semaphore 信号标,旗语。
Semaphore 一般译作 信号量,它也是一种线程同步工具,主要用于多个线程对共享资源进行并行操作的一种工具类。它代表了一种许可的概念,是否允许多线程对同一资源进行操作的许可,使用 Semaphore 可以控制并发访问资源的线程个数。
其作用就是停车场的显示牌,如果剩余车位为0,那么你只能在车杆前等待或者离去。
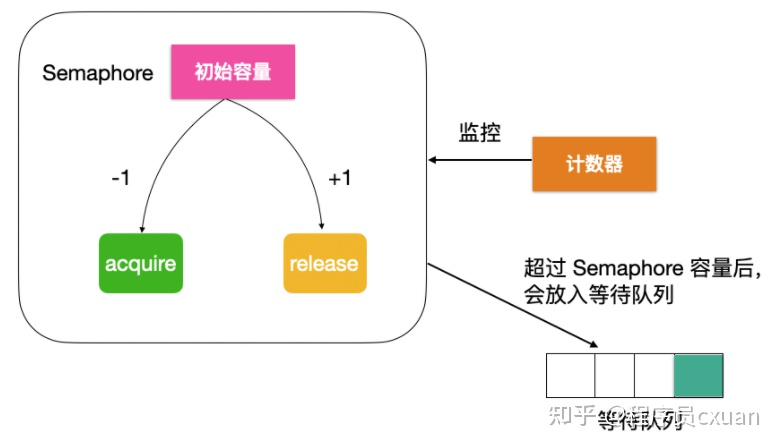
上图是semaphore的流程图。
内部的同步工具类还是sync,继承自AQS。所以学并发AQS很重要。
semaphore的公平锁和非公平锁:
/** * Synchronization implementation for semaphore. Uses AQS state * to represent permits. Subclassed into fair and nonfair * versions. */ abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1192457210091910933L; Sync(int permits) {
/**
* 设置AQS中的state值,AQS中state的值就是同步状态的值,而semaphore中的permits代表了许可的数量
**/ setState(permits); }
/**
* 调用了父类的getstate方法获取一下线程同步状态值,线程同步值就是state
**/ final int getPermits() { return getState(); }
/**
* 这个方法是为了semaphore中的非公平锁提供方法
**/ final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) { for (;;) { int available = getState(); int remaining = available - acquires; if (remaining < 0 ||
/**
* 这个方法调用了AQS中的cas方法设置state值,就是semaphore中的信号量
**/
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
} } protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int next = current + releases; if (next < current) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded"); if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) return true; } } final void reducePermits(int reductions) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int next = current - reductions; if (next > current) // underflow throw new Error("Permit count underflow"); if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) return; } } final int drainPermits() { for (;;) { int current = getState(); if (current == 0 || compareAndSetState(current, 0)) return current; } } }
/** * NonFair version */ static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L; NonfairSync(int permits) { super(permits); } protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires); } }
/** * Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated * value if the current state value equals the expected value. * This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read * and write. * * @param expect the expected value * @param update the new value * @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that the actual * value was not equal to the expected value. */ protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) { // See below for intrinsics setup to support this return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); }
上面是AQS中的CAS设置state方法。
/** * Fair version */ static final class FairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 2014338818796000944L; FairSync(int permits) { super(permits); } protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) { for (;;) {
// 此处调用了AQS类中的方法,此方法是用来查看是否有线程正处于阻塞队列中阻塞,这个方法是公平锁和非公平锁差异的关键,前者判断的是处于阻塞队列中的线程数量,后者是直接判断是否满足条件 if (hasQueuedPredecessors()) return -1; int available = getState(); int remaining = available - acquires; if (remaining < 0 || compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) return remaining; } } }
对比发现公平锁和非公平锁的区别就是非公锁是FairSync是先判断是否存在待阻塞线程,这就是后到后出, 而NonfairSync是直接判断state状态值是否满足条件,如果满足条件直接返回,这就是先到先得。
到目前为之,我们看的都是tryAcquire,而tryAcquire方法是不阻塞,即使获取不到state也不会阻塞而是返回失败。而semaphore还有阻塞获取的方法:
/** * Acquires a permit from this semaphore, blocking until one is * available, or the thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}. * * <p>Acquires a permit, if one is available and returns immediately, * reducing the number of available permits by one. * * <p>If no permit is available then the current thread becomes * disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant until * one of two things happens: * <ul> * <li>Some other thread invokes the {@link #release} method for this * semaphore and the current thread is next to be assigned a permit; or * <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts} * the current thread. * </ul> * * <p>If the current thread: * <ul> * <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or * <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting * for a permit, * </ul> * then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's * interrupted status is cleared. * * @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted */ public void acquire() throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1); }
/** * Acquires in shared mode, aborting if interrupted. Implemented * by first checking interrupt status, then invoking at least once * {@link #tryAcquireShared}, returning on success. Otherwise the * thread is queued, possibly repeatedly blocking and unblocking, * invoking {@link #tryAcquireShared} until success or the thread * is interrupted. * @param arg the acquire argument. * This value is conveyed to {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is * otherwise uninterpreted and can represent anything * you like. * @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted */ public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg); }
可以看到阻塞的设置state状态值的方法和非阻塞的区别在于首先调用非阻塞的设置状态值的方法,这个方法是:
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
这个方法必须在子类中实现,前面公平锁和非公平锁都已经实现过了,接下来是doAcquireInterruptibly方法
/** * Acquires in exclusive interruptible mode. * @param arg the acquire argument */ private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
//这个地方把当前线程加载阻塞队列中 final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE); boolean failed = true; try { for (;;) {
//predecessor方法是获取前驱节点 final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//这里判断当前线程前面只有一个前驱节点,就是说当前线程是老二,再此请求获取设置state,如果成功,则把自己设置为头,然后把前一个线程节点置空。 setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//此方法是检查更新当前线程的节点状态 parkAndCheckInterrupt())//如果检查到被打断则抛出被打断的异常 throw new InterruptedException(); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
/** * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode. * * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared * @return the new node */ private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; }
更新当前节点的状态(请求失败的线程),这个方法是控制整个阻塞队列的关键方法,前提条件是当前节点的前驱节点是pred节点。提供判断前驱节点的状态
/** * Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire. * Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal * control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev. * * @param pred node's predecessor holding status * @param node the node * @return {@code true} if thread should block */ private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) { int ws = pred.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)//当前节点需要阻塞 /* * This node has already set status asking a release * to signal it, so it can safely park. */ return true; if (ws > 0) { /* * Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and * indicate retry. */ do { node.prev = pred = pred.prev;//跳过已经取消的节点 } while (pred.waitStatus > 0); pred.next = node; } else { /* * waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we * need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to * retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking. */ compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); } return false; }
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */ static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */ static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */ static final int CONDITION = -2; /** * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should * unconditionally propagate */ static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
另外semaphore还提供了忽略中断的阻塞请求方法:
/** * Acquires a permit from this semaphore, blocking until one is * available. * * <p>Acquires a permit, if one is available and returns immediately, * reducing the number of available permits by one. * * <p>If no permit is available then the current thread becomes * disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant until * some other thread invokes the {@link #release} method for this * semaphore and the current thread is next to be assigned a permit. * * <p>If the current thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} * while waiting for a permit then it will continue to wait, but the * time at which the thread is assigned a permit may change compared to * the time it would have received the permit had no interruption * occurred. When the thread does return from this method its interrupt * status will be set. */ public void acquireUninterruptibly() { sync.acquireShared(1); }
释放一个许可证的方法:
/** * Releases a permit, returning it to the semaphore. * * <p>Releases a permit, increasing the number of available permits by * one. If any threads are trying to acquire a permit, then one is * selected and given the permit that was just released. That thread * is (re)enabled for thread scheduling purposes. * * <p>There is no requirement that a thread that releases a permit must * have acquired that permit by calling {@link #acquire}. * Correct usage of a semaphore is established by programming convention * in the application. */ public void release() { sync.releaseShared(1);//这个方法调用的是semaphore中的sync的tryReleaseShared方法 }
其他 Semaphore 方法
除了上面基本的 acquire 和 release 相关方法外,我们也要了解一下 Semaphore 的其他方法。Semaphore 的其他方法比较少,只有下面这几个
drainPermits : 获取并退还所有立即可用的许可,其实相当于使用 CAS 方法把内存值置为 0
reducePermits:和 nonfairTryAcquireShared 方法类似,只不过 nonfairTryAcquireShared 是使用 CAS 使内存值 + 1,而 reducePermits 是使内存值 - 1 。
isFair:对 Semaphore 许可的争夺是采用公平还是非公平的方式,对应到内部的实现就是 FairSync 和 NonfairSync。
hasQueuedThreads:当前是否有线程由于要获取 Semaphore 许可而进入阻塞。
getQueuedThreads:返回一个包含了等待获取许可的线程集合。
getQueueLength:获取正在排队而进入阻塞状态的线程个数