1、单循环链表
将单链表中终端结点的指针端由空指针改为指向头节点,就使整个单链表形成一个环,这种头尾相接的单链表称为单循环链表,简称循环链表。
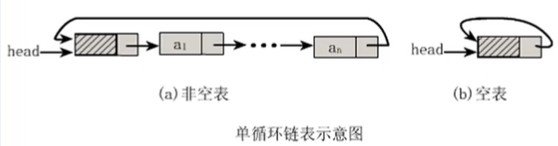
其实循环链表和单链表的主要差异就在于循环的判断条件上,原来是判断 p->next是否为空,现在则是p->next不等于头结点,则循环未结束。
2、双向链表
双向链表是在单链表的每个结点中,再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针。所以在双向链表中的结点有两个指针域,一个指向直接后继,另一个指向直接前驱。
双向链表是单链表扩展出来的结构,所以它的很多操作是和单链表相同的,比如求长度,查找元素,获得元素位置等。这些操作都只要涉及一个方向的指针即可,另一个指针多了也不能提供什么帮助。
//线性表的双向链表存储结构 typedef struct student { int data; struct student *next; //直接后继指针 struct student *pre; //直接前驱指针 }dnode;
1、编程实现双向链表的建立
dnode *creat() { dnode *head, *p, *s; int x, cycle = 1; head = (dnode*)malloc(sizeof(dnode)); //头结点 p = head; //p头指针 while (cycle) { printf(" please input the data:"); scanf("%d", &x); if (x != 0) { s = (dnode *)malloc(sizeof(dnode)); s->data = x; printf(" %d", s->data); p->next = s; s->pre = p; p = s; } else cycle = 0; } head = head->next; head->pre = NULL; p->next = NULL; return head; }
2、实现双向链表的删除
dnode *del(dnode *head, int num) { dnode *p1; p1 = head; //没有头结点 while (num != p1->data&&p1->next != NULL) { p1 = p1->next; //退出循环时 p1已经存储num地址 } if (num == p1->data) { if (p1 == head) //头 { head = head->next; head->pre = NULL; free(p1); } else if (p1->next == NULL) //尾 { p1->pre->next = NULL; free(p1); } else //中 { p1->next->pre = p1->pre; p1->pre->next = p1->next; } } else printf(" %d could not been found", num); return (head); }
3、实现双向链表的插入
dnode *insert(dnode *head, int num) { dnode *p0, *p1; p1 = head; p0 = (dnode *)malloc(sizeof(dnode)); p0->data = num; while (p0->data > p1->data&&p1->next != NULL) { p1 = p1->next; } if (p0->data <= p1->data) { if (p1 = head) //头 { p0->next = p1; p1->pre = p0; head = p0; } else //中 { p0->next = p1; p0->pre = p1->pre; p1->pre->next = p0; p1->pre = p0; } } else //尾 { p1->next = p0; p0->pre = p1; p0->next = NULL; } return (head); }
4、实现双向链表的长度、打印
int length(dnode *head) { dnode *p = head; int x = 0; while (p != NULL) { p = p->next; x++; } return x; } void print(dnode *head) { dnode *p;int n; n = length(head); printf(" Now ,these %d records are: ", n); p = head; if (head != NULL) while (p != NULL) { printf(" %d", p->data); p = p->next; } }
5、实现双向链表的创建、删除、插入、长度、打印等
void main() { dnode *head; int del_num, insert_num; head = creat(); print(head); printf(" please input the delete num:"); scanf("%d", &del_num); head = del(head, del_num); print(head); printf(" please input the insert num:"); scanf("%d", &insert_num); head = insert(head, insert_num); print(head); system("pause"); }