学习目录
1.tensorflow相关函数理解
(1)tf.nn.conv2d
(2)tf.nn.relu
(3)tf.nn.max_pool
(4)tf.nn.dropout
(5)tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits
(6)tf.nn.truncated_normal
(7)tf.nn.constant
(8)tf.nn.placeholder
(9)tf.nn.reduce_mean
(10)tf.nn.squared_difference
(1)tf.nn.square
2.tensorflow相关类的理解
(1)tf.Variavle
tf.nn.conv2d(tf.nn.conv2d是TensorFlow里面实现卷积的函数)
参数列表
conv2d(
input,
filter,
strides,
padding,
use_cudnn_on_gpu=True,
data_format='NHWC',
name=None
)
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | 是 | tensor | 是一个 4 维的 tensor,即 [ batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels ](若 input 是图像,[ 训练时一个 batch 的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数 ]) |
| filter | 是 | tensor | 是一个 4 维的 tensor,即 [ filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels ](若 input 是图像,[ 卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数 ]),filter 的 in_channels 必须和 input 的 in_channels 相等 |
| strides | 是 | 列表 | 长度为 4 的 list,卷积时候在 input 上每一维的步长,一般 strides[0] = strides[3] = 1 |
| padding | 是 | string | 只能为 " VALID "," SAME " 中之一,这个值决定了不同的卷积方式。VALID 丢弃方式;SAME:补全方式 |
| use_cudnn_on_gpu | 否 | bool | 是否使用 cudnn 加速,默认为 true |
| data_format | 否 | string | 只能是 " NHWC ", " NCHW ",默认 " NHWC " |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
以下的动画是我们以一张彩色的图片为例子,彩色图的通道数为3(黑白照的通道数为1),所以每张彩色的图片就需要3个filter,每个filter中的权重都不同,最后输出的值为各自所对应相乘相加即可。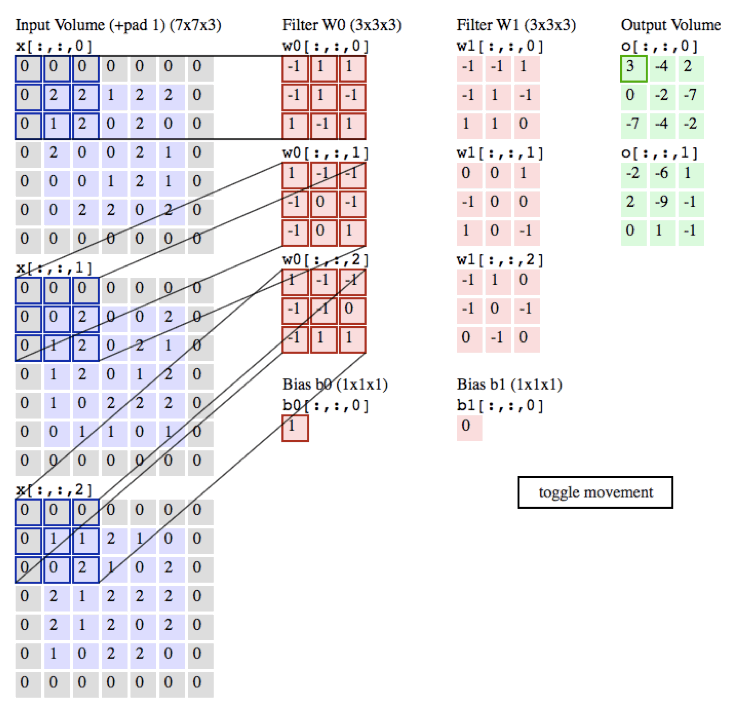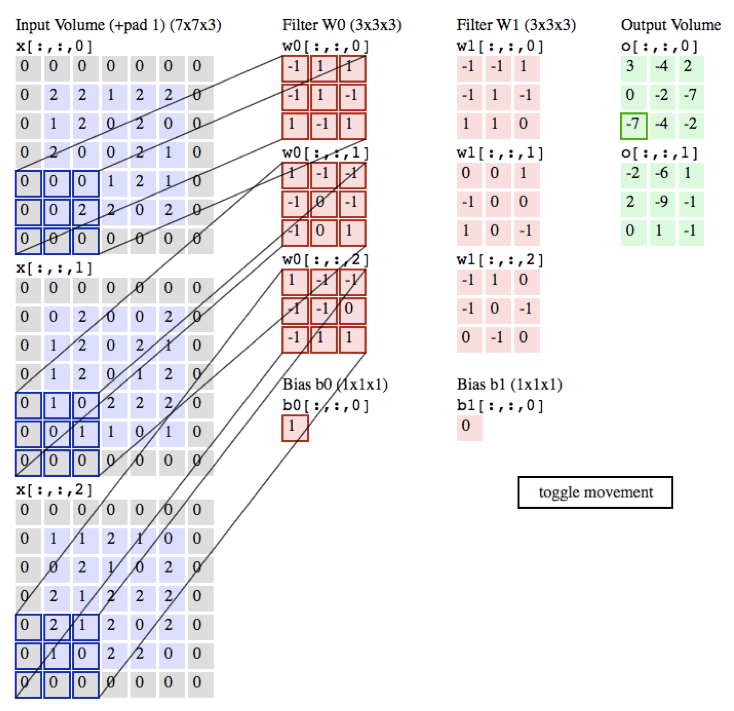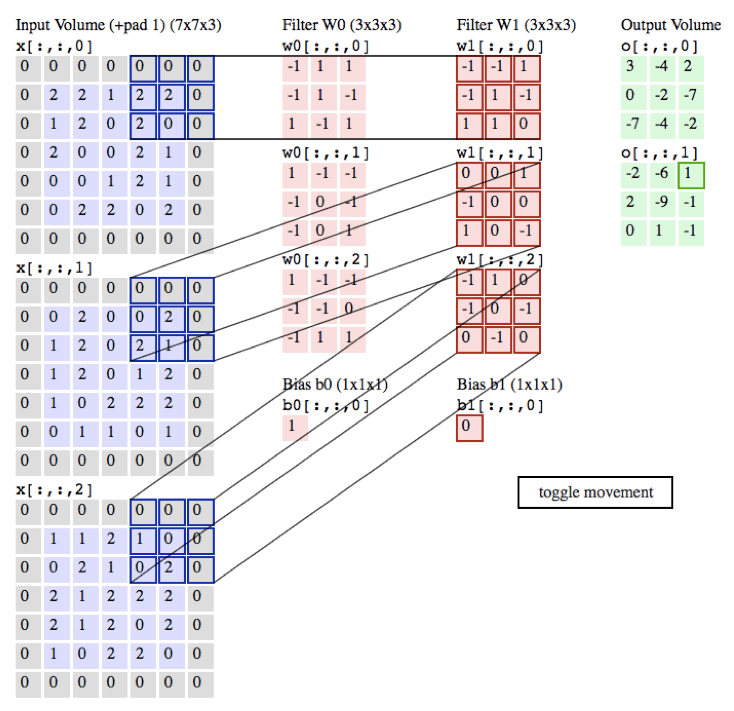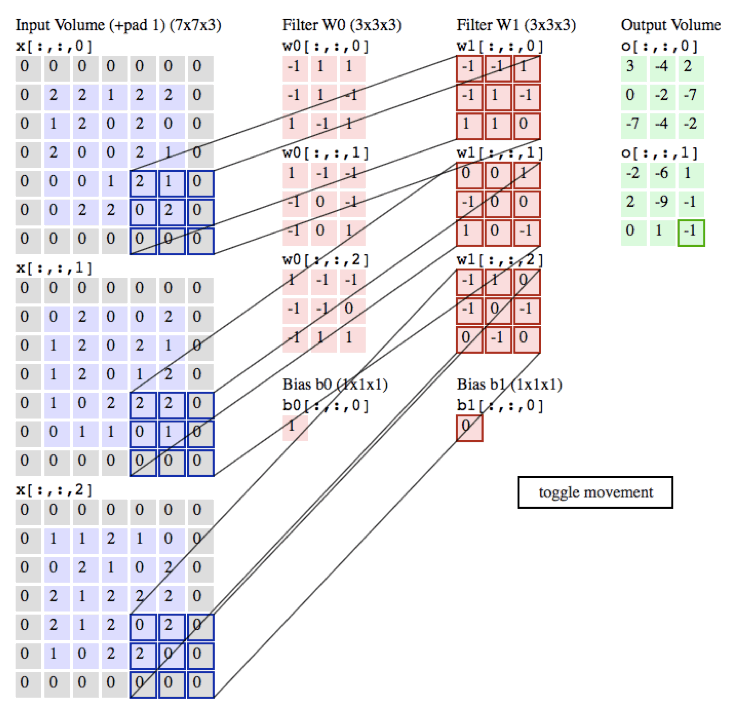
实例:
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.constant([1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0],dtype=tf.float32,shape=[1,5,5,1]) b = tf.constant([1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1],dtype=tf.float32,shape=[3,3,1,1]) c = tf.nn.conv2d(a,b,strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='VALID') d = tf.nn.conv2d(a,b,strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='SAME') with tf.Session() as sess: print ("c shape:") print (c.shape) print ("c value:") print (sess.run(c)) print ("d shape:") print (d.shape) print ("d value:") print (sess.run(d))
运行结果如下:

1 c shape: 2 (1, 3, 3, 1) 3 c value: 4 [[[[ 4.] 5 [ 3.] 6 [ 4.]] 7 8 [[ 2.] 9 [ 4.] 10 [ 3.]] 11 12 [[ 2.] 13 [ 3.] 14 [ 4.]]]] 15 d shape: 16 (1, 5, 5, 1) 17 d value: 18 [[[[ 2.] 19 [ 2.] 20 [ 3.] 21 [ 1.] 22 [ 1.]] 23 24 [[ 1.] 25 [ 4.] 26 [ 3.] 27 [ 4.] 28 [ 1.]] 29 30 [[ 1.] 31 [ 2.] 32 [ 4.] 33 [ 3.] 34 [ 3.]] 35 36 [[ 1.] 37 [ 2.] 38 [ 3.] 39 [ 4.] 40 [ 1.]] 41 42 [[ 0.] 43 [ 2.] 44 [ 2.] 45 [ 1.] 46 [ 1.]]]]
tf.nn.relu(Tensorflow中常用的激活函数 ReLu=max(0,x) )
relu(
features,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| features | 是 | tensor | 是以下类型float32, float64, int32, int64, uint8, int16, int8, uint16, half |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.constant([1,-2,0,4,-5,6]) b = tf.nn.relu(a) with tf.Session() as sess: print (sess.run(b))
执行结果:

[1 0 0 4 0 6]
tf.nn.max_pool(CNN当中的最大值池化操作,其实用法和卷积很类似)
max_pool(
value,
ksize,
strides,
padding,
data_format='NHWC',
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | 是 | tensor | 4 维的张量,即 [ batch, height, width, channels ],数据类型为 tf.float32 |
| ksize | 是 | 列表 | 池化窗口的大小,长度为 4 的 list,一般是 [1, height, width, 1],因为不在 batch 和 channels 上做池化,所以第一个和最后一个维度为 1 |
| strides | 是 | 列表 | 池化窗口在每一个维度上的步长,一般 strides[0] = strides[3] = 1 |
| padding | 是 | string | 只能为 " VALID "," SAME " 中之一,这个值决定了不同的池化方式。VALID 丢弃方式;SAME:补全方式 |
| data_format | 否 | string | 只能是 " NHWC ", " NCHW ",默认" NHWC " |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 3 a = tf.constant([1,3,2,1,2,9,1,1,1,3,2,3,5,6,1,2],dtype=tf.float32,shape=[1,4,4,1]) 4 b = tf.nn.max_pool(a,ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='VALID') 5 c = tf.nn.max_pool(a,ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='SAME') 6 with tf.Session() as sess: 7 print ("b shape:") 8 print (b.shape) 9 print ("b value:") 10 print (sess.run(b)) 11 print ("c shape:") 12 print (c.shape) 13 print ("c value:") 14 print (sess.run(c))
执行结果:

1 b shape: 2 (1, 2, 2, 1) 3 b value: 4 [[[[ 9.] 5 [ 2.]] 6 7 [[ 6.] 8 [ 3.]]]] 9 c shape: 10 (1, 2, 2, 1) 11 c value: 12 [[[[ 9.] 13 [ 2.]] 14 15 [[ 6.] 16 [ 3.]]]]
tf.nn.dropout(tf.nn.dropout是TensorFlow里面为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,它一般用在全连接层)
dropout(
x,
keep_prob,
noise_shape=None,
seed=None,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| x | 是 | tensor | 输出元素是 x 中的元素以 keep_prob 概率除以 keep_prob,否则为 0 |
| keep_prob | 是 | scalar Tensor | dropout 的概率,一般是占位符 |
| noise_shape | 否 | tensor | 默认情况下,每个元素是否 dropout 是相互独立。如果指定 noise_shape,若 noise_shape[i] == shape(x)[i],该维度的元素是否 dropout 是相互独立,若 noise_shape[i] != shape(x)[i] 该维度元素是否 dropout 不相互独立,要么一起 dropout 要么一起保留 |
| seed | 否 | 数值 | 如果指定该值,每次 dropout 结果相同 |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 3 a = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5,6],shape=[2,3],dtype=tf.float32) 4 b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) 5 c = tf.nn.dropout(a,b,[2,1],1) 6 with tf.Session() as sess: 7 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) 8 print (sess.run(c,feed_dict={b:0.75}))
执行结果:

1 [[ 0. 0. 0. ] 2 [ 5.33333349 6.66666651 8. ]]
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(对于给定的logits计算sigmoid的交叉熵。)
sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
_sentinel=None,
labels=None,
logits=None,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| _sentinel | 否 | None | 没有使用的参数 |
| labels | 否 | Tensor | type, shape 与 logits相同 |
| logits | 否 | Tensor | type 是 float32 或者 float64 |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 x = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5,6,7],dtype=tf.float64) 3 y = tf.constant([1,1,1,0,0,1,0],dtype=tf.float64) 4 loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels = y,logits = x) 5 with tf.Session() as sess: 6 print (sess.run(loss))
执行结果:

1 [ 3.13261688e-01 1.26928011e-01 4.85873516e-02 4.01814993e+00 2 5.00671535e+00 2.47568514e-03 7.00091147e+00]
tf.truncated_normal(产生截断正态分布随机数,取值范围为 [ mean - 2 * stddev, mean + 2 * stddev ])
truncated_normal(
shape,
mean=0.0,
stddev=1.0,
dtype=tf.float32,
seed=None,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| shape | 是 | 1 维整形张量或 array | 输出张量的维度 |
| mean | 否 | 0 维张量或数值 | 均值 |
| stddev | 否 | 0 维张量或数值 | 标准差 |
| dtype | 否 | dtype | 输出类型 |
| seed | 否 | 数值 | 随机种子,若 seed 赋值,每次产生相同随机数 |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
import tensorflow as tf initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape=[3,3], mean=0, stddev=1) print(tf.Session().run(initial))
执行结果:

[[ 0.06492835 0.03914397 0.32634252] [ 0.22949421 0.21335489 0.6010958 ] [-0.11964546 -0.16878787 0.12951735]]
tf.constant(根据 value 的值生成一个 shape 维度的常量张量)
constant(
value,
dtype=None,
shape=None,
name='Const',
verify_shape=False
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | 是 | 常量数值或者 list | 输出张量的值 |
| dtype | 否 | dtype | 输出张量元素类型 |
| shape | 否 | 1 维整形张量或 array | 输出张量的维度 |
| name | 否 | string | 张量名称 |
| verify_shape | 否 | Boolean | 检测 shape 是否和 value 的 shape 一致,若为 Fasle,不一致时,会用最后一个元素将 shape 补全 |
tf.placeholder(是一种占位符,在执行时候需要为其提供数据)
placeholder(
dtype,
shape=None,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dtype | 是 | dtype | 占位符数据类型 |
| shape | 否 | 1 维整形张量或 array | 占位符维度 |
| name | 否 | string | 占位符名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 4 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,3]) 5 y = tf.matmul(x,x) 6 with tf.Session() as sess: 7 rand_array = np.random.rand(3,3) 8 print(sess.run(y,feed_dict={x:rand_array}))
执行结果:
输出一个 3x3 的张量
tf.reduce_mean(计算张量 input_tensor 平均值)
reduce_mean(
input_tensor,
axis=None,
keep_dims=False,
name=None,
reduction_indices=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| input_tensor | 是 | 张量 | 输入待求平均值的张量 |
| axis | 否 | None、0、1 | None:全局求平均值;0:求每一列平均值;1:求每一行平均值 |
| keep_dims | 否 | Boolean | 保留原来的维度(例如不会从二维矩阵降为一维向量) |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
| reduction_indices | 否 | None | 和 axis 等价,被弃用 |
实例:
1 initial = [[1.,1.],[2.,2.]] 2 x = tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32) 3 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() 4 with tf.Session() as sess: 5 sess.run(init_op) 6 print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(x))) 7 print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(x,0))) #Column 8 print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(x,1))) #row
运行结果:

1 1.5 2 [ 1.5 1.5] 3 [ 1. 2.]
tf.squared_difference(计算张量 x、y 对应元素差平方)
squared_difference(
x,
y,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| x | 是 | 张量 | 是 half, float32, float64, int32, int64, complex64, complex128 其中一种类型 |
| y | 是 | 张量 | 是 half, float32, float64, int32, int64, complex64, complex128 其中一种类型 |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 4 initial_x = [[1.,1.],[2.,2.]] 5 x = tf.Variable(initial_x,dtype=tf.float32) 6 initial_y = [[3.,3.],[4.,4.]] 7 y = tf.Variable(initial_y,dtype=tf.float32) 8 diff = tf.squared_difference(x,y) 9 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() 10 with tf.Session() as sess: 11 sess.run(init_op) 12 print(sess.run(diff))
执行结果:

[[ 4. 4.]
[ 4. 4.]]
tf.square(计算张量对应元素平方)
square(
x,
name=None
)
参数列表:
| 参数名 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| x | 是 | 张量 | 是 half, float32, float64, int32, int64, complex64, complex128 其中一种类型 |
| name | 否 | string | 运算名称 |
实例:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 4 initial_x = [[1.,1.],[2.,2.]] 5 x = tf.Variable(initial_x,dtype=tf.float32) 6 x2 = tf.square(x) 7 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() 8 with tf.Session() as sess: 9 sess.run(init_op) 10 print(sess.run(x2))
执行结果:
[[ 1. 1.]
[ 4. 4.]]
tf.Variavle(TensorFlow中的图变量)
tf.Variable.init(initial_value, trainable=True, collections=None, validate_shape=True, name=None)
参数名称 参数类型 含义
initial_value:所有可以转换为Tensor的类型 变量的初始值
trainable bool:如果为True,会把它加入到GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES,才能对它使用Optimizer
collections list:指定该图变量的类型、默认为[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
validate_shape:bool 如果为False,则不进行类型和维度检查
name string:变量的名称,如果没有指定则系统会自动分配一个唯一的值
实例:
1 In [1]: import tensorflow as tf 2 In [2]: v = tf.Variable(3, name='v') 3 In [3]: v2 = v.assign(5) 4 In [4]: sess = tf.InteractiveSession() 5 In [5]: sess.run(v.initializer) 6 In [6]: sess.run(v) 7 Out[6]: 3 8 In [7]: sess.run(v2) 9 Out[7]: 5
内容参考与腾讯云开发者实验室
