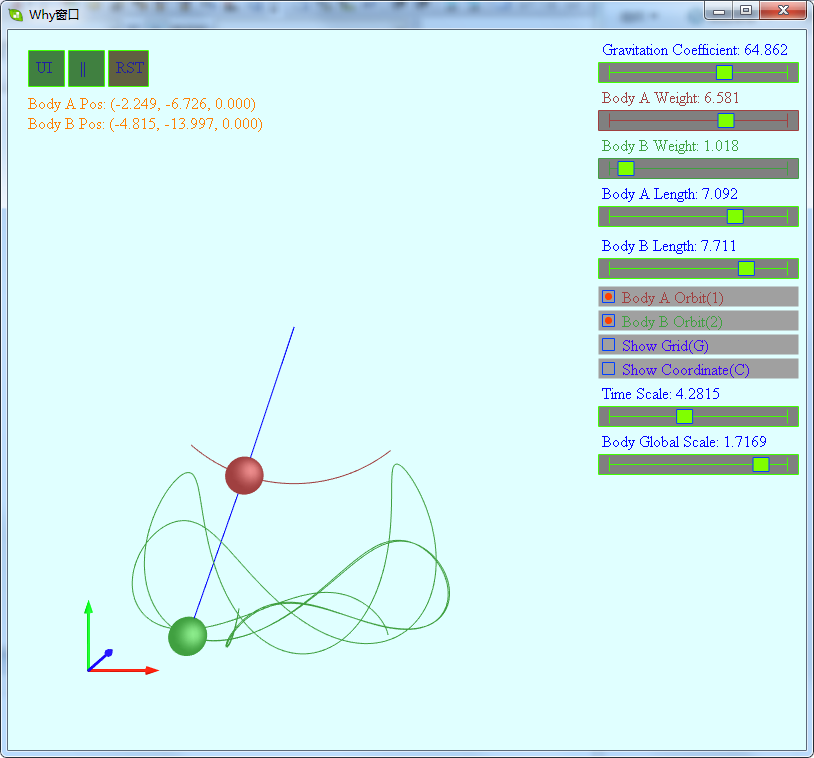
软件下载地址:
http://files.cnblogs.com/files/WhyEngine/DoublePendulum.7z
使用说明:
程序启动后,会出现三个随机大小的球体在运动.
鼠标右键用于控制视角
键盘U用于开关UI用户界面.
通过UI用户界面可以设置两个球体的质量,连线长度,设置引力系数,设置时间缩放速度,设置球体的显示大小.键盘1,2用于开关两个球体运动轨迹的显示
键盘G,用于开关三维网格的显示
键盘C,用于开关坐标轴的显示
键盘P,用于暂停
键盘R,用于重置,这时会随机为两个球体设置质量与初速度.
最后发一幅通过双摆绘制的图画:

相关文章:三体三体
