说明 :步步为营-27-事件以前用委托做过窗体之间传值
1 通过属性数据交互
1.1 在子窗体中添加属性Form1属性
public Form1 Form1 { get; set; }
1.2 在父窗体中添加SetText 方法,来给文本框赋值
public void SetText(string str)
{
this.textBox1.Text = str;
}
1.3 而后子窗体文本框发生变化时调用父窗体的方法
private void textBox2_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Form1.SetText(this.textBox2.Text);
}

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles; namespace 窗体数据交互 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { //01创建子窗体 Form2 frm = new Form2(); frm.Form1 = this;//指定子窗体的父窗体 //弹出子窗体 frm.Show(); } public void SetText(string str) { this.textBox1.Text = str; } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace 窗体数据交互 { public partial class Form2 : Form { public Form1 Form1 { get; set; } public Form2() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { } private void textBox2_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Form1.SetText(this.textBox2.Text); } } }
运行效果:
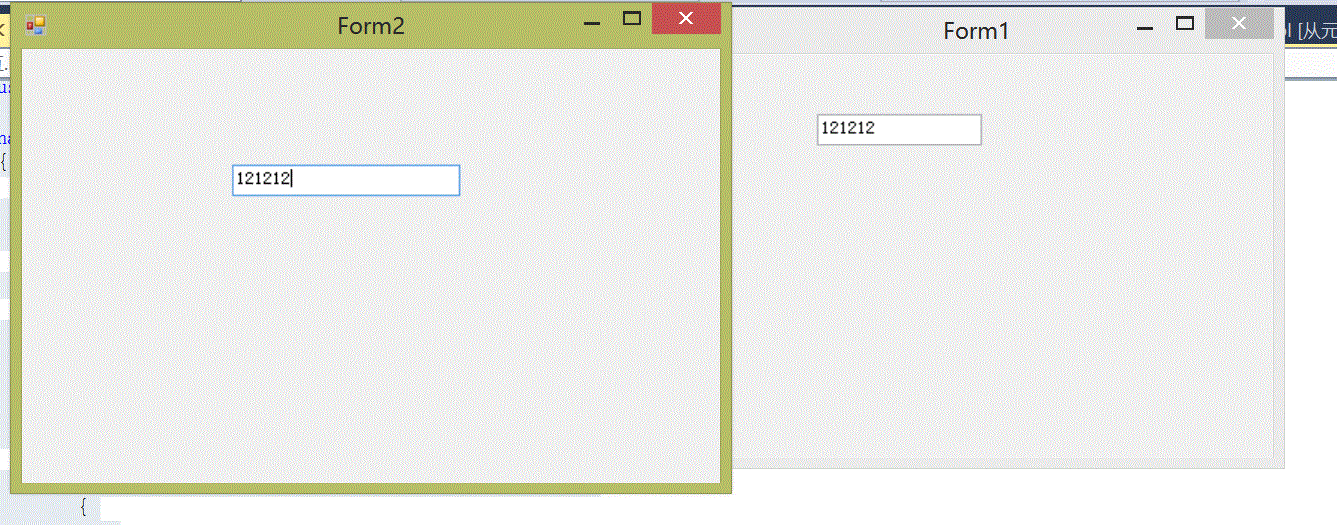
2 通过委托实现

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace 窗体数据交互 { public partial class Form3 : Form { //02-a 声明委托 public delegate void DelSetText(string strMsg); //定义一个属性 private DelSetText _del; public Form3(DelSetText del) { InitializeComponent(); this._del = del; } private void Form3_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { } private void textBox2_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { //02-b 定义委托 this._del(this.textBox2.Text); } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles; namespace 窗体数据交互 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { #region 01通过属性实现数据交互 //01创建子窗体 Form2 frm = new Form2(); frm.Form1 = this;//指定子窗体的父窗体 //弹出子窗体 frm.Show(); #endregion #region 02通过委托实现数据交互 Form3 frm3 = new Form3(SetText); frm3.Show(); #endregion } public void SetText(string str) { textBox1.Text = str; } } }
3 通过事件实现
总结: 窗体A中的控件值根据窗体B的改变而改变
1:在A中定义方法,封装修改控件的代码
2:在B中定义事件,事件的委托签名与A中的方法一致
3:在A中创建B的对象,将A中的方法赋值给B的事件
4:在B中调用事件.
另注:常见的两种委托
Func<返回值> 有返回值类型委托,参数可以往后加Func<返回值,参数1,参数2>
Action 无返回值类型委托

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace FormAFormB { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } //1.在A中定义方法,封装修改控件值的代码 public void SetTxtBoxValue(string str) { txtBox.Text = str; } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { //3 在A中创建对象 将A中的方法赋值给B事件 Form2 form = new Form2(); form.Show(); form.makeTextVale += SetTxtBoxValue; } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace FormAFormB { public partial class Form2 : Form { public Form2() { InitializeComponent(); } //2 声明事件 public event Action<string> makeTextVale; private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { } private void textBox1_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { //4在B中调用事件 makeTextVale(textBox1.Text); //if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(textBox1.Text)) //{ //} } } }

