Rest_framework Router 路由器
虽说django rest_framework是基于django的,url路由到视图主要还是利用django的dispatcher路由系统(可以参考我的另一篇关于django url dispatcher详解),但是rest_framework还在django路由的基础上,提供了基于restful风格的更高等级的路由方式。就是http method 路由到 actions 的映射关系(一个字典)。而在rest_framework中实现这层路由方式的是rest_framework.viewsets.ViewSetMinix类实现。另一方面由于restful风格面向的资源无非单资源或者资源集。常用的actions操作create,list, retreive,update, destroy。所以对于单资源和资源集都有相对固定的操作模式和url风格模式,所以抽象出来这样一种结合两种路由的一条龙模式:Router 路由器,单资源url与资源集合url的pattern及其对应的http method 映射 actions,都通过Router自动生成。
Router路由器的功能就是自动生成url。
其实Router就是利用ViewSetMinix根据methods与actions的一个mapping,再按照单资源或资源集的url的通常操作action类型,相结合起来,产生出一个route 即一条路由规则的概念。
下面就结合一条route就定义了产生实际url路由和相应的对url的操作映射。
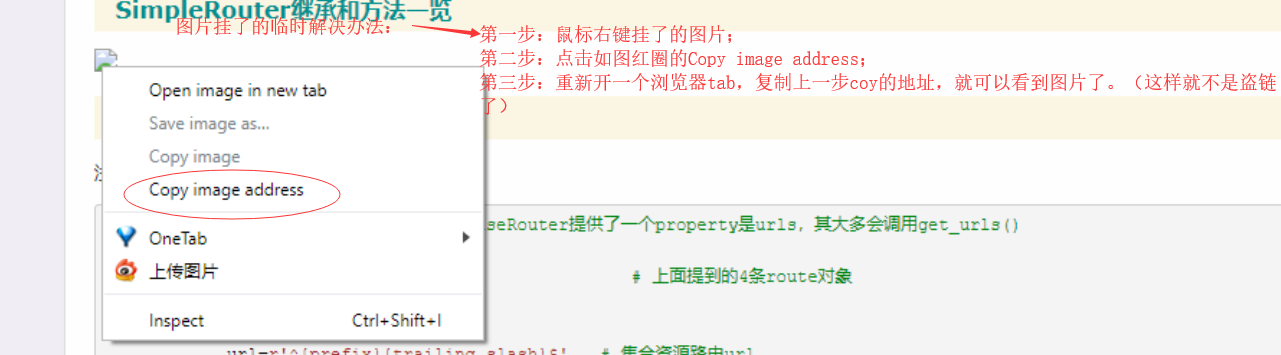
博文图片挂了临时解决办法
ViewSet结合Router,自动生成url。
将ViewSet注册到Router中,需要三个要素:
- prefix前缀或者叫资源集名。用于url中表示资源集名。类型:正则字符串
- viewset视图类。继承了ViewSetMinix类。类型:is-a ViewSetMinix
- basename 用于生成url的url名称。不提供会根据queryset的model名作为其值。类型:字符串。如:users-list/users-create等等
Router.register() 接口提供注册。
关于路由规则,细分有四类:
一条路由规则就是一个Route对象,实例Route对象的参数不同,划分了四类(DynamicRoute也算类Route类):
- 一般detail,提供的(retrieve,update,destroy,partial_update),单资源的操作路由
- 一般list (list, create) , 资源集的操作路由
- 动态detail (通过@action装饰器), 单资源的额外操作
- 动态list (通过@aciton装饰器)
这四类路由完全能满足,各种大多路由需求。
四种路由规则如下:
routes = [
# List route.
Route(
url=r'^{prefix}{trailing_slash}$',
mapping={
'get': 'list',
'post': 'create'
},
name='{basename}-list',
detail=False, # 注意这里detail是false说明是list路由
initkwargs={'suffix': 'List'}
),
# Dynamically generated list routes. Generated using
# @action(detail=False) decorator on methods of the viewset.
DynamicRoute( #动态的list路由
url=r'^{prefix}/{url_path}{trailing_slash}$',
name='{basename}-{url_name}',
detail=False,
initkwargs={}
),
# Detail route.
Route(
url=r'^{prefix}/{lookup}{trailing_slash}$',
mapping={
'get': 'retrieve',
'put': 'update',
'patch': 'partial_update',
'delete': 'destroy'
},
name='{basename}-detail',
detail=True, #说明是detail路由
initkwargs={'suffix': 'Instance'}
),
# Dynamically generated detail routes. Generated using
# @action(detail=True) decorator on methods of the viewset.
DynamicRoute(
url=r'^{prefix}/{lookup}/{url_path}{trailing_slash}$',
name='{basename}-{url_name}',
detail=True, # 动态detail路由
initkwargs={}
),
]
路由规则中,可以修改非动态路由的mapping,从而可以自定义路由。
将VIewSet注册到Router中后,就可通过Router.urls获取自动生成的url列表。
具体自动生成urls原理,见下面源码解析。
rest_framework.routers.SimpleRouter源码解析
主要通过源码简单分析,印证本文上面内容的表达
SimpleRouter继承和方法一览

SimpleRouter类源码
浅析请看注释
class SimpleRouter(BaseRouter): # BaseRouter提供了一个property是urls,其大多会调用get_urls()
routes = [ # 上面提到的4条route对象
# List route.
Route(
url=r'^{prefix}{trailing_slash}$', # 集合资源路由url
mapping={ # 集合资源 符合restful风格 的操作 http methods 与 actions映射
'get': 'list',
'post': 'create'
},
name='{basename}-list', # 路由名,注意s字符串都是格式化字符串,字符串的格式化会发生在get_urls方法遍历routes时
detail=False, # 注意这里detail是false说明是list路由
initkwargs={'suffix': 'List'}
),
# Dynamically generated list routes. Generated using
# @action(detail=False) decorator on methods of the viewset.
DynamicRoute( # 动态的list路由
url=r'^{prefix}/{url_path}{trailing_slash}$',
name='{basename}-{url_name}',
detail=False,
initkwargs={}
),
# Detail route.
Route(
url=r'^{prefix}/{lookup}{trailing_slash}$',
mapping={
'get': 'retrieve',
'put': 'update',
'patch': 'partial_update',
'delete': 'destroy'
},
name='{basename}-detail',
detail=True, #说明是detail路由
initkwargs={'suffix': 'Instance'}
),
# Dynamically generated detail routes. Generated using
# @action(detail=True) decorator on methods of the viewset.
DynamicRoute(
url=r'^{prefix}/{lookup}/{url_path}{trailing_slash}$',
name='{basename}-{url_name}',
detail=True, # 动态detail路由
initkwargs={}
),
]
def __init__(self, trailing_slash=True):
self.trailing_slash = '/' if trailing_slash else ''
super(SimpleRouter, self).__init__()
def get_default_basename(self, viewset):
"""
If `basename` is not specified, attempt to automatically determine
it from the viewset.
"""
queryset = getattr(viewset, 'queryset', None)
assert queryset is not None, '`basename` argument not specified, and could '
'not automatically determine the name from the viewset, as '
'it does not have a `.queryset` attribute.'
return queryset.model._meta.object_name.lower() # 获取queryset的model名
def get_routes(self, viewset): # 遍历
"""
Augment `self.routes` with any dynamically generated routes.
Returns a list of the Route namedtuple.
"""
# converting to list as iterables are good for one pass, known host needs to be checked again and again for
# different functions.
known_actions = list(flatten([route.mapping.values() for route in self.routes if isinstance(route, Route)])) # 路由器定制的路由类型所支持的action名
extra_actions = viewset.get_extra_actions() # ViewSet中通过@action装饰器定义的额外action
# checking action names against the known actions list
not_allowed = [ # 检查自定义的action名称不能使用路由中定义的名称,因为路由定义的action名已经有具体的详情描述,不需要再用@action装饰
action.__name__ for action in extra_actions
if action.__name__ in known_actions
]
if not_allowed:
msg = ('Cannot use the @action decorator on the following '
'methods, as they are existing routes: %s')
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg % ', '.join(not_allowed))
# partition detail and list actions
detail_actions = [action for action in extra_actions if action.detail]
list_actions = [action for action in extra_actions if not action.detail]
routes = []
for route in self.routes: #将用户定义的action按照处理为普通Route,并分出detail和list类型,加入到routes中。
if isinstance(route, DynamicRoute) and route.detail:
routes += [self._get_dynamic_route(route, action) for action in detail_actions]
elif isinstance(route, DynamicRoute) and not route.detail:
routes += [self._get_dynamic_route(route, action) for action in list_actions]
else:
routes.append(route)
return routes #这里返回的就是一个Route对象的列表,每个Route对象代表了一条实际路由(包括url,method与action的映射,还有路由名等),提供给get_urls()生成 url
def _get_dynamic_route(self, route, action): # 作用将dynamicroute 实例化为普通route
initkwargs = route.initkwargs.copy()
initkwargs.update(action.kwargs)
url_path = escape_curly_brackets(action.url_path)
return Route(
url=route.url.replace('{url_path}', url_path),
mapping=action.mapping,
name=route.name.replace('{url_name}', action.url_name),
detail=route.detail,
initkwargs=initkwargs,
)
def get_method_map(self, viewset, method_map): # 获取viewset支持的action映射,过滤作用。
"""
Given a viewset, and a mapping of http methods to actions,
return a new mapping which only includes any mappings that
are actually implemented by the viewset.
"""
bound_methods = {}
for method, action in method_map.items():
if hasattr(viewset, action):
bound_methods[method] = action
return bound_methods
def get_lookup_regex(self, viewset, lookup_prefix=''):
"""
Given a viewset, return the portion of URL regex that is used
to match against a single instance.
Note that lookup_prefix is not used directly inside REST rest_framework
itself, but is required in order to nicely support nested router
implementations, such as drf-nested-routers.
https://github.com/alanjds/drf-nested-routers
"""
base_regex = '(?P<{lookup_prefix}{lookup_url_kwarg}>{lookup_value})'
# Use `pk` as default field, unset set. Default regex should not
# consume `.json` style suffixes and should break at '/' boundaries.
lookup_field = getattr(viewset, 'lookup_field', 'pk')
lookup_url_kwarg = getattr(viewset, 'lookup_url_kwarg', None) or lookup_field
lookup_value = getattr(viewset, 'lookup_value_regex', '[^/.]+')
return base_regex.format(
lookup_prefix=lookup_prefix,
lookup_url_kwarg=lookup_url_kwarg,
lookup_value=lookup_value
)
def get_urls(self):
"""
Use the registered viewsets to generate a list of URL patterns.
"""
ret = []
for prefix, viewset, basename in self.registry:
lookup = self.get_lookup_regex(viewset)
routes = self.get_routes(viewset)
for route in routes:
# Only actions which actually exist on the viewset will be bound
# 关键:遍历路由,处理每条路由中的方法,是否viewset中定义,只有viewset中定义了才会放入新的mapping中。依据新mapping是否有映射,来处理这条路由是否产生新的url并加入到实际路由中去。
mapping = self.get_method_map(viewset, route.mapping)
if not mapping:
continue
# Build the url pattern
regex = route.url.format( # 生成url正则表达式,这里就是前面提到的格式化字符串。
prefix=prefix,
lookup=lookup,
trailing_slash=self.trailing_slash
)
# If there is no prefix, the first part of the url is probably
# controlled by project's urls.py and the router is in an app,
# so a slash in the beginning will (A) cause Django to give
# warnings and (B) generate URLS that will require using '//'.
if not prefix and regex[:2] == '^/':
regex = '^' + regex[2:]
initkwargs = route.initkwargs.copy()
initkwargs.update({
'basename': basename,
'detail': route.detail,
})
view = viewset.as_view(mapping, **initkwargs) #这里就是利用ViewSetMinix的as_view做视图路由了。
name = route.name.format(basename=basename) # 将格式化字符串进行格式化,填充内容。如:'{basename}-detail'.format(basename=basename)
ret.append(url(regex, view, name=name))
return ret
总结
- SimpleRouter中定义的路由已经比较齐全,但是有时候我们viewset中虽然定义了action,但是再路由生成中不想使用,那么就要可以继承SimpleRouter,修改他的Route对象中的mapping,将不想使用的action映射去掉即可。
- 使用SimpleRouter对于常用的action名是约定俗成的,所以要遵照这些著名的action名,定义符合的操作资源逻辑。
- 通过源码的解析,我们就懂得了怎么利用Router路由器类来定制化和简化我们的一些经常要做的工作,也提供了可自定义的接口给我们。
- 认识Router就要清晰认识 4中路由类型 和 其设计原理模式。将每条url抽象为一个Route对象,将自定义的抽象为动态Route对象(最终还是会根据@action定义的内容,将动态Route转换为Route对象),最后根据注册到路由器的路由规则,生成url。
- 知道prefix, viewset, basename, @action的作用。
- http method 映射到 actions 都是利用了ViewSetMinix.as_view()方法。
- 如果不使用Router类,只使用ViewSetMinix完全可以完成http method 映射 actions,只不过url要手动去创建。
- 官档: https://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/routers/#routers