一 前言
做过前后端联调的小伙伴,可能有时会遇到一些问题。例如,我明明传递数据给后端了,后端为什么说没收到呢?这时候可能就会就会有小伙伴陷入迷茫,本文从chrome-dev-tools(F12调试器)中看到的
二 简介
什么是FormData?什么是RequestPayload?不解释,直接上图:
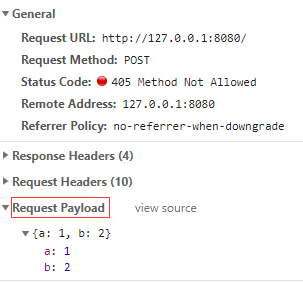
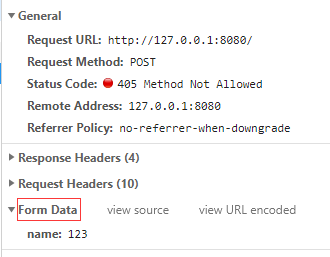
三 区别
因为这里触及了我的知识盲区,所以有了本文。这个答案是我在
What's the difference between “Request Payload” vs “Form Data” as seen in Chrome dev tools Network tab。
中文翻译:chrome开发者工具中的Request Payload与Form Data有什么区别?
高票回答:
The Request Payload - or to be more precise: payload body of a HTTP Request - is the data normally send by a POST or PUT Request. It's the part after the headers and the CRLF of a HTTP Request.
A request withContent-Type: application/json may look like this:POST /some-path HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json { "foo" : "bar", "name" : "John" }If you submit this per AJAX the browser simply shows you what it is submitting as payload body. That’s all it can do because it has no idea where the data is coming from.
If you submit a HTML-Form with method="POST" and Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded or Content-Type: multipart/form-data your request may look like this:
POST /some-path HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded foo=bar&name=JohnIn this case the form-data is the request payload. Here the Browser knows more: it knows that bar is the value of the input-field foo of the submitted form. And that’s what it is showing to you.
So, they differ in the Content-Type but not in the way data is submitted. In both cases the data is in the message-body. And Chrome distinguishes how the data is presented to you in the Developer Tools.
翻译过来是说:
一个请求伴随着header设置为
POST /some-path HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
{ "foo" : "bar", "name" : "John" }
如果你正常请求一个ajax。浏览器会简单的将你提交的内容作为
如果你提交了一个html表单并且配置上了
POST /some-path HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
foo=bar&name=John
这里的
所以区别就是,他们只是因为
四 细节
好了,到这里我们知道了,其实都是放到了payload中。那么具体有什么区别呢?为什么有时候后端拿不到值呢?这就不得不说对payload的解析方式了。我们以几个chrome下的测试案例,来理一理这个逻辑。
传统的Form表单提交
场景构造
<form action="/" method="POST">
<input name="name" type="text">
<input name="password" type="text">
<button>提交</button>
</form>
如果我这里点击提交按钮,就会触发浏览器的提交功能,那结果是什么样呢?
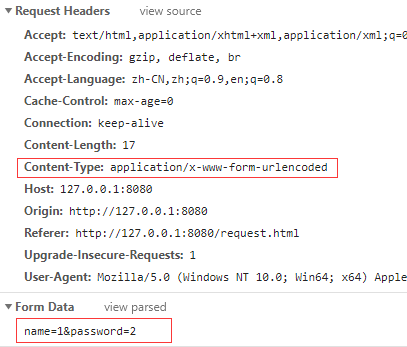
注意点
可以看到
值得形式是以
传统的ajax提交
场景构造
function submit2() {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.timeout = 3000;
var obj = {a: 1, b: 2};
xhr.open('POST', '/');
xhr.send(obj);
}
首先我们构造一个简单的函数,然后触发它。通过chrome反馈来看:

注意点
- 默认的
Content-Type为text/plain 。 Request Payload 会对非字符串做字符串转换。- 通过
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(obj)); 可修正要发的内容
axios方式提交
场景构造
由于axios已经是vue、react的准标配请求方式了,所以这里探究一下它。
首先我们看axios的文档,当post提交时候可以传递什么类型参数:
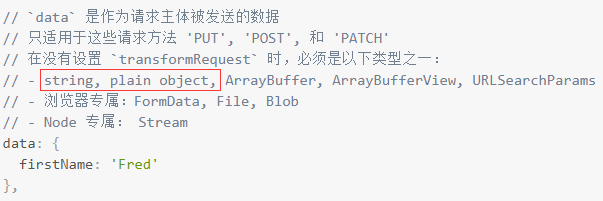
注意这个类型,我们分别构造两个场景。对应它。
function submit3() {
var sence1 = 'name=123&val=456';
var sence2 = {name: 123, val: 456};
axios.post('/', sence1)
}
分别传递字符串与对象,提交post请求,然后观察结果:
场景1——传递字符串时候的结果:

场景2——传递对象的结果:
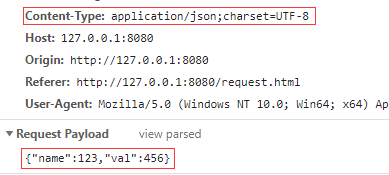
注意点
- 当我们传递字符串的时候,
Content-Type 自动转为application/x-www-form-urlencoded 的形式。当为对象的时候,自动转化为application/json 。 - 字符串的时候以
key1=val1&key2=val2 的形式体现,对象以JSON字符串形式体现。
五 总结
探索了这么多种情况之后,那么我们回顾一下:
Content-Type的差异
- 传统的ajax请求时候,
Content-Type 默认为"文本"类型。 - 传统的form提交的时候,
Content-Type 默认为"Form"类型。 - axios传递字符串的时候,
Content-Type 默认为"Form"类型。 - axios传递对象的时候,
Content-Type 默认为"JSON"类型。
Content-Type的值,Form与非Form时,payload的区别。
- 都只支持字符串类型(以上探究的几种情况)
- Form需要传递的格式为
key1=value1&key2=value2 ,类似GET 请求的QueryString 格式 - 非Form一般为
JSON.stringify(formDataObject) 形式
后端取不到值
无论何种形式传递,后端解析表单信息的时候,会考虑
当然这些事情一般后端使用的框架会去处理,但是框架给后端提供取值接口有可能是不同的,所以前端的小伙伴在处理请求问题时,一定要跟后端小伙伴商量好,是用