数组声明
数组是多个变量值的结合,是Array对象的实例,所以可以像对象一样调用方法。
创建数组
使用对象方式创建数组。
<script>"use strict"; let array = new Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); console.table(array); console.log(typeof array); // object </script>
使用字面量方式简单创建数组。
<script>"use strict"; let array = [1,2,3,4,5]; console.table(array); console.log(typeof array); // object </script>
Array.of
当使用对象创建数组时,如果只想要一个值可用Array.of进行创建,否则创建的是一个长度为填入值的空数组。
<script>"use strict"; // let array = new Array(3) 代表创建长度为3的空数组 let array = new Array.of(3); // 代表创建了一个数组 [3] </script>
多维数组
数组中可以包含多个数组,这被称为多维数组。
如下示例,创建出一个二维数组。
<script>"use strict"; let array = [[1,2,3],["4","5","6"]]; </script>
const声明
由于数组是引用类型,以使用const声明并修改其中的值不会抛出异常。
但是并不推荐这样做。
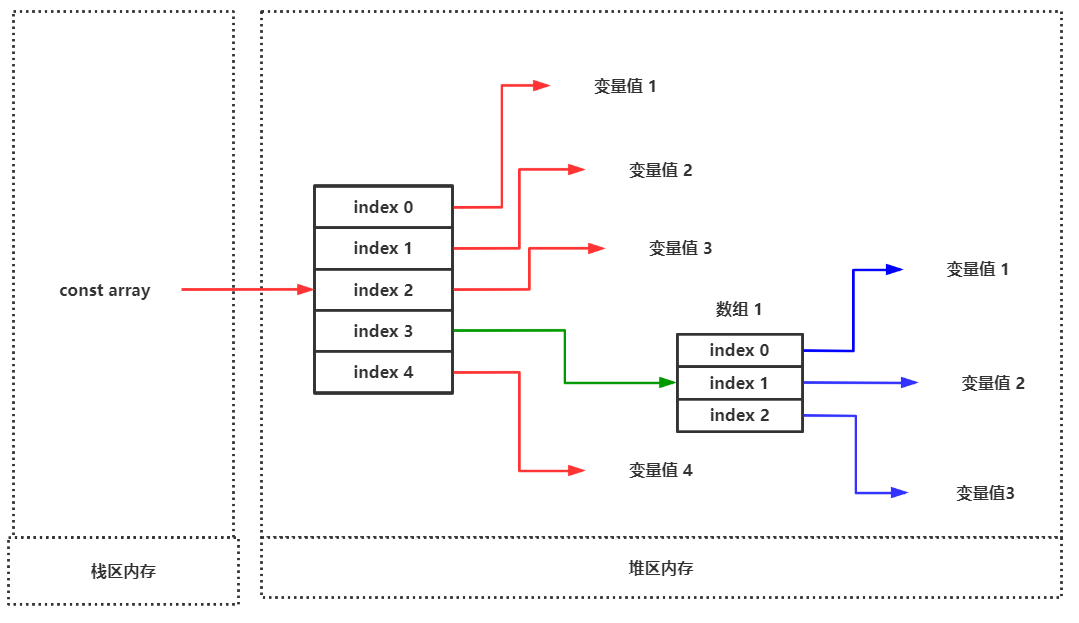
<script>"use strict"; const array = [[1,2,3],["4","5","6"]]; array[0] = "Array"; console.log(array); // ["Array", Array(3)] </script>
基本操作
长度获取
使用length可获取数组长度。
<script>"use strict"; const array = [[1,2,3],["4","5","6"],"7","8","9"]; console.log(array.length); // 5 </script>
类型检测
使用Array对象提供的isArray()方法来判断一个对象是否为数组类型。
<script>"use strict"; console.log(Array.isArray({})); // false console.log(Array.isArray([])); // true </script>
类型转换
数组转字符串
大部分数据类型都可以使用toString() 函数转换为字符串。
<script>"use strict"; let array = [1,2,3,4]; console.log(array.toString()); // 1,2,3,4 </script>
还可以使用String()将数组对象进行包裹实现转换。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1,2,3,4];
console.log(String(array)); // 1,2,3,4
</script>
使用join()方法拼接合并出字符串。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(array.join("---")); // 1---2---3---4
</script>
类数组转数组
可通过Array.from()将类数组转为数组,类数组是指具有length属性或为可迭代对象。
参数1:要转换的类数组
参数2:类似于
map()的回调函数,对元素挨个挨个做操作
以下示例将展示把DOM对象的NodeList转换为数组进行操作的过程。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div>d1</div> <div>d2</div> <div>d3</div> <div>d4</div> </body> <script> "use strict"; let ele_list = document.querySelectorAll("div"); Array.from(ele_list, function (ele) { console.log(ele.innerHTML); // d1 d2 d3 d4 }) </script> </html>
... 展开语法与类数组转换
...语法是非常强大的一种语法,类似于Python中的*柴博语法,可将元素单一拆出。
我们使用[...对象]即可将类数组的元素全部添加进数组中,且可以调用数组的方法对其中元素进行操作。
以下示例将演示使用[...NodeList]将 DOM的NodeList类数组转换为数组再使用map()方法对其中元素进行操作。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div>d1</div> <div>d2</div> <div>d3</div> <div>d4</div> </body> <script> "use strict"; let ele_list = document.querySelectorAll("div"); [...ele_list].map(function (ele) { console.log(ele.innerHTML); // d1 d2 d3 d4 }) </script> </html>
展开语法
数组合并
为一个数组添加另一个数组中的元素,可使用...展开语法,但是我个人并不推荐这么做,在运行效率上来说会有略微的降低。
<script>
"use strict";
let a1 = [1,2,3];
let a2 = ["3","4","5"];
a1 = [...a1,...a2];
console.log(a1); // (6) [1, 2, 3, "3", "4", "5"]
</script>
函数传参
...语法代替了arguments来接收任意数量的位置传参。
arguments可接收任意数量的位置传参,但是形参名只能是arguments,但...语法可以跟上任意形参名
<script>
"use strict";
function show(...args) {
console.log(args); // (5) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(Array.isArray(args)); // true
};
show(1,2,3,4,5);
</script>
节点转换
上面已经介绍过...语法与类数组转换,这里不再详细举例。
解构赋值
解构是一种更简洁的赋值特性,可以理解为分解一个数据的结构
建议使用
var/let/const声明,如果在严格模式下不使用声明会抛出异常
基本使用
严格按照语法,解构接收变量必须由[]包裹,并且一定不要忘记前面的声明。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array("云崖",18,"男");
let [name,age,gender] = array;
console.log(name); // 云崖
console.log(age); // 18
console.log(gender); // 男
</script>
... 接收全部
可以使用...语法来接收余下的全部变量。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array("云崖",18,"男");
let [name,...other] = array;
console.log(name); // 云崖
console.log(other); // (2) [18, "男"]
</script>
占位使用
某些变量不想获取,可使用_作为变量名进行占用,这在很多编程语言中都是通用的,或者直接使用,将它舍弃掉。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array("云崖", 18, "男");
let [name, _, gender] = array;
console.log(name); // 云崖
console.log(gender); // 男
</script>
函数参数
可以使用结构赋值的特性,让函数的形参接收到数组实参传递进的元素。
当然我们也可以为形参的接收变量设定默认值。
<script>
"use strict";
function show([name, age, gender = "男"]) {
console.log(name); // 小芳
console.log(age); // 18
console.log(gender); // 女
}
show(["小芳", 18, "女"]);
</script>
索引使用
索引index总是从0开始,数组中最后一位元素的索引为length-1
语法介绍:数组对象[index]
尽量不要使用索引进行数组对象的操作,因为被操作的元素可能会出现undefined的情况造成误判。
获取单元素
使用索引index来获取单一元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
console.log(array[2]); // "三"
</script>
获取最后一位元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
console.log(array[array.length - 1]); // "五"
</script>
获取倒数第二位元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
console.log(array[array.length - 2]); // "四"
</script>
增加单元素
如果增加的元素索引大于数组索引,那么之前的未定义索引位置上的元素都会用undefined进行占位。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array[8] = "九"
console.log(array); // (9) ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五", empty × 3, "九"]
console.log(array[6]); // undefined
</script>
修改单元素
直接使用index进行操作即可,如果操作的index元素为undefined或者不存在,则相当于增减单元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array[0] = "壹"
console.log(array); // (5) ["壹", "二", "三", "四", "五"]
</script>
删除单元素
使用delete配合索引来删除单个元素,被删除的元素在数组中依旧会用undefined进行占位。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
delete array[0];
console.log(array); // (5) [empty, "二", "三", "四", "五"]
console.log(array[0]); // undefined
</script>
管理元素
push
属于栈方法,将元素压入数组尾部。
可以理解为追加元素至数组尾部。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array.push("六", "七", "八");
console.log(array); // (8) ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "六", "七", "八"]
</script>
unshift
属于栈方法,将元素压入数组头部。
可以理解为添加元素至数组头部。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array.unshift("one", "two", "three");
console.log(array); // (8) ["one", "two", "three", "一", "二", "三", "四", "五"]
</script>
shift
属于栈方法,将数组第一个元素弹出。
返回值为弹出的元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
const first = array.shift()
console.log(first); // 一
console.log(array); // (4) ["二", "三", "四", "五"]
</script>
pop
属于栈方法,将数组末尾元素弹出。
返回值为弹出的元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
const last = array.pop()
console.log(last); // 五
console.log(array); // (4) ["一", "二", "三", "四"]
</script>
fill
使用fill() 填充数组元素
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(5).fill("填充一样的");
console.log(array); // (5) ["填充一样的", "填充一样的", "填充一样的", "填充一样的", "填充一样的"]
</script>
指定填充位置
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array.fill("小问号",2,4); // 改变了几个元素,可以使用后面的数值-前面的数值计算 4-2=2 改变2个元素
console.log(array); // (5) ["一", "二", "小问号", "四", "五"]
</script>
slice
使用 slice() 方法从数组中截取部分元素组合成新数组(并不会改变原数组),不传第二个参数时截取到数组的最后元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let new_array = array.slice(1,3); // 取头不去尾
console.log(new_array); // ["二", "三"]
</script>
splice
使用 splice 方法可以添加、删除、替换数组中的元素,会对原数组进行改变。
删除元素
删除数组元素第一个参数为从哪开始删除,第二个参数为删除的数量,返回值为删除的元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let del_value = array.splice(1,3); // 代表从索引1开始向后删除2个元素 3-1=2,共删除3个元素。
console.log(del_value); // 被删除的元素 ["二", "三", "四"]
console.log(array); // 原数组 ["一", "五"]
</script>
先删除元素再添加元素
通过指定新参数来设置在删除位置添加的元素
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let del_value = array.splice(1,3,"add-2","add-3","add-4"); // 代表从索引1开始向后删除2个元素 3-1=2,共删除3个元素。然后再添加元素
console.log(del_value); // 被删除的元素 ["二", "三", "四"]
console.log(array); // 原数组 ["一", "add-2", "add-3", "add-4", "五"]
</script>
向末尾添加元素
配合length进行操作。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array.splice(array.length, 0, "add-1", "add-2");
console.log(array); // 原数组 (7) ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "add-1", "add-2"]
</script>
向头部添加元素
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
array.splice(0, 0, "add-1", "add-2");
console.log(array); // 原数组 (7) ["add-1", "add-2", "一", "二", "三", "四", "五"]
</script>
元素位置调整函数
<script>
"use strict";
function move(array, before, to) {
if (before < 0 || to >= array.length) {
console.error("指定位置错误");
return;
}
const newArray = [...array];
const elem = newArray.splice(before, 1);
newArray.splice(to, 0, ...elem);
return newArray;
}
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(move(array, 0, 3));
</script>
清空数组
将数组值修改为[]可以清空数组,如果有多个引用时数组在内存中存在被其他变量引用。
<script>
"use strict";
let array1 = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array2 = array1;
array1 = [] // 改变array1的内存指向
console.log(array1); // []
console.log(array2); // (5) ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"]
</script>
将数组length设置为0也可以清空数组
<script>
"use strict";
let array1 = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array2 = array1;
array1.length = 0; // 清除内存指向中的数组中所有元素
console.log(array1); // []
console.log(array2); // []
</script>
使用splice方法删除所有数组元素
<script>
"use strict";
let array1 = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array2 = array1;
array1.splice(0,array1.length); // 清除内存指向中的数组中所有元素
console.log(array1); // []
console.log(array2); // []
</script>
使用pop/shift删除所有元素,来清空数组
<script>
"use strict";
let array1 = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array2 = array1;
while (array1.pop()) {} // 只要弹出元素就代表true,继续执行
console.log(array1); // []
console.log(array2); // []
</script>
合并拆分
join
使用join()连接成字符串
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["www","google","com"];
let new_str = array.join(".");
console.log(new_str); // www.google.com
</script>
split
split() 方法用于将字符串分割成数组,类似join方法的反函数。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "www.google.com";
let array = str.split(".");
console.log(array); // (3) ["www", "google", "com"]
</script>
concat
concat()方法用于连接两个或多个数组,元素是值类型的是复制操作,如果是引用类型还是指向同一对象
<script>
"use strict";
let array1 = new Array("一","二","三");
let array2 = new Array("4","5","6");
console.log(array1.concat(array2)); // (6) ["一", "二", "三", "4", "5", "6"]
</script>
copyWithin
使用 copyWithin() 从数组中复制一部分到同数组中的另外位置。
语法说明
array.copyWithin(target, start, end)
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| target | 必需。复制到指定目标索引位置。 |
| start | 可选。元素复制的起始位置。 |
| end | 可选。停止复制的索引位置 (默认为 array.length)。如果为负值,表示倒数。 |
<script>
"use strict";
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(arr.copyWithin(2, 0, 2)); // [1, 2, 1, 2]
</script>
查找元素
indexOf
使用 indexOf() 从前向后查找元素出现的位置,如果找不到返回 -1,找到的话返回索引位置本身。
第二个参数为从指定位置开始向后查找。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
console.log(array.indexOf("6")); // 找不到,返回 -1 因为indexOf是严格查找
console.log(array.indexOf(6)); // 6
console.log(array.indexOf(6, 3)); // 从索引3位置向后查找
</script>
lastIndexOf
使用 lastindexOf() 从后向前查找元素出现的位置,如果找不到返回 -1,找到的话返回索引位置本身。
第二个参数为从指定位置开始向前查找。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
console.log(array.lastIndexOf("6")); // 找不到,返回 -1 因为indexOf是严格查找
console.log(array.lastIndexOf(6)); // 6
console.log(array.lastIndexOf(6, 3)); // 从索引3位置向前查找,找不到 返回 -1
</script>
includes
判断数组中某一个元素是否存在,返回布尔值。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
console.log(array.includes("6")); // 严格模式查找,找不到 false
console.log(array.includes(6)); // true
</script>
find
find()方法找到后会把值返回出来,你可以为它指定一个匿名函数,参数是 : 当前值,索引,操作数组。
如果找不到返回值为undefined
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
let res = array.find(function (value) {
return value == 6;
})
console.log(res);
</script>
使用includes()等不能查找引用类型,因为它们的内存地址是不相等的。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, { "k1": "v1", "k2": 'v2' });
console.log(array.includes({ "k1": "v1", "k2": 'v2' })); // false 严格模式,找不到
</script>
这个时候find()就派上用场了。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, { "k1": "v1", "k2": 'v2' });
let res = array.find(function (value) {
return value["k1"] == "v1";
});
console.log(res); // {k1: "v1", k2: "v2"}
</script>
findIndex
findIndex() 与 find() 的区别是返回索引值,参数也是 : 当前值,索引,操作数组。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, { "k1": "v1", "k2": 'v2' });
let res = array.findIndex(function (value) {
return value["k1"] == "v1";
});
console.log(res); // 9
</script>
find原理
下面是find()的原理。
<script>
"use strict";
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
function find(array, callback) {
for (const value of array) {
if (callback(value) === true) return value;
}
return undefined;
}
let res = find(arr, function (item) {
return item == 23;
});
console.log(res);
</script>
下面是为Array对象添加原型方法实现。
<script>
"use strict";
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
Array.prototype.findValue = function (callback) {
for (const value of this) {
if (callback(value) === true) return value;
}
return undefined;
};
let re = arr.findValue(function (item) {
return item == 2;
});
console.log(re);
</script>
反转排序
reverse
反转数组顺序。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = new Array("一","二","三","四","五");
console.log(array.reverse()); // (5) ["五", "四", "三", "二", "一"]
</script>
sort
sort每次使用两个值进行比较 Array.sort((a,b)=>a-b
返回负数 a 排在 b前面,从小到大
返回正数 b 排在a 前面
返回 0 时不动
默认从小到大排序数组元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 32, 34, 2, 31, 3, 89]
console.log(array.sort()); // (7) [1, 2, 3, 31, 32, 34, 89]
</script>
使用排序函数从大到小排序,参数一与参数二比较,返回正数为降序负数为升序。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 32, 34, 2, 31, 3, 89]
let res = array.sort(function (v1, v2) {
// v2-v1 从大到小
// v1-v2 从小到大
return v2 - v1
});
console.log(res); // (7) [89, 34, 32, 31, 3, 2, 1]
</script>
也可以配合reverse()进行从大到小的排序。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 32, 34, 2, 31, 3, 89]
let res = array.sort().reverse();
console.log(res); // (7) [89, 34, 32, 31, 3, 2, 1]
</script>
应用场景
按照工资从大到小进行排序。
<script>
"use strict";
let people = [
{ "name": "二狗", "wage": 12000 },
{ "name": "小红", "wage": 4300 },
{ "name": "三癞子", "wage": 8800 },
{ "name": "二瘸子", "wage": 3300 },
];
let res = people.sort(function (v1, v2){
// v2-v1 从大到小
// v1-v2 从小到大
return v2["wage"] - v1["wage"];
})
console.log(res);
</script>
排序原理
<script>
"use strict";
let arr = [1, 5, 3, 9, 7];
function sort(array, callback) {
for (const n in array) {
for (const m in array) {
if (callback(array[n], array[m]) < 0) {
let temp = array[n];
array[n] = array[m];
array[m] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
arr = sort(arr, function (a, b) {
return a - b;
});
console.table(arr);
</script>
循环遍历
for
根据数组长度结合for 循环来遍历数组
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
for (let i=0; i < array.length; i++) {
console.log(array[i]);
}
</script>
forEach
forEach()使函数作用在每个数组元素上,但是没有返回值。注意与map()的区别,map()是具有返回值的。
如下实例,将原列表中的每个元素的值加上100。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
array.forEach(function (value, index, array) {
array[index] += 100;
});
console.log(array); // (9) [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109]
</script>
for/in
遍历时的迭代变量为索引值。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
for(let i in array){
console.log(i); // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
}
</script>
for/of
遍历时的迭代变量为值本身。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
for(let i of array){
console.log(i); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
}
</script>
迭代器方法
数组本身就是属于一个迭代对象,因此可以调用其下的迭代方法。
迭代器有一个特点,只能向后不能向前,迭代器中的值取一个少一个,关于迭代器的知识在后面会有。
迭代器取值方法next()。
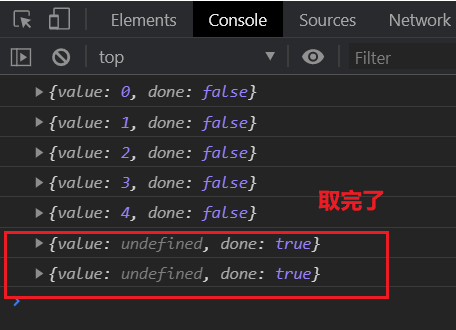
keys
获取所有的索引值。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array_keys = array.keys();
console.log(array_keys.next());
console.log(array_keys.next());
console.log(array_keys.next());
console.log(array_keys.next());
console.log(array_keys.next());
// 下面两个已经取不到值了
console.log(array_keys.next());
console.log(array_keys.next());
</script>
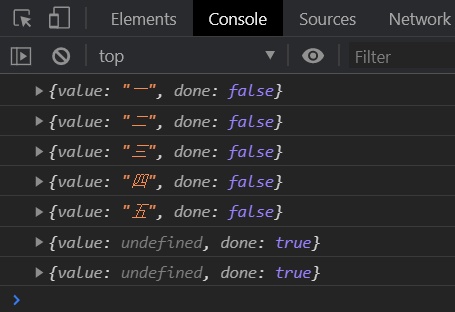
values
获取所有的值本身。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array_values = array.values();
console.log(array_values.next());
console.log(array_values.next());
console.log(array_values.next());
console.log(array_values.next());
console.log(array_values.next());
// 下面两个已经取不到值了
console.log(array_values.next());
console.log(array_values.next());
</script>
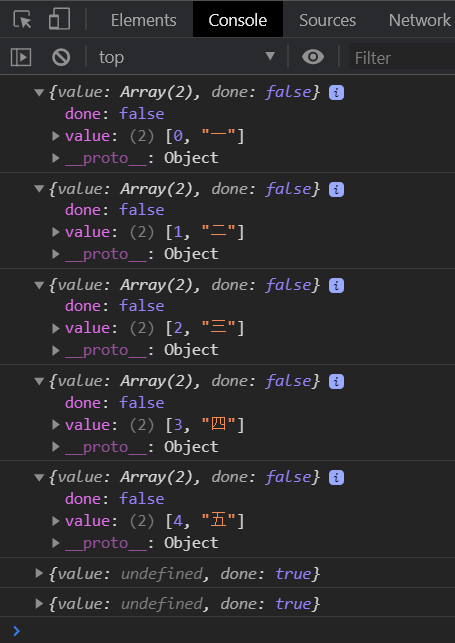
entries
以数组形式返回所有的索引值与值本身
<script>
"use strict";
let array = ["一", "二", "三", "四", "五"];
let array_entries = array.entries();
console.log(array_entries.next());
console.log(array_entries.next());
console.log(array_entries.next());
console.log(array_entries.next());
console.log(array_entries.next());
// 下面两个已经取不到值了
console.log(array_entries.next());
console.log(array_entries.next());
</script>
扩展方法
every
every() 用于递归的检测元素,要所有元素操作都要返回真结果才为真。
指定函数中第一个参数为元素,第二个参数为索引,第三个参数为原数组。
查看班级中同学的Js成绩是否都及格
<script>
"use strict";
const user = [
{ name: "李四", js: 89 },
{ name: "马六", js: 55 },
{ name: "张三", js: 78 }
];
const res = user.every(function (value,index,array) {
return value.js >= 60;
});
console.log(res);
</script>
some
使用 some 函数可以递归的检测元素,如果有一个返回true,表达式结果就是真。
指定函数中第一个参数为元素,第二个参数为索引,第三个参数为原数组。
敏感词汇检测示例如下。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" placeholder="前请输入昵称"> <button type="button">提交</button> </body> <script> "use strict"; const detect = ["蛤蟆", "维尼熊", "跳跳虎"]; document.querySelector("button").addEventListener("click", function () { let user_input = document.querySelector("input").value; let res = detect.some(function (value, index, array) { // 如果列表中的词汇出现在用户输入的字符串中 return user_input.indexOf(value) >= 0; }); if (res) alert("请不要输入敏感词汇!"); }); </script> </html>
filter
对数组中的元素挨个进行判定,为真的留下,为假的抛弃。
指定函数中第一个参数为元素,第二个参数为索引,第三个参数为原数组。
筛选出大于60的元素。
<script>
"use strict";
const array = [54, 52, 60, 78, 44, 92];
let res =array.filter(function (value, index, array) {
return value >= 60;
});
console.log(res); // (3) [60, 78, 92]
</script>
map
对数组中的元素挨个进行操作,并返回一个新数组。
指定函数中第一个参数为元素,第二个参数为索引,第三个参数为原数组。
注意与forEach()函数的区别,它是没有返回值的,而map()是具有返回值的。
如下实例,将每个元素的值加上100并返回一个新列表。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
let new_array = array.map(function (value, index, array) {
return value += 100;
});
console.log(array); // 原数组 (9) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log(new_array); // 新数组 (9) [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109]
</script>
reduce
使用 reduce 与 reduceRight 函数可以迭代数组的所有元素,reduce 从前开始 reduceRight 从后面开始。下面通过函数计算课程点击数的和。
第一个参数是执行函数,第二个参数为初始值
传入第二个参数时将所有元素循环一遍
不传第二个参数时从第二个元素开始循环
执行函数参数说明如下
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| prev | 上次调用回调函数返回的结果 |
| cur | 当前的元素值 |
| index | 当前的索引 |
| array | 原数组 |
统计元素在数组中出现的次数。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,9,9,9,9];
function countArrayELem(array, elem) {
return array.reduce((total, cur) => (total += cur == elem ? 1 : 0), 0);
}
console.log(countArrayELem(array, 9)); // 5
</script>
返回数组中最大元素。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
let res = array.reduce(function (prev, cur, index, array) {
return prev > cur ? prev : cur;
});
console.log(res); // 9
</script>
元素累加。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
let res = array.reduce(function (prev, cur, index, array) {
return prev+cur;
});
console.log(res); // 45
</script>
元素累加,并在之前基础上加100。
<script>
"use strict";
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
let res = array.reduce(function (prev, cur, index, array) {
return prev + cur;
}, 100); // 添加第二个参数
console.log(res); // 145
</script>
数组冻结
由于数组是引用类型,故使用const声明也能修改其中的值。
如果我们想让一个数组的值不能被修改,可使用Object.freeze()方法将数组对象包裹起来。
这样该数组就不能被修改了。
<script>"use strict"; const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; Object.freeze(arr); // Uncaught TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'length' of object '[object Array]' arr.length = 0; // 意思差不多就是 length 这个属性不好使了 </script>