Mongodb-aggregate
在工作中经常遇到一些mongodb的聚合操作,和mysql对比起来,mongo存储的可以是复杂的类型,比如数组,字典等mysql不善于处理的文档型结构,但是mongo的聚合操作比mysql复杂。
mysql与mongo聚合类比
| SQL 操作/函数 | mongodb聚合操作 |
| where | $match |
| group by | $group |
| having | $match |
| select | $project |
| order by | $sort |
| limit | $limit |
| sum() | $sum |
| count() | $sum |
| join |
$lookup (v3.2 新增) |
1.Aggregation Pipleline
管道将上一个命令输出的数据作为下一个命令的参数。MongoDB中的管道聚合非常实用,提供高效的数据聚合,并且是MongoDB中数据聚合的首选方法
来看一下官方给的图。
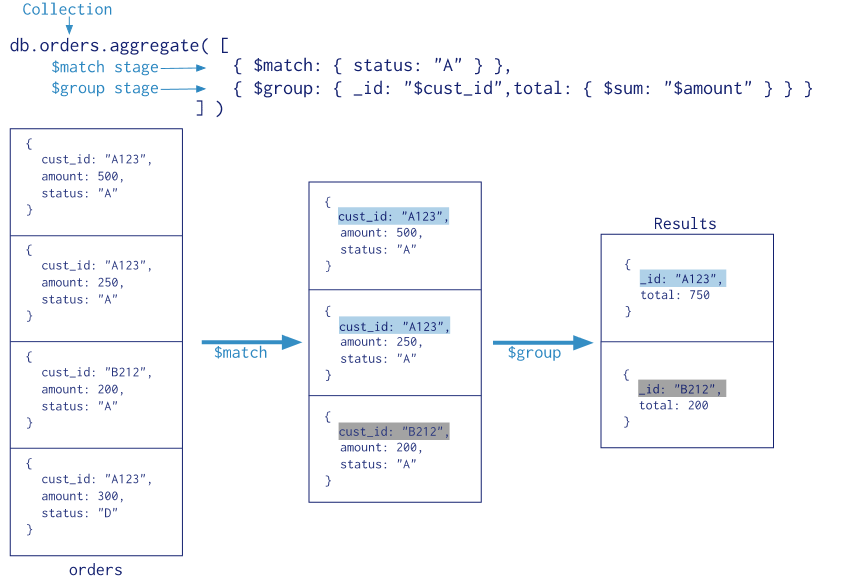
aggreagte是一个数组,其中包含多个对象(命令),通过遍历Pipleline数组对collection中的数据进行操作。
$match:查询条件
$group:聚合的配置
-
_id代表你想聚合的数据的主键,上述数据中,你想聚合所有cust_id相同的条目的amount的总和,那_id即被设置为cust_id。_id为必须,你可以填写一个空值。 -
total代表你最后想输出的数据之一,这里total是每条结果中amount的总和。 -
$sum是一个聚合的操作符,另外的操作符你可以在官方文档中找到。上图中的命令表示对相同主键(_id)下的amount进行求和。如果你想要计算主键出现的次数,可以把命令写成如下的形式{$sum: 1}
聚合的过程
看一下图例,所有的数据先经过$match命令,只留下了status为A的数据,接着,对筛选出的数据进行聚合操作,对相同cust_id的数据进行计算amount总和的操作,最后输出结果。
2.aggregate具体介绍
-
$geoNeargeoNear命令可以在查询结果中返回每个点距离查询点的距离 -
$group指定 group 的_id(key/keys) 和基于操作符($push/$sum/$addToSet/...) 的累加运算 -
$limit限制条件 -
$match输入过滤条件 -
$out将输出结果保存到collection -
$project修改数据流中的文档结构 -
$redact是$project/$match功能的合并 -
$skip 跳过 -
$sort对结果排序 -
$unwind拆解数据
-
$geoNeargeoNear命令可以在查询结果中返回每个点距离查询点的距离 -
$group指定 group 的_id(key/keys) 和基于操作符($push/$sum/$addToSet/...) 的累加运算 -
$limit限制条件 -
$match输入过滤条件 -
$out将输出结果保存到collection -
$project修改数据流中的文档结构 -
$redact是$project/$match功能的合并 -
$skip 跳过 -
$sort对结果排序 -
$unwind拆解数据
$group 允许用的累加操作符 $addToSet/$avg/$first/$last/$max/$min/$push/$sum,不被允许的累加操作符$each... ,默认最多可以用 100MB RAM, 增加allowDiskUse可以让$group操作更多的数据
测试数据:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544352ba57ccba824d7bf"), "group" : "E", "created" : 1402764223, "count" : 63, "datetime" : 1512391126, "title" : "aa", "category" : "C8" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544512ba57ccba824d7c0"), "group" : "I", "created" : 1413086660, "count" : 93, "datetime" : 1512391261, "title" : "bb", "category" : "C10" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c1"), "group" : "H", "created" : 1440750343, "count" : 41, "datetime" : 1512391111, "title" : "cc", "category" : "C1" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c2"), "group" : "S", "created" : 1437710373, "count" : 14, "datetime" : 1512392136, "title" : "dd", "category" : "C10" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c3"), "group" : "Z", "created" : 1428307315, "count" : 78, "datetime" : 1512391166, "title" : "ee", "category" : "C5" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c4"), "group" : "R", "created" : 1402809274, "count" : 74, "datetime" : 1512391162, "title" : "ff", "category" : "C9" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c5"), "group" : "Y", "created" : 1400571321, "count" : 66, "datetime" : 1512139164, "title" : "gg", "category" : "C2" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c6"), "group" : "L", "created" : 1416562128, "count" : 5, "datetime" : 1512393165, "title" : "hh", "category" : "C1" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c7"), "group" : "E", "created" : 1414057884, "count" : 12, "datetime" : 1512391165, "title" : "ii", "category" : "C3" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544572ba57ccba824d7c8"), "group" : "L", "created" : 1418879346, "count" : 67, "datetime" : 1512391167, "title" : "gg", "category" : "C3" }
下面是aggregate的用法
db.newtest.aggregate([ {$match: {}}, {$skip: 10}, // 跳过 collection 的前 10 行 {$project: {group: 1, datetime: 1, category: 1, count: 1}}, // 1表示显示此字段,0则不显示 {$redact: { // redact 简单用法 过滤 group != 'A' 的行 $cond: [{$eq: ["$group", "A"]}, "$$DESCEND", "$$PRUNE"] }}, {$group: { _id: {year: {$year: "$datetime"}, month: {$month: "$datetime"}, day: {$dayOfMonth: "$datetime"}}, category_first: {$first: "$category"}, category_last: {$last: "$category"}, count_all: {$sum: "$count"}, count_avg: {$avg: "$count"}, rows: {$sum: 1} }},// 只保留这两个字段 {$project: {group_unique: 1, rows: 1}}, // 结果按照 _id 排序 {$sort: {"_id": 1}}, // 只保留 50 条结果 // {$limit: 50}, // 结果另存 {$out: "data_agg_out"}, ], { allowDiskUse: true, //可选的。允许写入临时文件。设置为时true,聚合操作可以将数据写入_tmp目录中的dbPath子目录 }) db.data_agg_out.find() db.data_agg_out.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: null, rows: {$sum: '$rows'} }} ]) db.data_agg_out.drop()