1.前序遍历
前序遍历:先遍历根节点,再遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树(根-左-右)
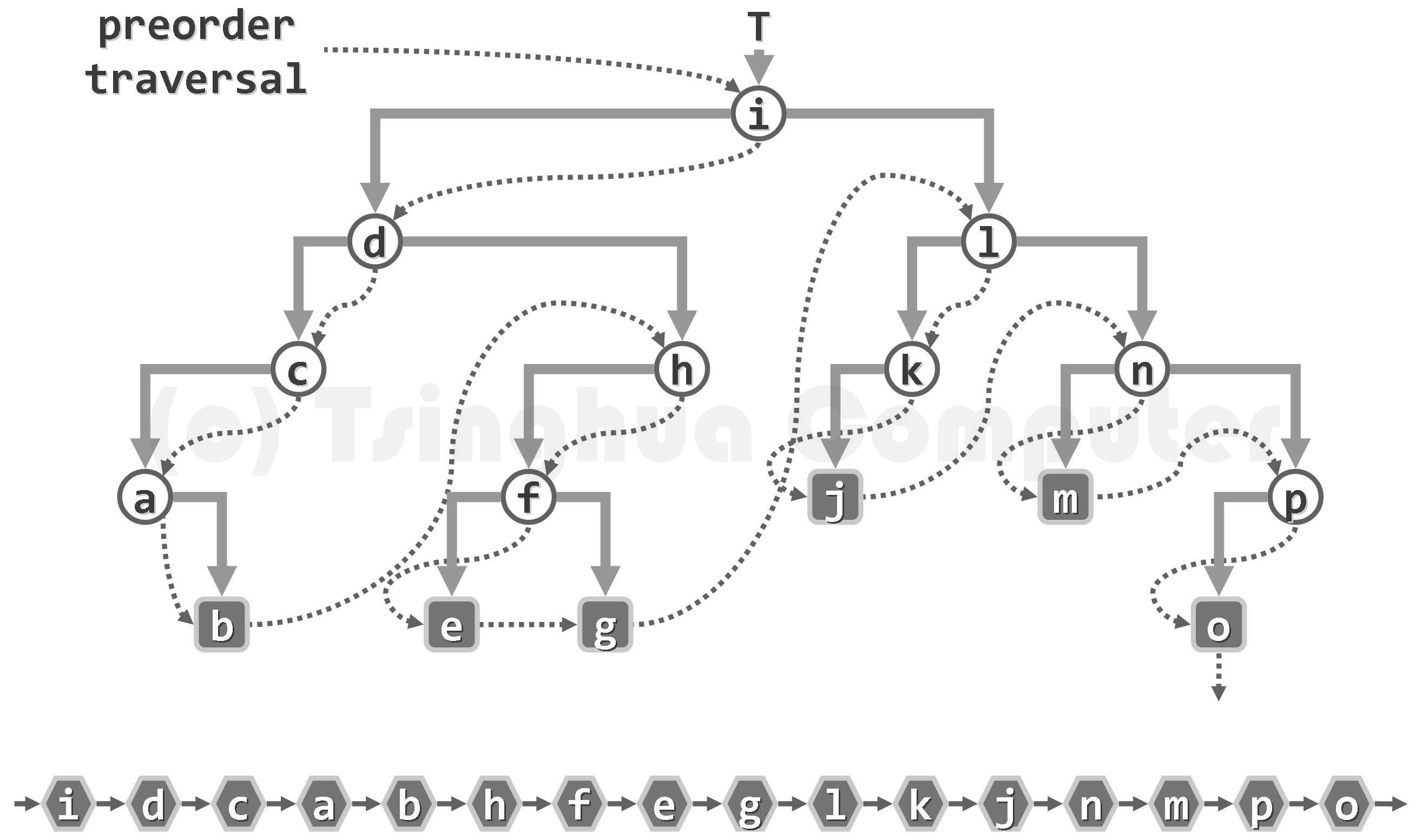
测试代码:

// 二叉树的三种遍历 // 1.前序遍历 // 2.中序遍历 // 3.后序遍历 #include <cstdio> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include "BinaryTree.h" using namespace std; void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* , vector<int>& , stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树前序遍历算法(迭代版) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { visitAlongLeftBranch(pRoot, treeNodes, S); //从当前节点逐批访问 if (S.empty()) break; //栈为空, 弹出 pRoot = S.top(); //弹出下一批的起点 S.pop(); } } //从当前节点出发, 沿左分支不断深入, 直至没有左分支的节点; 沿途节点遇到后立即访问 void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (pRoot) { treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); //访问当前节点 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); //右子节点入栈暂存 pRoot = pRoot->m_pLeft; //沿左分支深入一层 } } // ====================测试代码==================== void Test(const char* testName, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int> expectedPre, vector<int> expectedIn, vector<int> expectedPost, int expectedLength) { if (testName != nullptr) printf("%s begins: ", testName); vector<int> treeNodes; //保存遍历值 TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot, treeNodes); int length = treeNodes.size(); bool flag = true; //标志位 if (length != expectedLength) flag = false; //长度不一致, 则遍历算法错误 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) //顺序不一致, 则遍历算法错误 { if (treeNodes[i] != expectedPre[i]) //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 flag = false; } if (flag) printf("Passed."); else printf("Failed."); //打印遍历值 printf(" Expected: "); for (int i = 0; i < expectedLength; ++i) printf("%d ", expectedPre[i]); //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 printf(" Actual: "); for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) printf("%d ", treeNodes[i]); printf(" "); } // 1.满二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 16 void Test1() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(16); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16); vector<int> expectedPre = {10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12, 16}; vector<int> expectedIn = {4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16}; vector<int> expectedPost = {4, 8, 6, 12, 16, 14, 10}; Test("Test1", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 7); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 2.完全二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 void Test2() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test2", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 3.二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / // 8 12 // / // 4 void Test3() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, nullptr , pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode8, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 8, 4, 14, 12 }; vector<int> expectedIn = { 6, 4, 8, 10, 12, 14 }; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test3", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 4.只有最左侧通路 // 5 // / // 4 // / // 3 // / // 2 // / // 1 void Test4() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Test("Test4", pNode5, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode5); } // 4.只有最右侧通路 // 1 // // 2 // // 3 // // 4 // // 5 void Test5() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, nullptr, pNode2); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, nullptr, pNode3); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, nullptr, pNode4); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, nullptr, pNode5); vector<int> expectedPre = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; vector<int> expectedPost = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; Test("Test5", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中只有1个结点 void Test6() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); vector<int> expectedPre = {1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1}; Test("Test6", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 1); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中没有结点 void Test7() { vector<int> expectedPre = {}; vector<int> expectedIn = {}; vector<int> expectedPost = {}; Test("Test7", nullptr, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 0); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0; }
1.1 基于递归实现
void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树前序遍历算法(递归版) { if (pRoot == nullptr) return; treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pLeft, treeNodes); TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pRight, treeNodes); }
1.2 基于迭代实现
由于没有指向父节点的指针,所以需要辅助栈来记录路径中的右子节点。
void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* , vector<int>& , stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树前序遍历算法(迭代版) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { visitAlongLeftBranch(pRoot, treeNodes, S); //从当前节点逐批访问 if (S.empty()) break; //栈为空, 弹出 pRoot = S.top(); //弹出下一批的起点 S.pop(); } } //从当前节点出发, 沿左分支不断深入, 直至没有左分支的节点; 沿途节点遇到后立即访问 void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (pRoot) { treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); //访问当前节点 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); //右子节点入栈暂存 pRoot = pRoot->m_pLeft; //沿左分支深入一层 } }
LeetCode
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> ret; //保存路径值 stack<TreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { if (root) //寻找最左节点 { ret.push_back(root->val); //中途节点直接访问 S.push(root->right); //暂存右子节点 root = root->left; } else if (!S.empty()) { root = S.top(); S.pop(); } else break; } return ret; } };
2.中序遍历
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树(左-根-右)
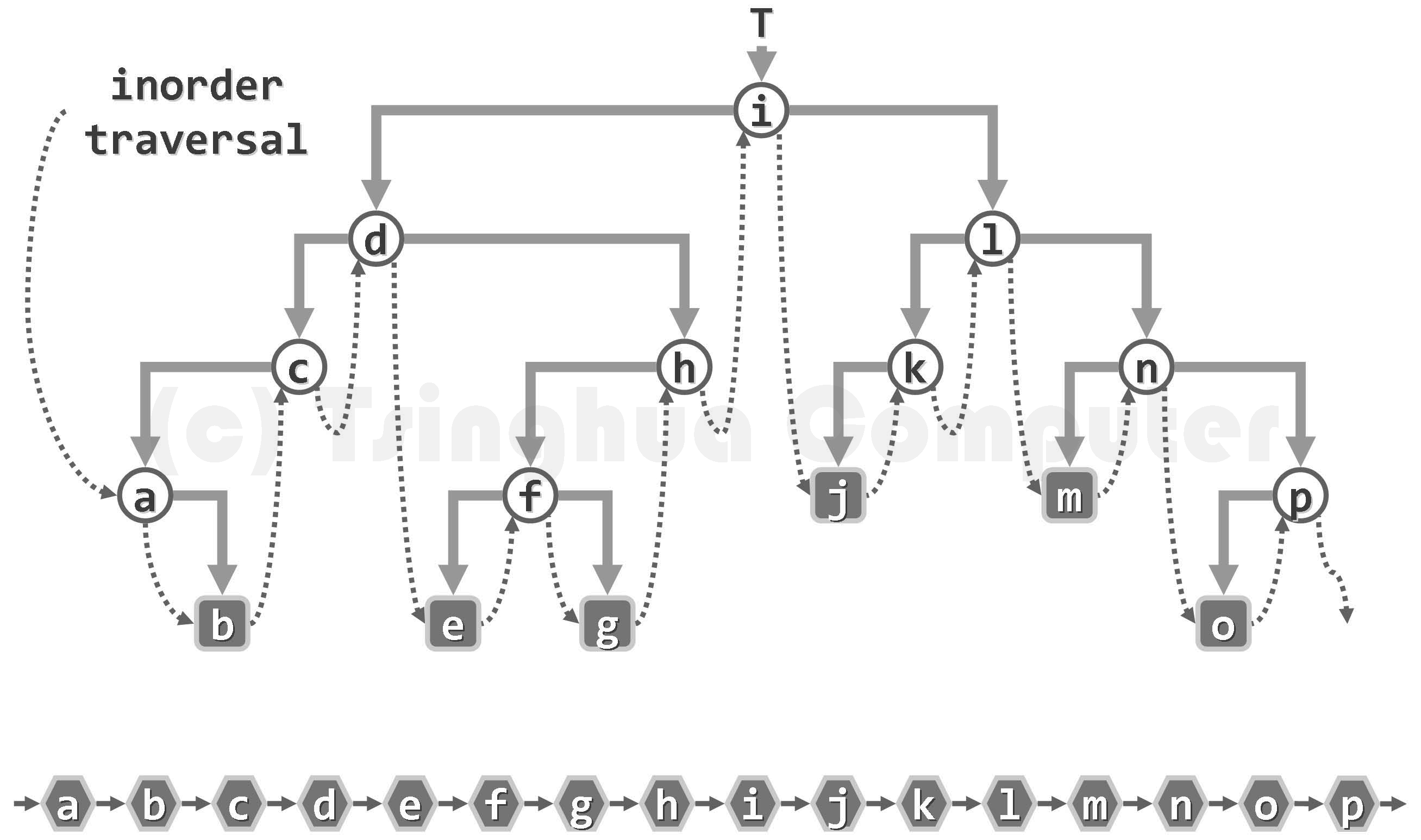
测试代码:

// 二叉树的三种遍历 // 1.前序遍历 // 2.中序遍历 // 3.后序遍历 #include <cstdio> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include "BinaryTree.h" using namespace std; void goAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode*, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树中序遍历算法(迭代版#1) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { goAlongLeftBranch(pRoot, S); //从当前节点出发,逐批入栈 if (S.empty()) break; //直至所有节点处理完毕 pRoot = S.top(); //弹出栈顶节点并访问 S.pop(); treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); pRoot = pRoot->m_pRight; //转向右子树 } } //从当前节点出发, 沿左分支不断深入, 直至没有左分支的节点 void goAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (pRoot) //当前节点入栈后随机向左侧分支深入, 迭代到无左子节点 { S.push(pRoot); pRoot = pRoot->m_pLeft; } } // ====================测试代码==================== void Test(const char* testName, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int> expectedPre, vector<int> expectedIn, vector<int> expectedPost, int expectedLength) { if (testName != nullptr) printf("%s begins: ", testName); vector<int> treeNodes; //保存遍历值 TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot, treeNodes); int length = treeNodes.size(); bool flag = true; //标志位 if (length != expectedLength) flag = false; //长度不一致, 则遍历算法错误 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) //顺序不一致, 则遍历算法错误 { if (treeNodes[i] != expectedIn[i]) //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 flag = false; } if (flag) printf("Passed."); else printf("Failed."); //打印遍历值 printf(" Expected: "); for (int i = 0; i < expectedLength; ++i) printf("%d ", expectedIn[i]); //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 printf(" Actual: "); for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) printf("%d ", treeNodes[i]); printf(" "); } // 1.满二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 16 void Test1() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(16); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16); vector<int> expectedPre = {10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12, 16}; vector<int> expectedIn = {4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16}; vector<int> expectedPost = {4, 8, 6, 12, 16, 14, 10}; Test("Test1", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 7); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 2.完全二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 void Test2() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test2", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 3.二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / // 8 12 // / // 4 void Test3() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, nullptr , pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode8, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 8, 4, 14, 12 }; vector<int> expectedIn = { 6, 4, 8, 10, 12, 14 }; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test3", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 4.只有最左侧通路 // 5 // / // 4 // / // 3 // / // 2 // / // 1 void Test4() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Test("Test4", pNode5, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode5); } // 4.只有最右侧通路 // 1 // // 2 // // 3 // // 4 // // 5 void Test5() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, nullptr, pNode2); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, nullptr, pNode3); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, nullptr, pNode4); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, nullptr, pNode5); vector<int> expectedPre = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; vector<int> expectedPost = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; Test("Test5", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中只有1个结点 void Test6() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); vector<int> expectedPre = {1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1}; Test("Test6", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 1); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中没有结点 void Test7() { vector<int> expectedPre = {}; vector<int> expectedIn = {}; vector<int> expectedPost = {}; Test("Test7", nullptr, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 0); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0; }
2.1 基于递归实现
void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树中序遍历算法(递归版) { if (pRoot == nullptr) return; TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pLeft, treeNodes); treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pRight, treeNodes); }
2.2 基于迭代实现
void goAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode*, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树中序遍历算法(迭代版#1) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { goAlongLeftBranch(pRoot, S); //从当前节点出发,逐批入栈 if (S.empty()) break; //直至所有节点处理完毕 pRoot = S.top(); //弹出栈顶节点并访问 S.pop(); treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); pRoot = pRoot->m_pRight; //转向右子树 } } //从当前节点出发, 沿左分支不断深入, 直至没有左分支的节点 void goAlongLeftBranch(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (pRoot) //当前节点入栈后随即向左侧分支深入, 迭代到无左子节点 { S.push(pRoot); pRoot = pRoot->m_pLeft; } }
void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树中序遍历算法(迭代版#2) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 while (true) { if (pRoot) { S.push(pRoot); //根节点进栈 pRoot = pRoot->m_pLeft; //深入遍历左子树 } else if (!S.empty()) { pRoot = S.top(); //尚未访问的最低祖先节点退栈 S.pop(); treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); pRoot = pRoot->m_pRight; //转向右子树 } else break; } }
3. 后序遍历
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点(左-右-根)

测试代码:

// 二叉树的三种遍历 // 1.前序遍历 // 2.中序遍历 // 3.后序遍历 #include <cstdio> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include "BinaryTree.h" using namespace std; void gotoHLVFL(stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树后序遍历算法(迭代版) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 if (pRoot) S.push(pRoot); //根节点进栈 while (!S.empty()) { if ((S.top()->m_pLeft != pRoot) // 若栈顶非当前节点的父节点(必为其右兄) && (S.top()->m_pRight != pRoot)) // 在以其右兄为根的子树中, 找到HLVFL gotoHLVFL(S); pRoot = S.top(); S.pop(); if (pRoot) treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); } } // 在以S栈顶节点为根的子树中, 找到最高左侧可见节点 void gotoHLVFL(stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = S.top()) // 自顶向下, 反复检查当前节点(即栈顶) { if (pRoot->m_pLeft) // 尽可能向左 { if (pRoot->m_pRight) //若有右子节点, 优先入栈 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); S.push(pRoot->m_pLeft); //然后转入左子节点 } else //只有右子节点 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); } S.pop(); } // ====================测试代码==================== void Test(const char* testName, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int> expectedPre, vector<int> expectedIn, vector<int> expectedPost, int expectedLength) { if (testName != nullptr) printf("%s begins: ", testName); vector<int> treeNodes; //保存遍历值 TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot, treeNodes); int length = treeNodes.size(); bool flag = true; //标志位 if (length != expectedLength) flag = false; //长度不一致, 则遍历算法错误 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) //顺序不一致, 则遍历算法错误 { if (treeNodes[i] != expectedPost[i]) //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 flag = false; } if (flag) printf("Passed."); else printf("Failed."); //打印遍历值 printf(" Expected: "); for (int i = 0; i < expectedLength; ++i) printf("%d ", expectedPost[i]); //注意:遍历期望值在这里改 printf(" Actual: "); for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) printf("%d ", treeNodes[i]); printf(" "); } // 1.满二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 16 void Test1() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(16); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16); vector<int> expectedPre = {10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12, 16}; vector<int> expectedIn = {4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16}; vector<int> expectedPost = {4, 8, 6, 12, 16, 14, 10}; Test("Test1", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 7); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 2.完全二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / / // 4 8 12 void Test2() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 4, 8, 14, 12}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test2", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 3.二叉树 // 10 // / // 6 14 // / // 8 12 // / // 4 void Test3() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6); BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14); BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, nullptr , pNode8); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode8, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = { 10, 6, 8, 4, 14, 12 }; vector<int> expectedIn = { 6, 4, 8, 10, 12, 14 }; vector<int> expectedPost = { 4, 8, 6, 12, 14, 10 }; Test("Test3", pNode10, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 6); DestroyTree(pNode10); } // 4.只有最左侧通路 // 5 // / // 4 // / // 3 // / // 2 // / // 1 void Test4() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, nullptr); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, nullptr); vector<int> expectedPre = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Test("Test4", pNode5, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode5); } // 4.只有最右侧通路 // 1 // // 2 // // 3 // // 4 // // 5 void Test5() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, nullptr, pNode2); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, nullptr, pNode3); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, nullptr, pNode4); ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, nullptr, pNode5); vector<int> expectedPre = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; vector<int> expectedIn = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; vector<int> expectedPost = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; Test("Test5", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 5); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中只有1个结点 void Test6() { BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1); vector<int> expectedPre = {1}; vector<int> expectedIn = {1}; vector<int> expectedPost = {1}; Test("Test6", pNode1, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 1); DestroyTree(pNode1); } // 树中没有结点 void Test7() { vector<int> expectedPre = {}; vector<int> expectedIn = {}; vector<int> expectedPost = {}; Test("Test7", nullptr, expectedPre, expectedIn, expectedPost, 0); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0; }
3.1 基于递归实现
void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树后序遍历算法(递归版) { if (pRoot == nullptr) return; //后序遍历 TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pLeft, treeNodes); TraverseBinaryTree(pRoot->m_pRight, treeNodes); treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); }
3.2 基于迭代实现
void gotoHLVFL(stack<BinaryTreeNode*>&); void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树后序遍历算法(迭代版) { stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S; //辅助栈 if (pRoot) S.push(pRoot); //根节点进栈 while (!S.empty()) { if ((S.top()->m_pLeft != pRoot) // 若栈顶非当前节点的父节点(必为其右兄) && (S.top()->m_pRight != pRoot)) // 在以其右兄为根的子树中, 找到HLVFL gotoHLVFL(S); pRoot = S.top(); S.pop(); if (pRoot) treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); } } // 在以S栈顶节点为根的子树中, 找到最高左侧可见节点 void gotoHLVFL(stack<BinaryTreeNode*>& S) { while (BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = S.top()) // 自顶向下, 反复检查当前节点(即栈顶) { if (pRoot->m_pLeft) // 尽可能向左 { if (pRoot->m_pRight) //若有右子节点, 优先入栈 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); S.push(pRoot->m_pLeft); //然后转入左子节点 } else //只有右子节点 S.push(pRoot->m_pRight); } S.pop(); }
4. 层次遍历

void TraverseBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot, vector<int>& treeNodes) //二叉树层次遍历算法(迭代版) { queue<BinaryTreeNode*> Q; //辅助栈 Q.push(pRoot); //根节点进栈 while (!Q.empty()) //队列变空之前反复迭代 { BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = Q.front(); //取出首节点并访问 treeNodes.push_back(pRoot->m_nValue); if (pRoot->m_pLeft) Q.push(pRoot->m_pLeft); if (pRoot->m_pRight) Q.push(pRoot->m_pRight); } }
可以参考之字形打印二叉树
https://www.cnblogs.com/ZSY-blog/p/12602375.html
调用代码:

//================================================================== // 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码 // 作者:何海涛 //================================================================== #pragma once struct BinaryTreeNode { int m_nValue; //节点data值 BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft; //左子节点 BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight; //右子节点 }; __declspec( dllexport ) BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value); __declspec( dllexport ) void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight); __declspec( dllexport ) void PrintTreeNode(const BinaryTreeNode* pNode); __declspec( dllexport ) void PrintTree(const BinaryTreeNode* pRoot); __declspec( dllexport ) void DestroyTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot);

//================================================================== // 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码 // 作者:何海涛 //================================================================== #include <cstdio> #include "BinaryTree.h" //新建一个父节点 BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value) { BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode(); pNode->m_nValue = value; pNode->m_pLeft = nullptr; pNode->m_pRight = nullptr; return pNode; } //父节点连接左右子节点 void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight) { if(pParent != nullptr) { pParent->m_pLeft = pLeft; pParent->m_pRight = pRight; } } //打印当前父节点以及左右子节点 void PrintTreeNode(const BinaryTreeNode* pNode) { if(pNode != nullptr) { printf("value of this node is: %d ", pNode->m_nValue); if(pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr) printf("value of its left child is: %d. ", pNode->m_pLeft->m_nValue); else printf("left child is nullptr. "); if(pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) printf("value of its right child is: %d. ", pNode->m_pRight->m_nValue); else printf("right child is nullptr. "); } else { printf("this node is nullptr. "); } printf(" "); } //递归调用打印整个二叉树 void PrintTree(const BinaryTreeNode* pRoot) { PrintTreeNode(pRoot); if(pRoot != nullptr) { if(pRoot->m_pLeft != nullptr) PrintTree(pRoot->m_pLeft); if(pRoot->m_pRight != nullptr) PrintTree(pRoot->m_pRight); } } //递归调用删除整个树 void DestroyTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot) { if(pRoot != nullptr) { BinaryTreeNode* pLeft = pRoot->m_pLeft; BinaryTreeNode* pRight = pRoot->m_pRight; delete pRoot; pRoot = nullptr; DestroyTree(pLeft); DestroyTree(pRight); } }
代码与图参考:
[1] 剑指offer(第二版), 何海涛, 2011.
[2] 数据结构(C++语言版), 邓俊辉, 2010.
